Arctic Regional Synopsis
Regional charts and associated synopsis write-up capture ice and environmental conditions throughout the Arctic which are based on the U.S. National Ice Center’s weekly analysis. Charts and synopses are updated weekly on Fridays. Note: Baltic Sea analysis is provided by the Finnish Meteorological Institute. The Canadian Archipelago (Canada East, Canada North, Canada West, and Hudson Bay) analysis is provided by the Canadian Ice Service.
Regional Quick Access
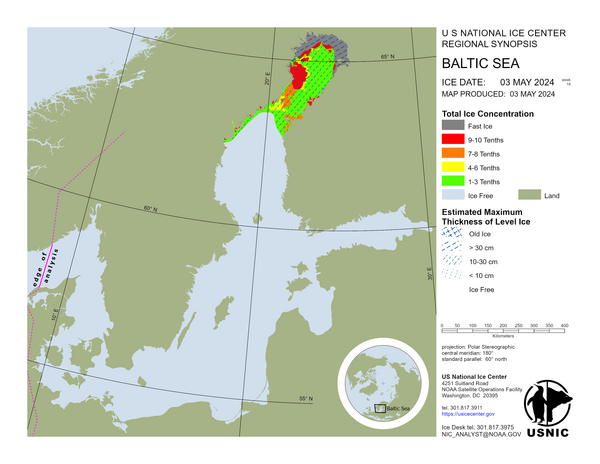
Baltic Sea
In the Northern Bay of Bothnia 40-80 cm thick fast ice and 20-50 cm thick consolidated drift ice to Kemi 2, Oulu 1 and Johan. Farther out 20-50 cm thick, in places ridged, very close ice. In the Southern Bay of Bothnia 20-45 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago. Farther out 15-45 cm thick, in places ridged, very close ice. In the Quark 20-40 cm thick, in places ridged, very close ice. In the Vaasa archipelago 20-50 cm thick fast ice and consolidated drift ice to Norrskär. In the Sea of Bothnia 20-55 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago. Off the fast ice 10-40 cm thick close shuga. In the Åland Sea there is open water. In the Archipelago Sea 15-40 cm thick fast ice in the inner archipelago. In the outer archipelago 10-20 cm thick level ice to Utö. In the western Gulf of Finland 15-40 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago. Farther out 10-30 cm thick, in places rafted, close and very close ice. West of Helsinki lighthouse is mainly open and very open ice. The southern boundary of the ice field runs along the center line of the Gulf of Finland. In the eastern Gulf of Finland 20-50 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago to Orrengrund. Farther out 10-40 cm thick, rafted and in places ridged, very close ice approximately 20 nautical miles south of Tiiskeri. In the Lake Saimaa 25-45 cm thick ice.
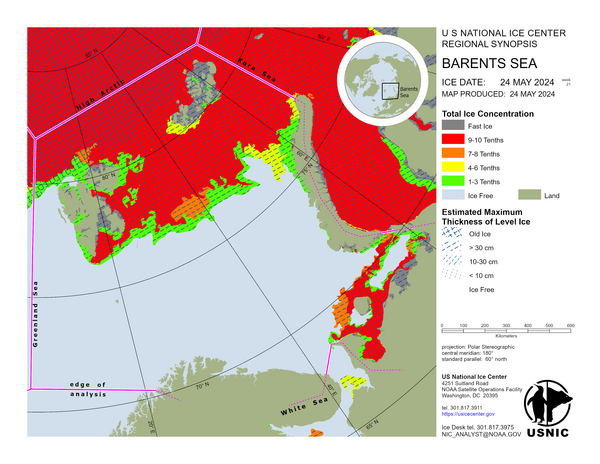
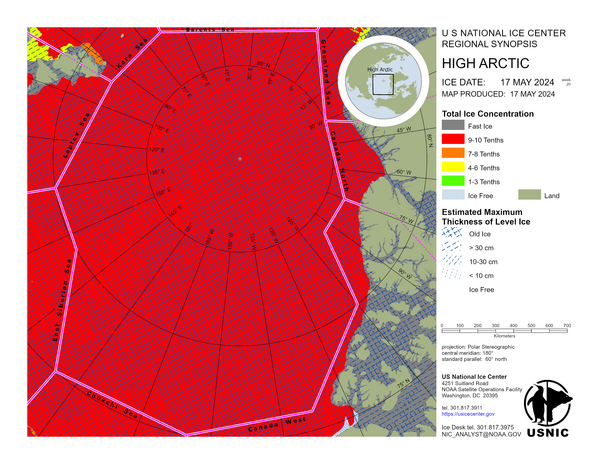
Barents Sea
In the Barents Sea, strong southerly winds have caused the sea ice to drift northward. A large polynya has opened on the lee side of Franz Josef Land, and is slow to refreeze, due to air temperatures ranging from 0°C near Svalbard to -10°C along the boundary with High Arctic East region. An increase of sea ice was analyzed this week along the western coast of Novaya Zemlya. In the southern Barents Sea the winds have caused the sea ice to drift northward as much as 50 nautical miles. New and young sea ice is rapidly forming along the Russian coast in air temperatures ranging from -08°C at the ice edge to -24°C near the Kara Gates.
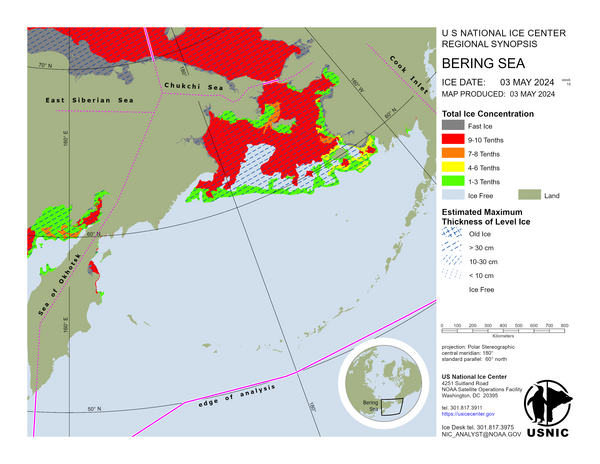
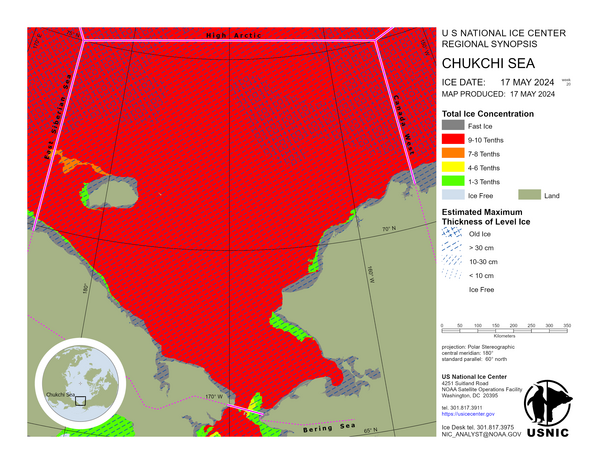
Bering Sea
In the Kamchatka region ice is fairly similar to the previous week with some minor melting along the ice edge with some new and young ice developing along the islands. Land fasted ice in the protected and shallow bays are remaining consistent. Some areas of blow out are being seen near the coastline. In the Bering Sea the ice edge has advanced 120 to 180 nautical miles under the influence of strong northeasterly winds. A Polynya has formed along the Alaskan coastline and have quickly frozen over in air temperatures as cold as -20°C.
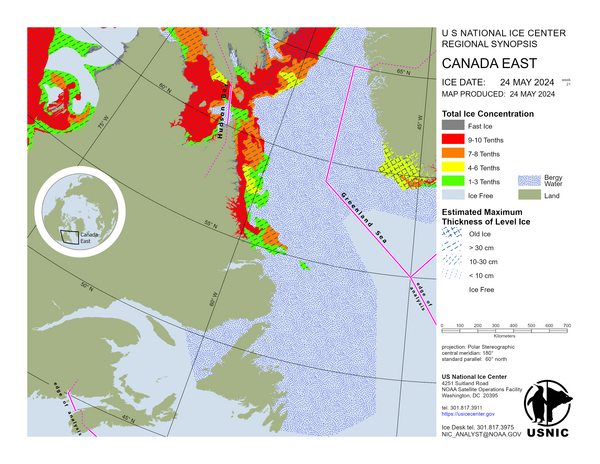
Canada East
Eureka Sound and Jones Sound contain first-year ice and some old ice. There is young ice present along the ice edge. Foxe Basin contains mostly first-year ice with some young and new ice present in the western section. Cumberland Sound contains first-year ice, young ice, and new ice. The Labrador Sea is bergy water with a mixture of first-year, young and new ice along the Labrador coast with a trace of old ice extending southward to 59N. Frobisher Bay contains a mixture of first-year, young and new ice.
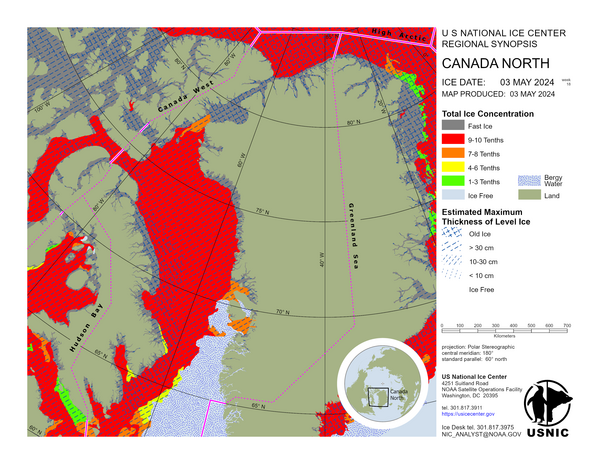
Canada North
The Arctic Ocean comprises old ice. Nares Strait contains a mixture of old ice and first-year ice. Lancaster Sound contain mostly first-year ice with some old ice. Baffin Bay and Davis Strait contain mostly first-year ice with some old ice. The Gulf of Boothia contains first-year ice. Cumberland Sound contains a mixture of first-year, young and new ice.
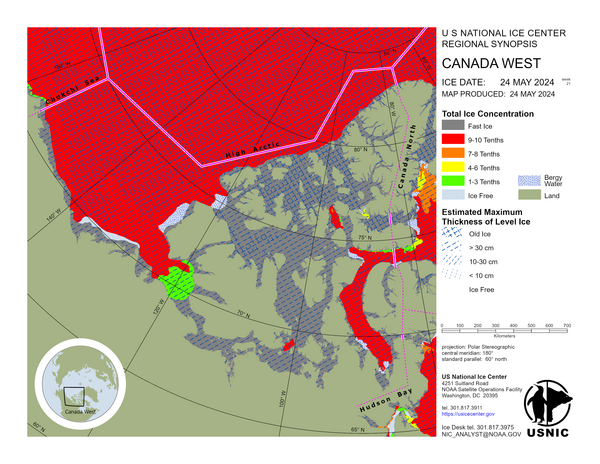
Canada West
The waters around the Queen Elizabeth Islands are fast old ice and first-year ice. M’Clure Strait and Viscount Melville Sound contain predominantly fast old ice with some first-year ice. Barrow Strait is fast first-year ice with some old ice in the western section; in the eastern section there is mobile first-year ice with a trace of old ice. M’Clintock Channel is fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice. Peel Sound is fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice. Victoria Strait is fast first-year ice. There is an area of mobile first-year ice in the southern section. Queen Maud Gulf and Coronation Gulf are fast first-year ice. Amundsen Gulf is mostly fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice in the northern section. Canada Basin is predominantly old ice with some first-year ice. The Beaufort Sea is predominantly first-year ice with some old ice. New and young ice formed during the movement of the ice.
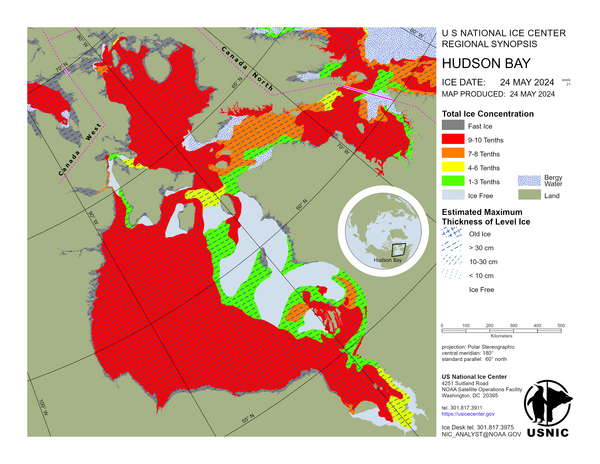
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay is predominantly first-year ice with young and new ice where the pack moves away from the coast. Hudson Strait contains mostly first-year ice with young and new ice in the northern section. Ungava Bay contains mostly first-year ice with young and new ice along the southwestern coast and south of Akpatok Island. James Bay is predominantly first-year ice with some young and new ice.
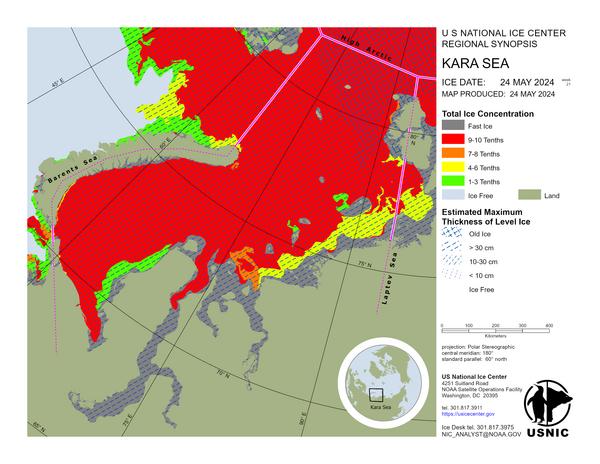
Kara Sea
Frigid air temperatures are in place over the Kara Sea, ranging from -14°C over northern Novaya Zemlya to -30°C over the pack ice in the southern Kara Sea. Sea ice has generally drifted northward, with polynyas rapidly freezing over with new and young ice on the lee side of islands and adjacent fast ice.
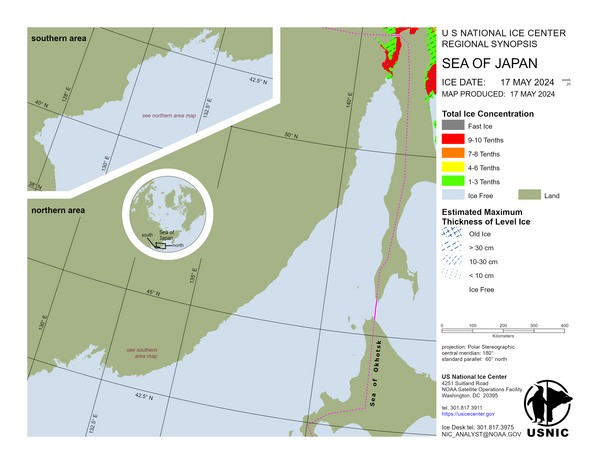
Sea of Japan
In the northern Sea of Japan south of the fast ice in the Tartar Strait, the sea ice is drifting southward. Air temperatures over the strait are -10°C, allowing for new and young sea ice to form and drift southward as well. This is known as the ice conveyor belt process. As the first year ice continues to drift southward it melts as it encounters warmer waters near the 47° north latitude. Along the Sakhalin Islands an area of newly observed land-fast ice has developed just south of the Tartar Strait. In the northern portion of Peter the Great Bay sea ice is in high concentrations. The port of Vladivostok has low concentrations of sea ice.
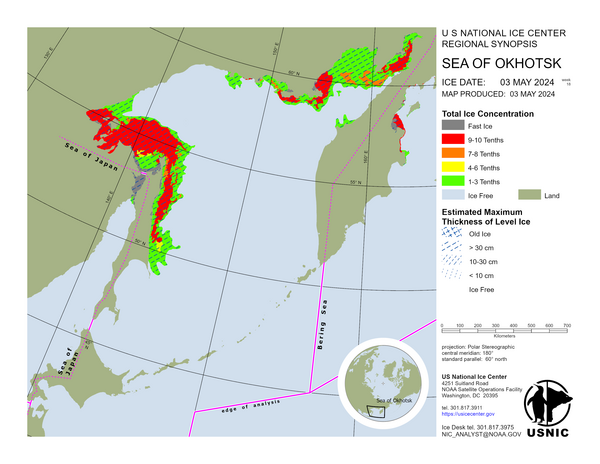
Sea of Okhotsk
In the Sea of Okhotsk, ice compaction occurred in the west and melting in the south over the past week. Ice continued drifting southward along Sakhalin Island in the East Sakhalin Current. In Aniva Bay, ice drifted eastward with some melting, while ice in the Shelikhov Gulf continued drifting southward. Air temperatures remain below the freezing point for sea ice formation but are considerably warmer than last month, allowing edge ice to melt when encountering warmer waters.