NEWS
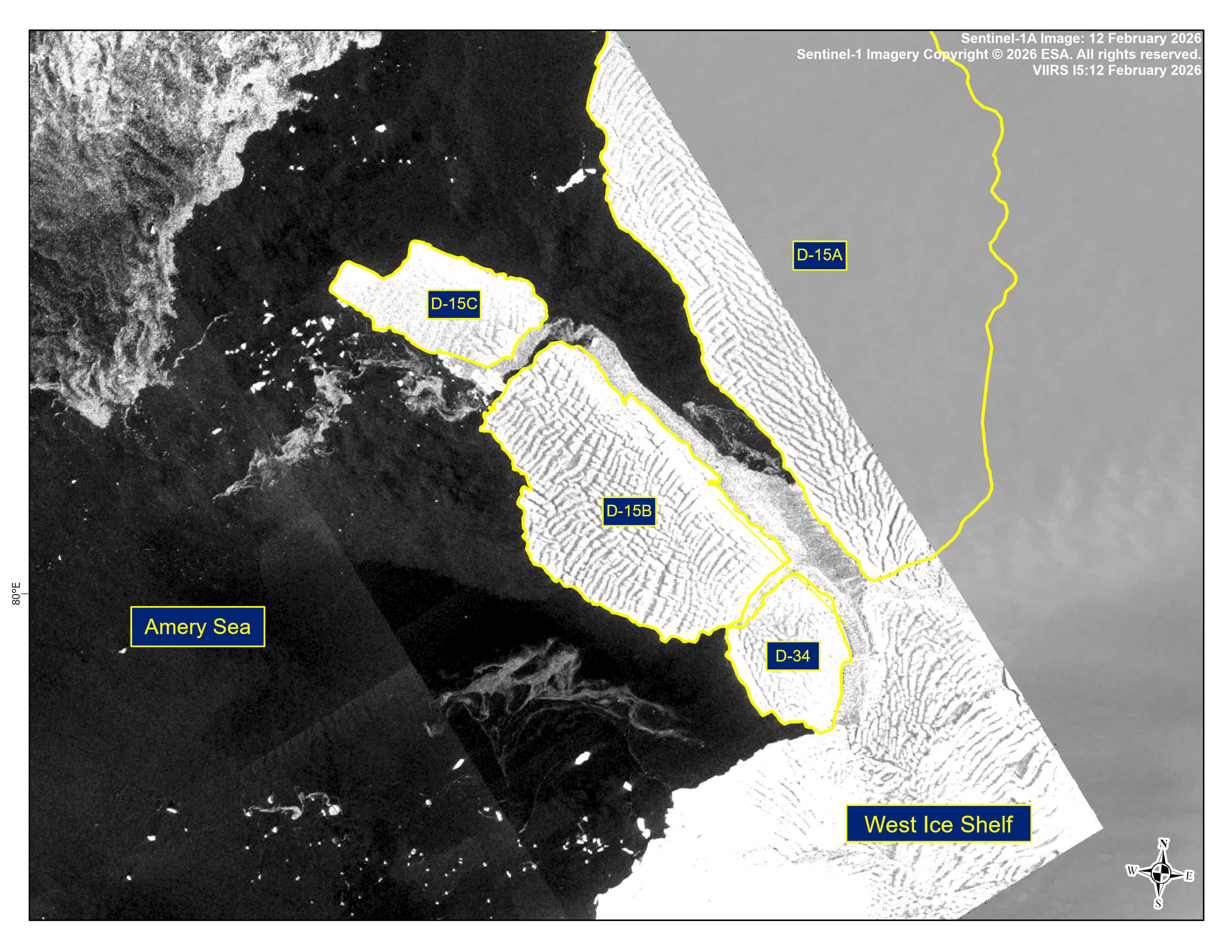
Press Release - Iceberg D-15C Has Calved from Iceberg D-15B
13 February 2026 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-15C calved from D-15B in the southern Amery Sea along the West Ice Shelf. As of February 13th, D-15B was centered at 67° 02' South and 81° 34' East and measured 21 nautical miles on its longest axis and 12 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-15C was centered at 66° 50' South and 81° 03' East and measured 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-15 originally calved form the West Ice Shelf and once held the title of world’s largest iceberg.
Go to Article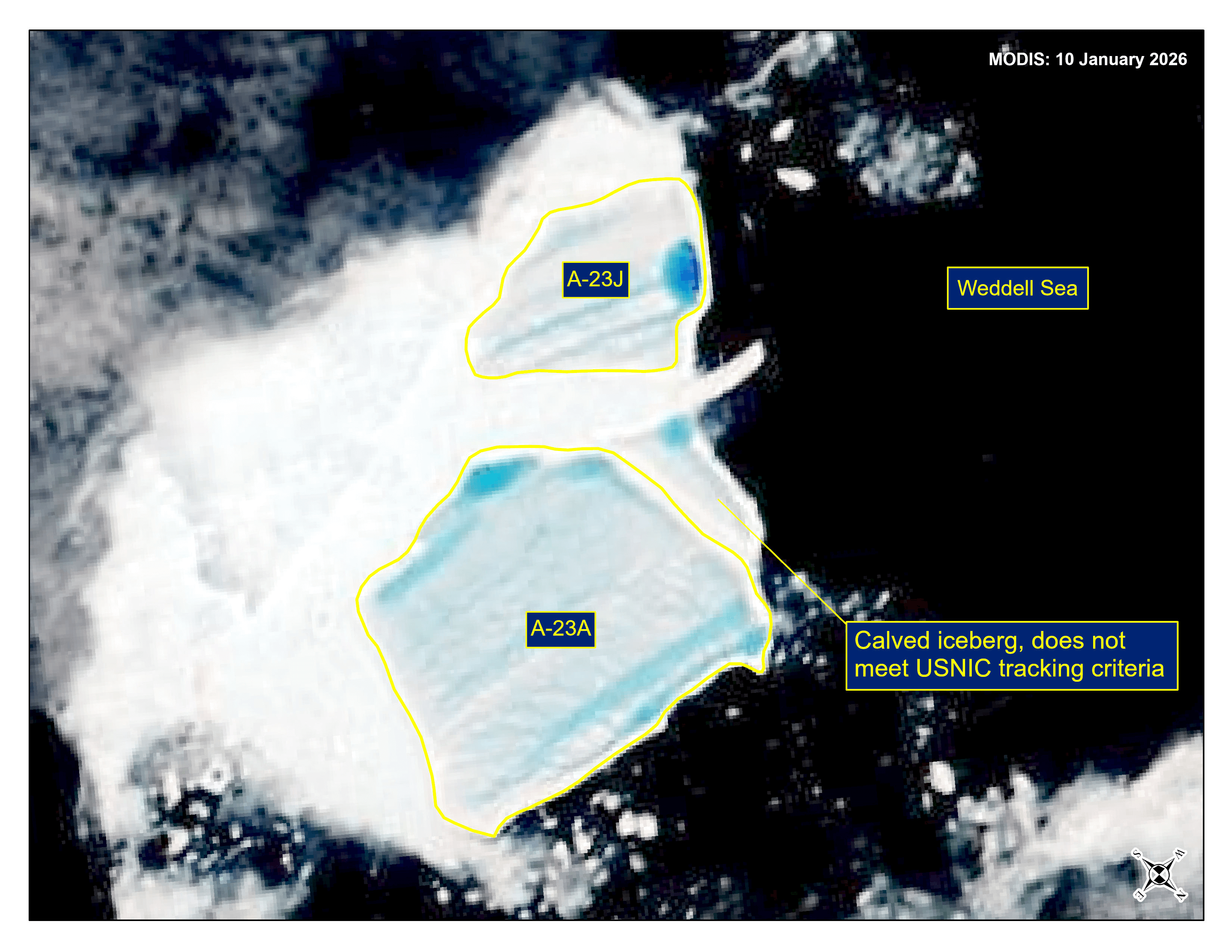
Press Release - Iceberg A-23J Has Calved from Iceberg A-23A
16 January 2026 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-23J calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of January 16th, A-23A was centered at 52° 44' South and 41° 21' West and measured 16 nautical miles on its longest axis and 15 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23J was centered at 52° 51' South and 41° 43' West and measured 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23A first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986.
Go to Article
Great Lakes Experiences Rapid Early Winter Ice Growth Followed by a Late-December Thaw
29 December 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has been tracking the fast start to the Great Lakes ice season. USNIC and the Canadian Ice Service began the annual production of joint Great Lakes daily ice charts on 29 November 2025, following observations of ice formation in Black Bay (Lake Superior). Colder than normal temperatures were experienced through the first two weeks of December which led to unseasonably high ice coverage across the Great Lakes.
Go to Article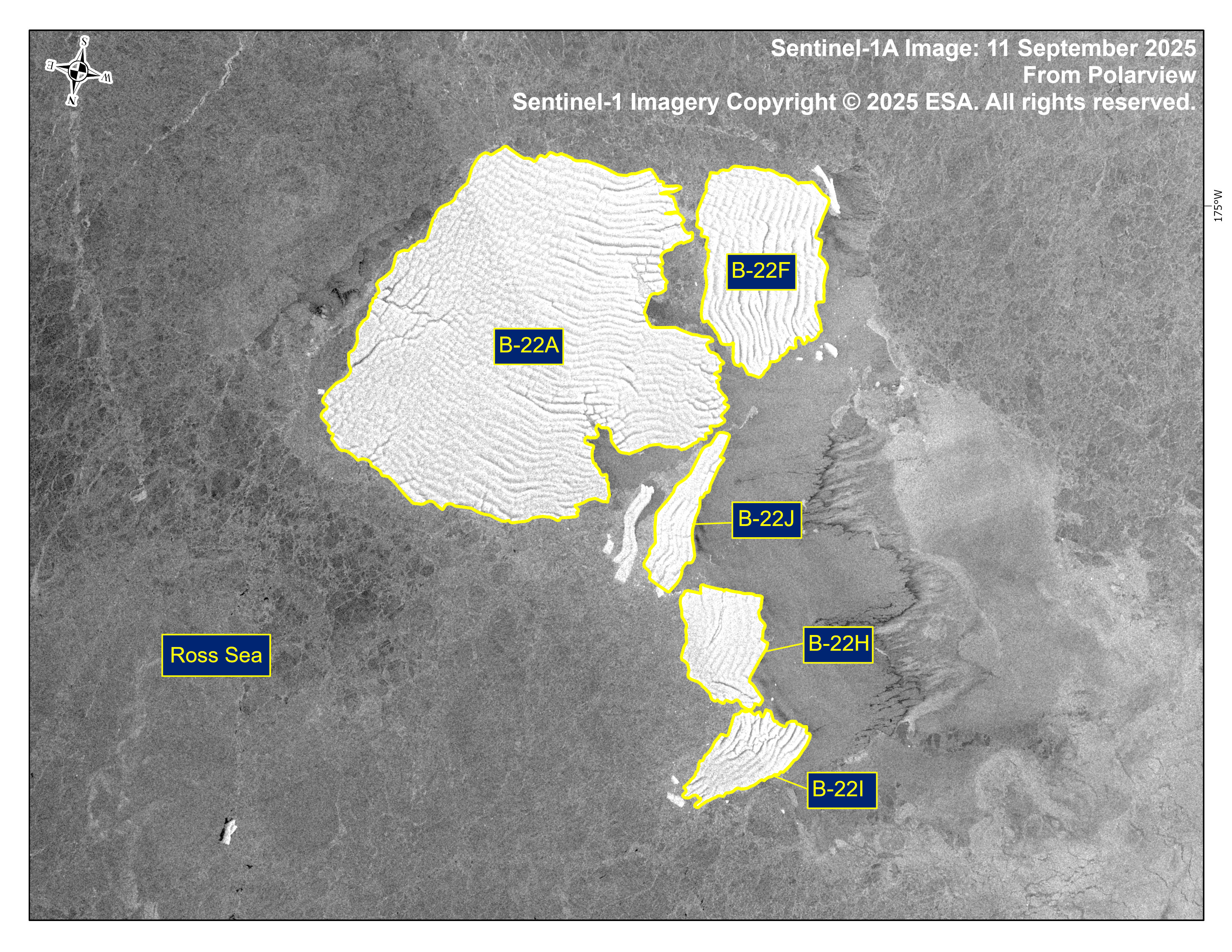
Press Release - Iceberg B-22J Has Calved From B-22H
11 September 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg B-22J (Figure 1, below) calved from the iceberg B-22H. As of August 30, B-22H was centered at 71° 50' South and 173° 30' West and measured 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. As of 30 August, B-22J was centered at 73° 58' South and 173° 15' West and measured 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article
Press Release - Iceberg A-23I Has Calved from Iceberg A-23A
11 September 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-23I calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of August 30, A-23A was centered at 52° 46' South and 36° 47' West and measured 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 23 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23I was centered at 53° 00' South and 36° 56' West and measured 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 11 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23A first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986.
Go to Article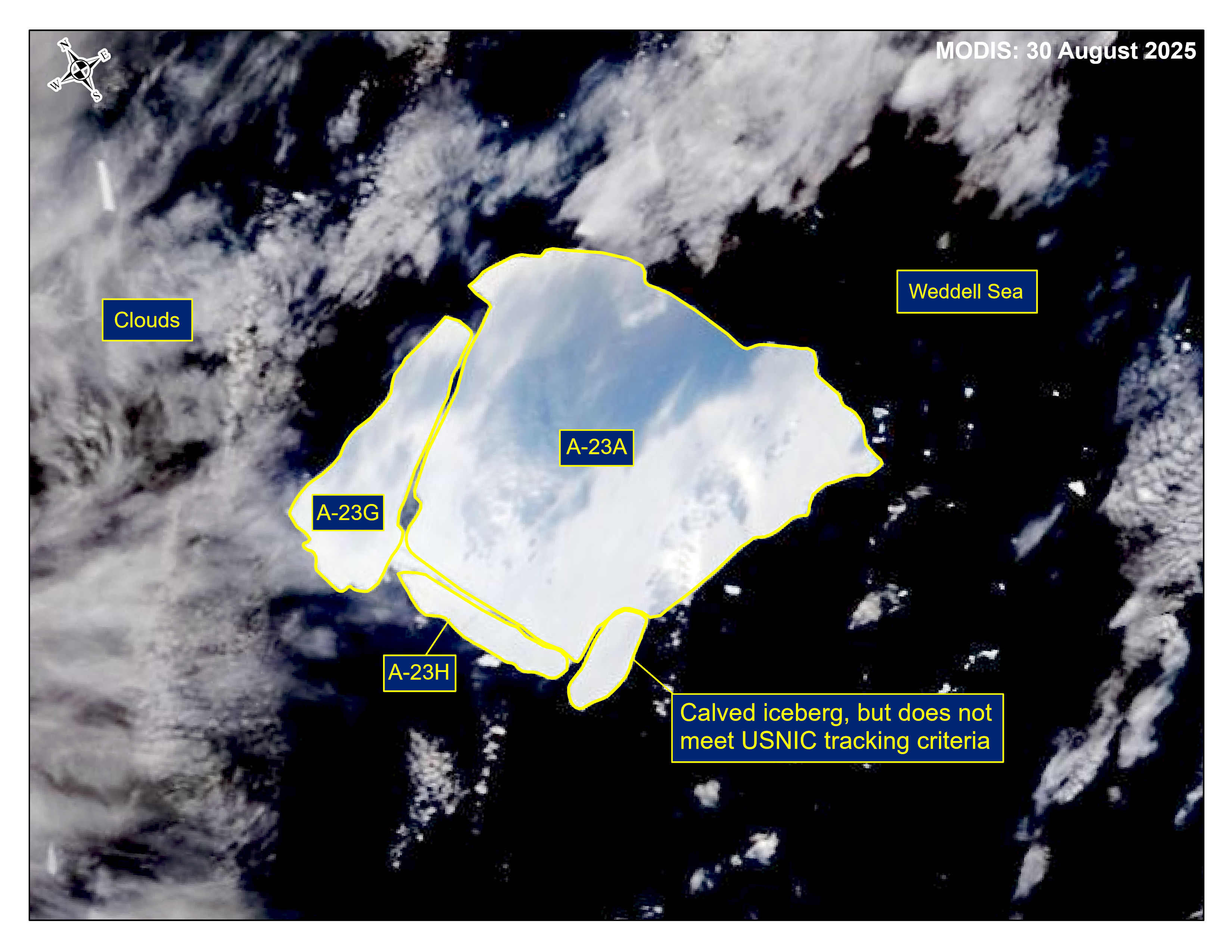
Press Release - Icebergs A-23G and A-23H Have Calved from Iceberg A-23A
18 August 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs A-23G and A-23H calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of August 30, A-23A was centered at 53° 17' South and 36° 51' West and measured 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 30 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23G was centered at 53° 09' South and 37° 10' West and measured 20 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23H was centered at 53° 22' South and 37° 11' West and measured 13 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23A first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986.
Go to Article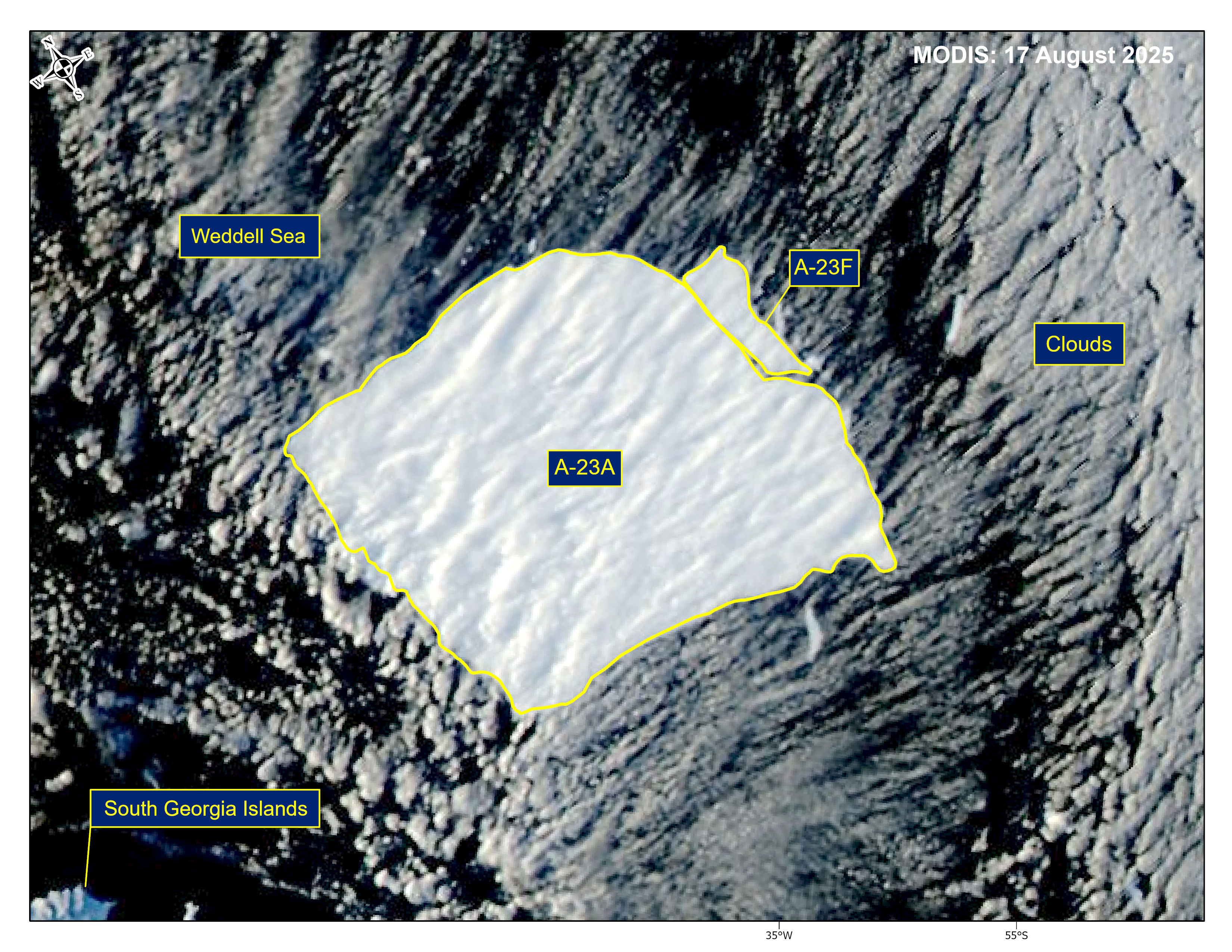
Press Release - Iceberg A-23F Has Calved from Iceberg A-23A
18 August 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-23F calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of August 17, A-23A was centered at 54° 22' South and 34° 54' West. It measured 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 32 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23F was centered at 54° 18' South and 34° 31' West. It measured 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23A first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986.
Go to Article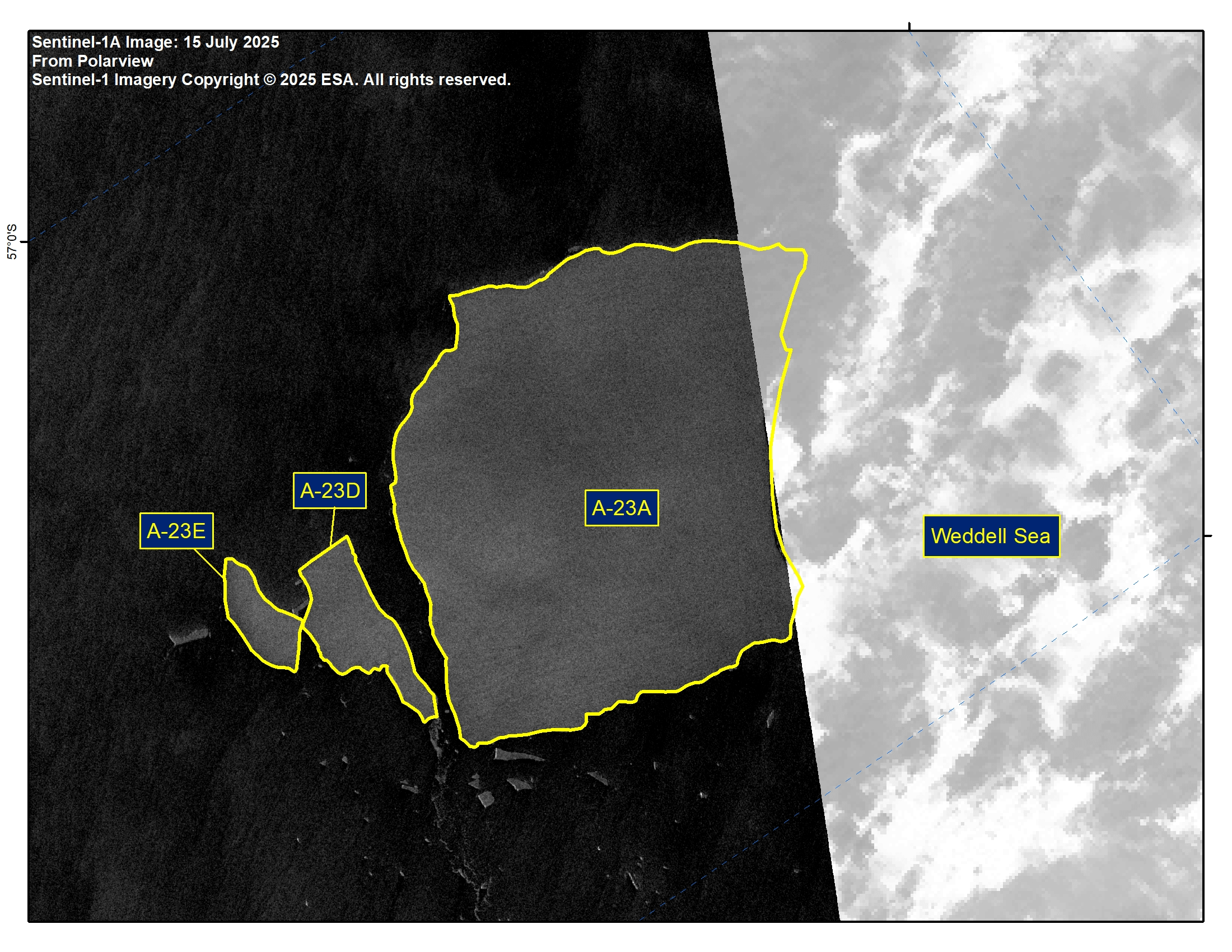
Press Release - Icebergs A-23D and A-23E Have Calved from Iceberg A-23A
15 July 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs A-23D and A-23E calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of July 15, A-23A was centered at 56° 26' South and 33° 59' West and measured 40 nautical miles on its longest axis and 28 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23D was centered at 56° 26' South and 33° 25' West and measured 13 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-23E was centered at 56° 31' South and 33° 16' West and measured 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis A-23A first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986.
Go to Article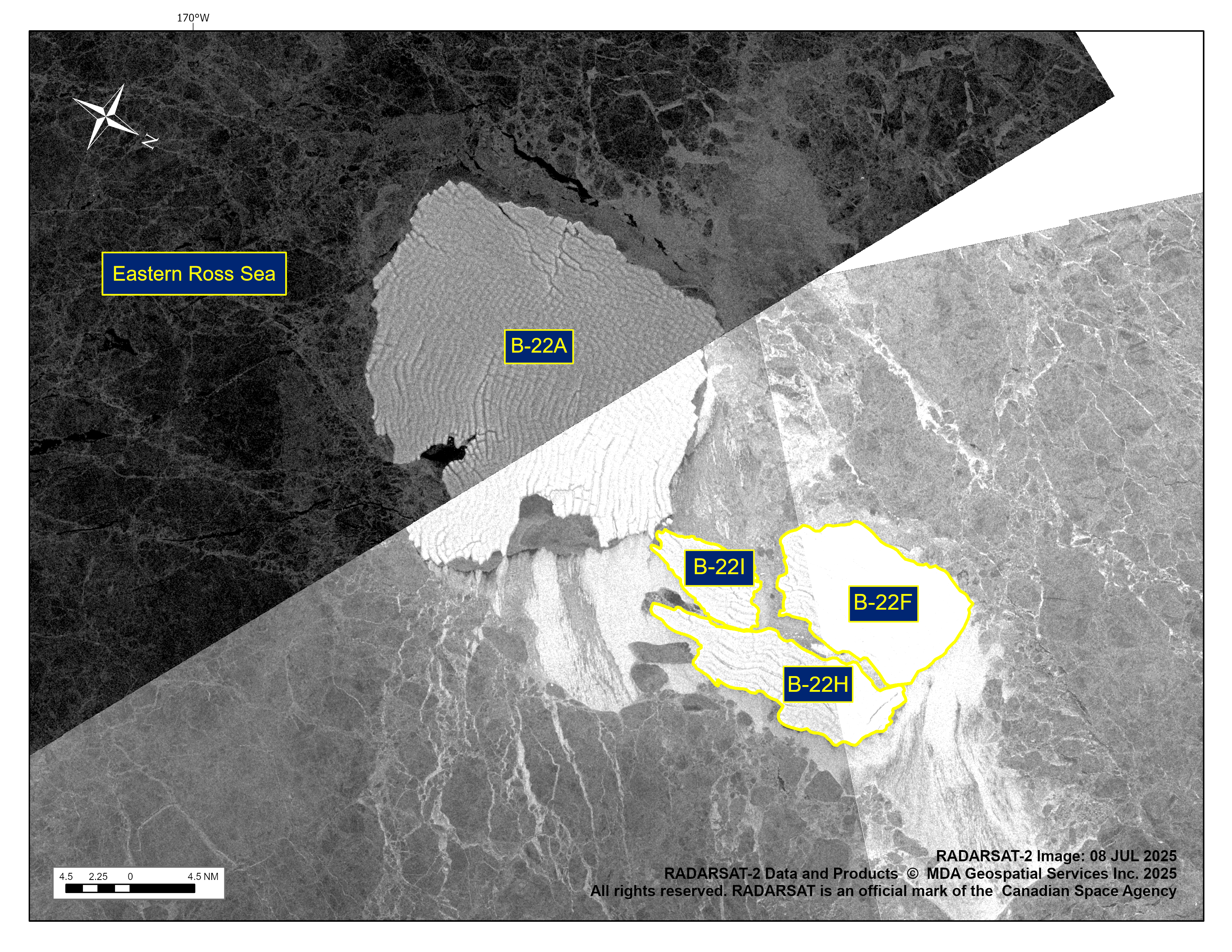
Press Release - Icebergs B-22H and B-22I Have Calved From B-22F
14 July 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg B-22H and B-22I calved from the iceberg B-22F. As of July 8, B22-H was centered at 73° 43' South and 168° 44' West and measured 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis. As of July 8, B22-I was centered at 73° 51' South and 168° 58' West and measured 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article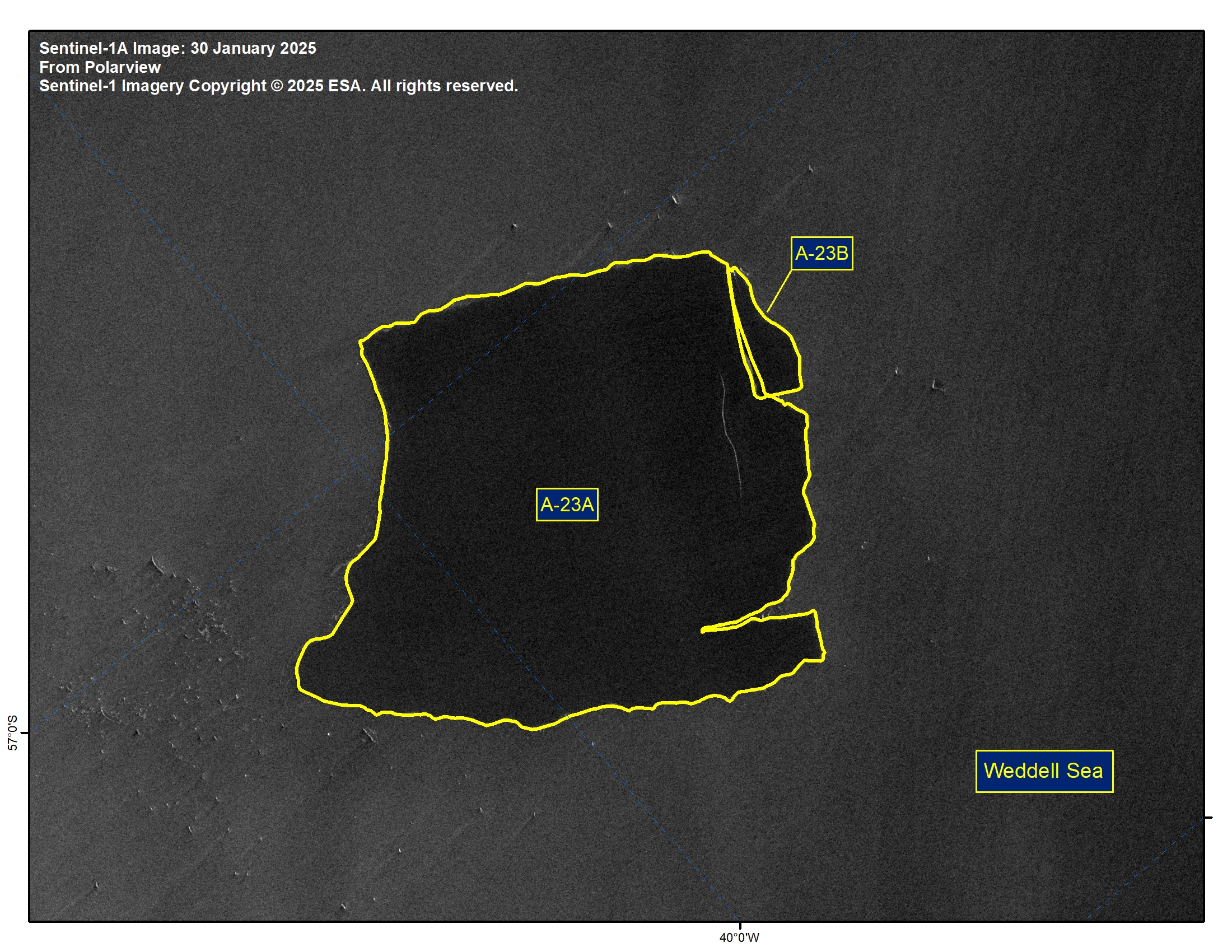
Press Release - Iceberg A-23B Has Calved from Iceberg A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea
18 April 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-36B calved from D-36A in the southern Amery Sea. As of April 15, D-36A was centered at 66° 18' South and 86° 33' East and measured 6 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-36B was centered at 66° 15' South and 86° 44' West and measured 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-36A first calved from the West Ice Shelf in 2024.
Go to Article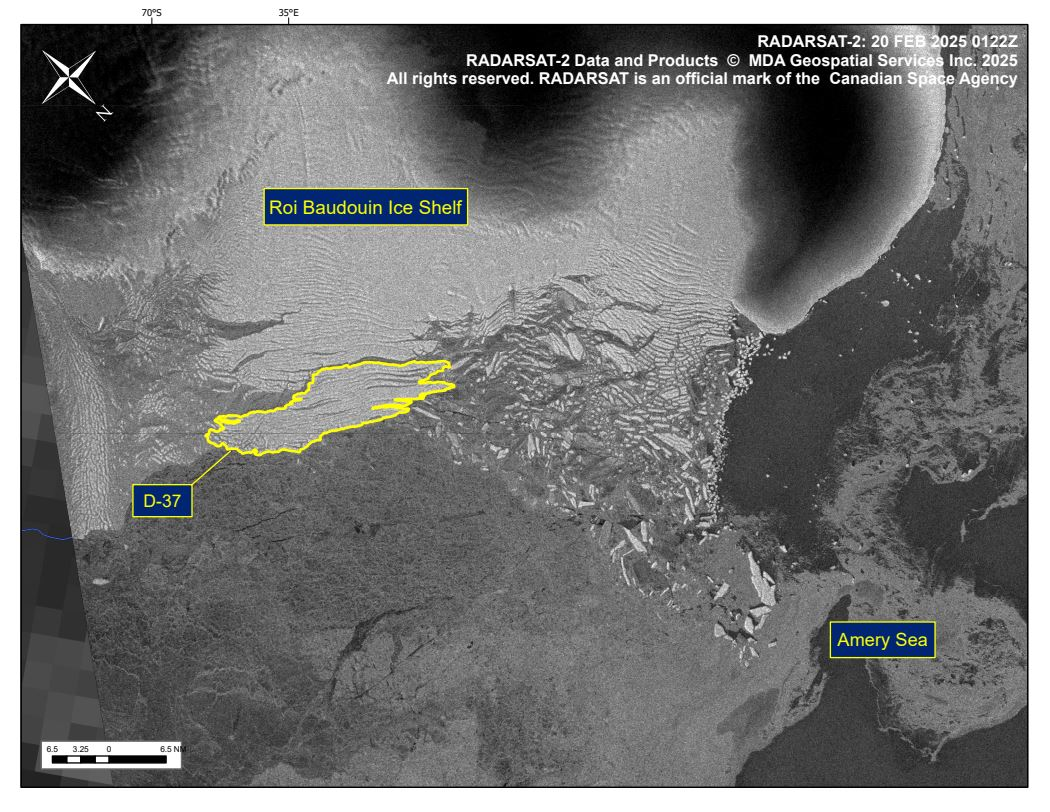
Press Release - Iceberg D-37 Has Calved From Roi Baudouin Ice Shelf
21 February 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-37 calved from the Roi Baudouin Ice Shelf. As of February 20, D-37 was centered at 69° 12' South and 36° 20' East and measured 30 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article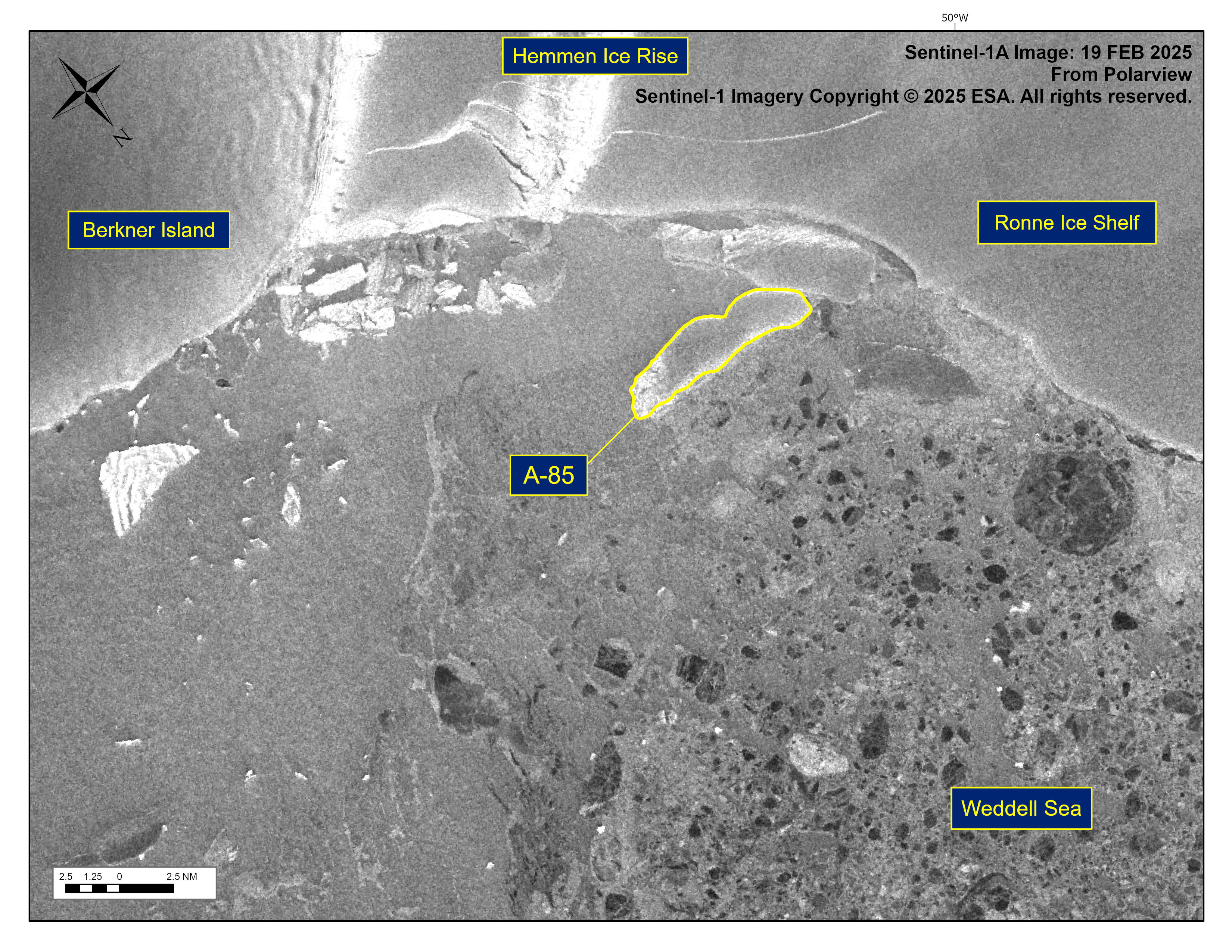
Press Release - Iceberg A-85 Has Calved From Ronne Ice Shelf
21 February 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-85 calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf. As of February 19, A-85 was centered at 77° 30' South and 48° 32' West and measured 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article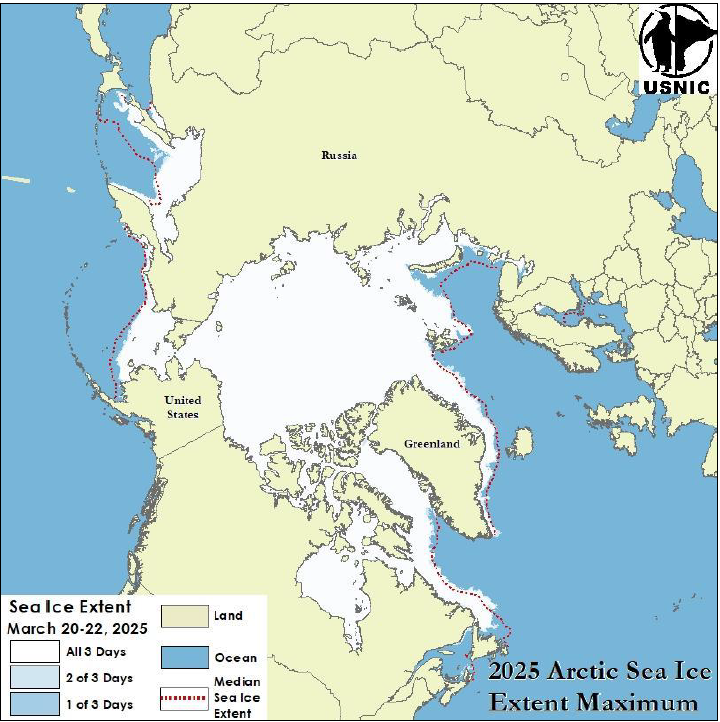
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Maximum Extent
01 April 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the 2025 maximum Arctic sea ice extent occurred in mid-March 2025 with an area of 14.47 million square kilometers. This estimate is based on the Multisensor Analyzed Sea Ice Extent (MASIE) product, which is created jointly with the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), and is ultimately derived from analysis on the USNIC’s Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS).
Go to Article
Press Release - Iceberg A-23B Has Calved from Iceberg A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea
31 January 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-23B calved from A-23A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of January 31, A-23A was centered at 56° 47' South and 40° 19' West and measured 40 nautical miles on its longest axis and 32 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article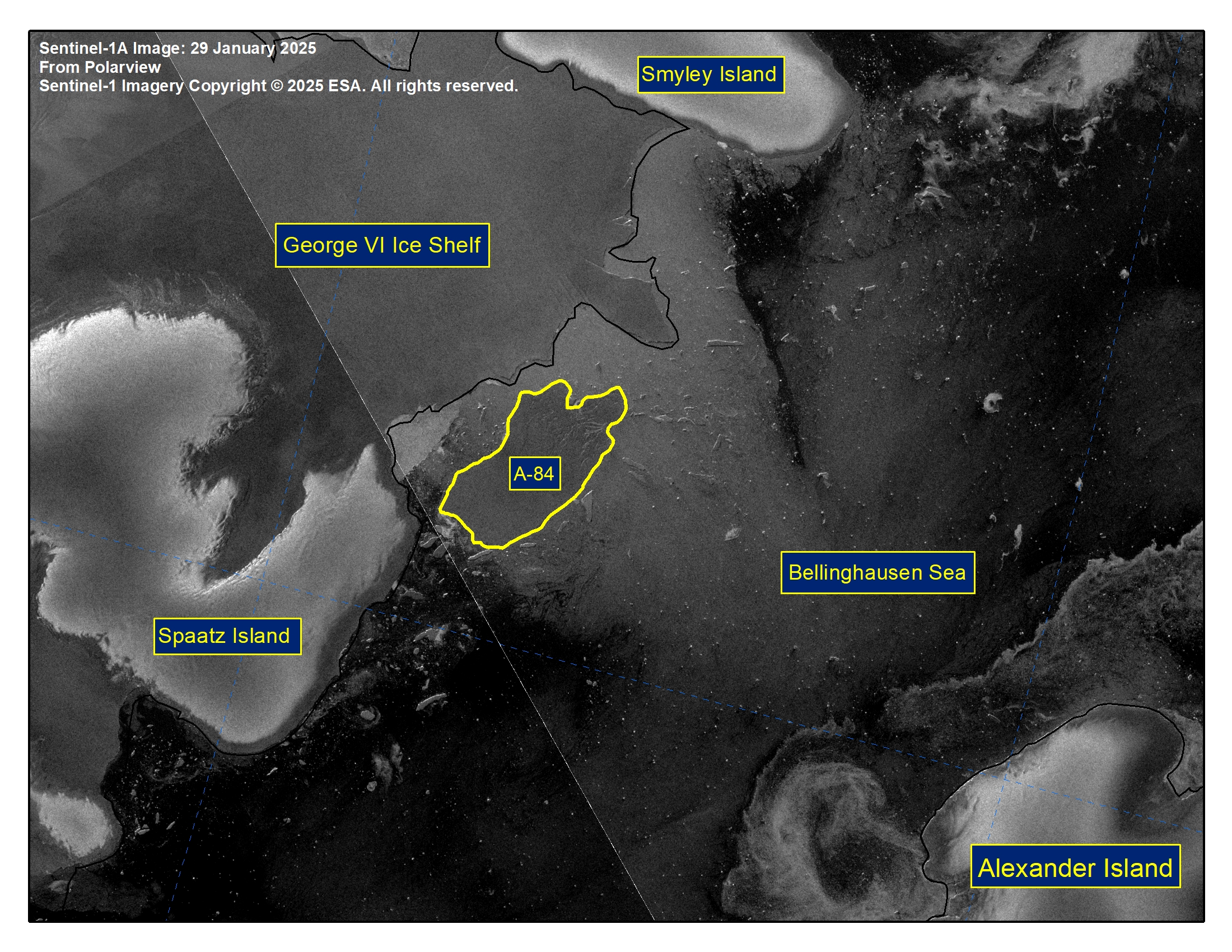
Press Release - Iceberg A-84 Has Calved From George VI ice shelf
31 January 2025 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-84 calved from the George VI ice shelf. As of January 31, A-84 was centered at 72° 41' South and 75° 48' West and measured 16 nautical miles on its longest axis and 9 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article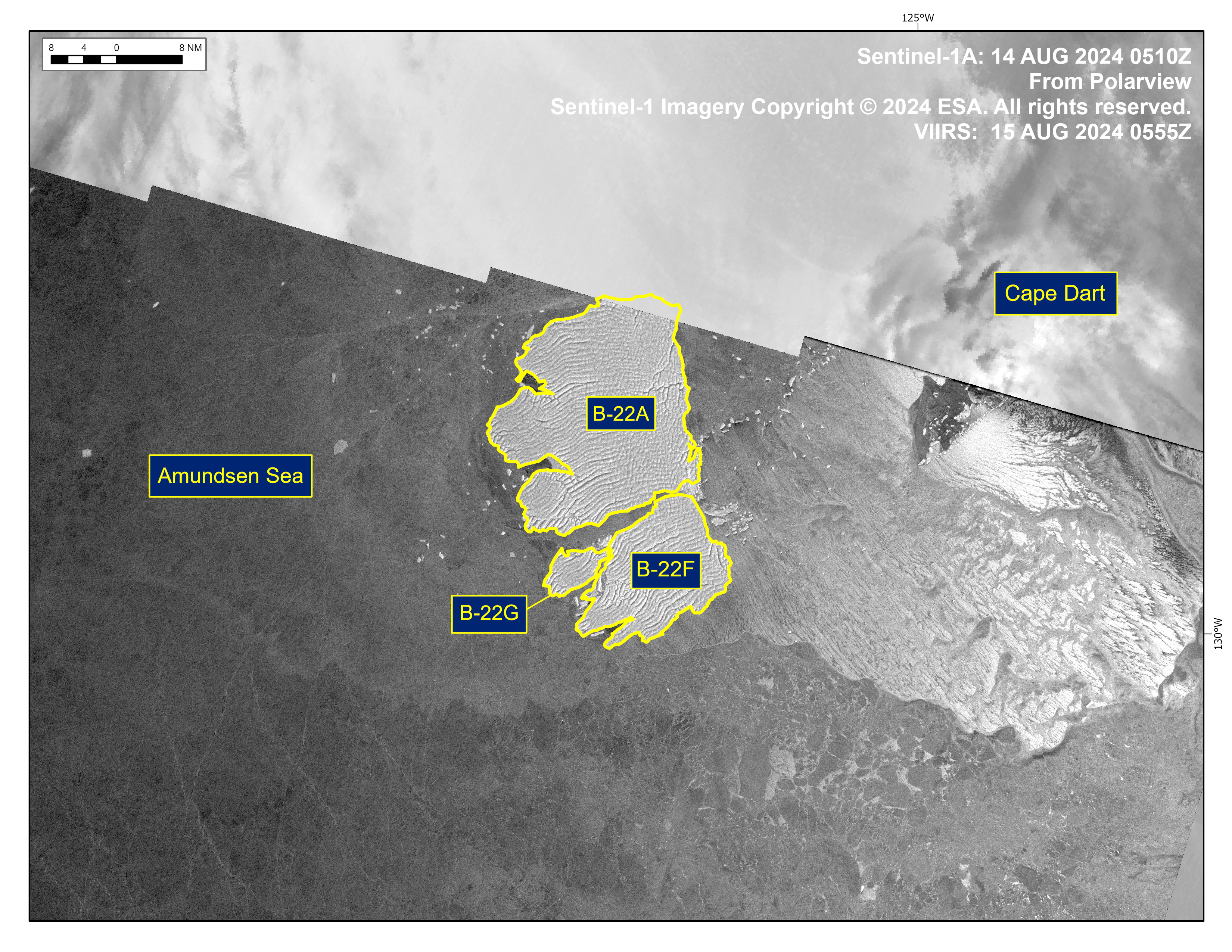
Press Release - Icebergs B-22F and B-22G Have Calved from B-22A in the Amundsen Sea
15 August 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs B-22F and B-22G calved from iceberg B-22A in the Amundsen Sea. As of August 15th, B-22A was centered at 72°41' South and 126°14' West and measured 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 26 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article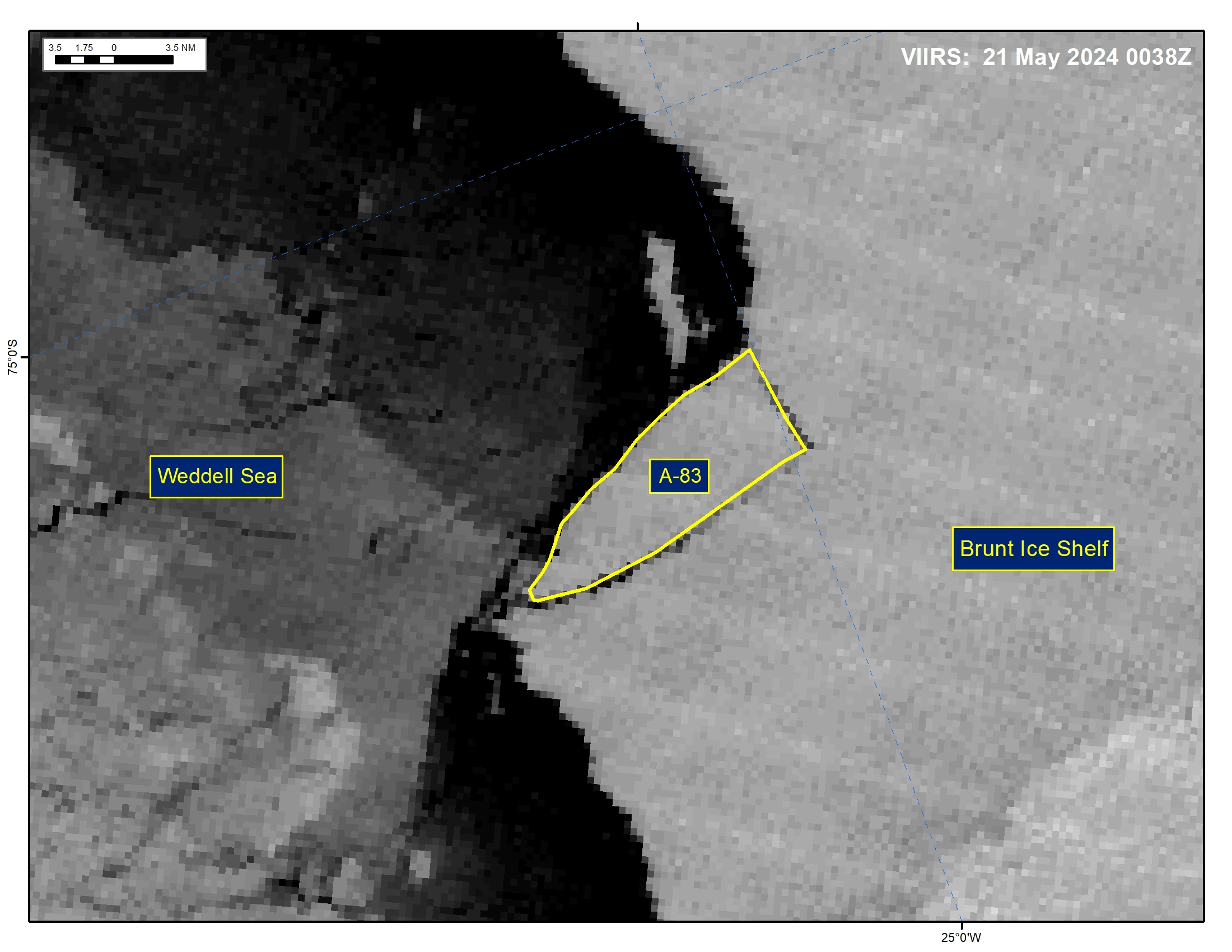
Press Release - Iceberg A-83 Has Calved From Brunt Ice Shelf
21 May 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs A-83 calved from the Brunt Ice Shelf. As of May 21, A-83 was centered at 75°21' South and 25°29' West and measured 20 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article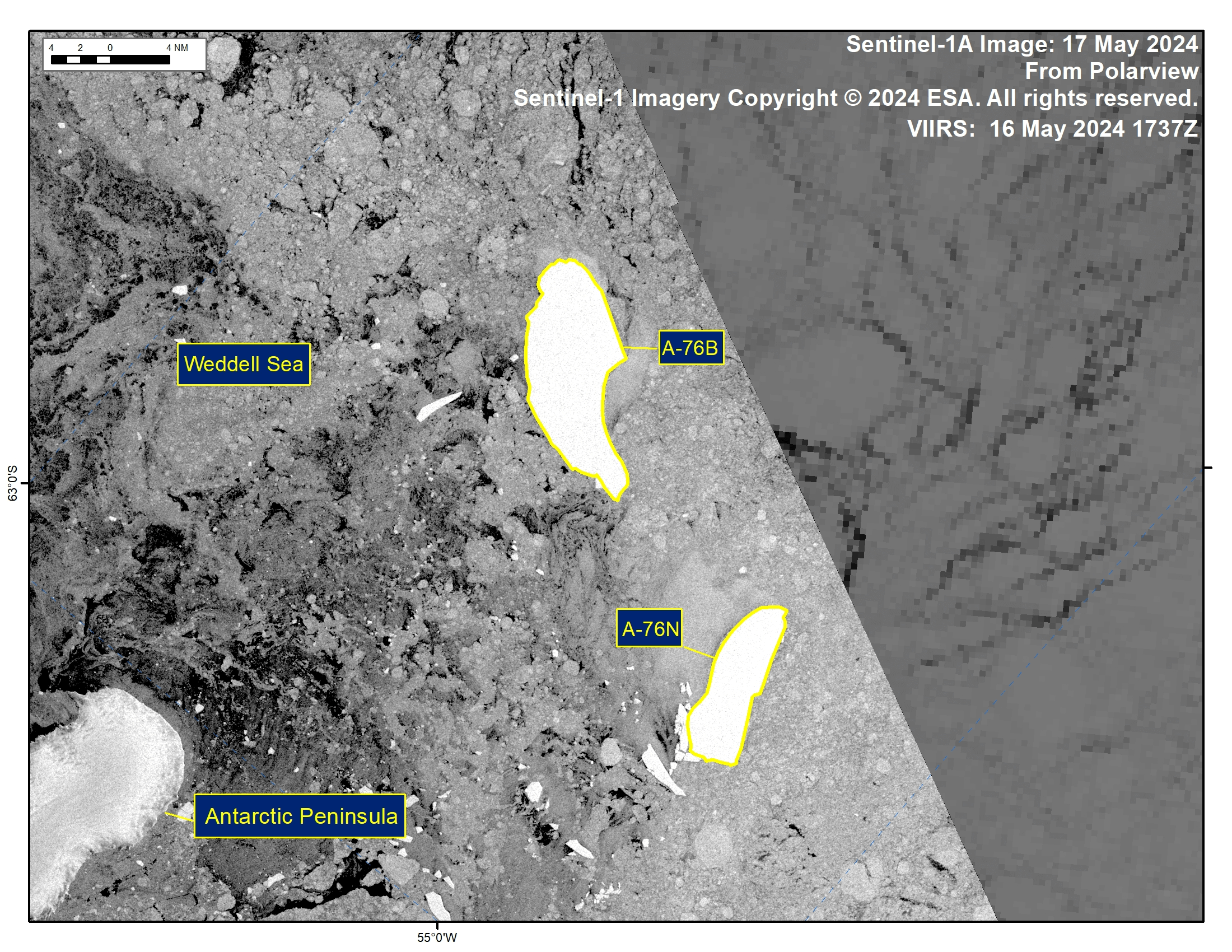
Press Release - Iceberg A-76N Has Calved from Iceberg A-76B in the Weddell Sea
17 May 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs A-76N calved from iceberg A-76B in the Weddell Sea. As of May 17, A-76N was centered at 63°46' South and 54°02' West and measured 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and four nautical miles on its widest axis. A-76B was centered at 63°23' South and 53°42' West and measured 17 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. The break was first seen on satellite imagery on May 17. A-76B first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in May 2021.
Go to Article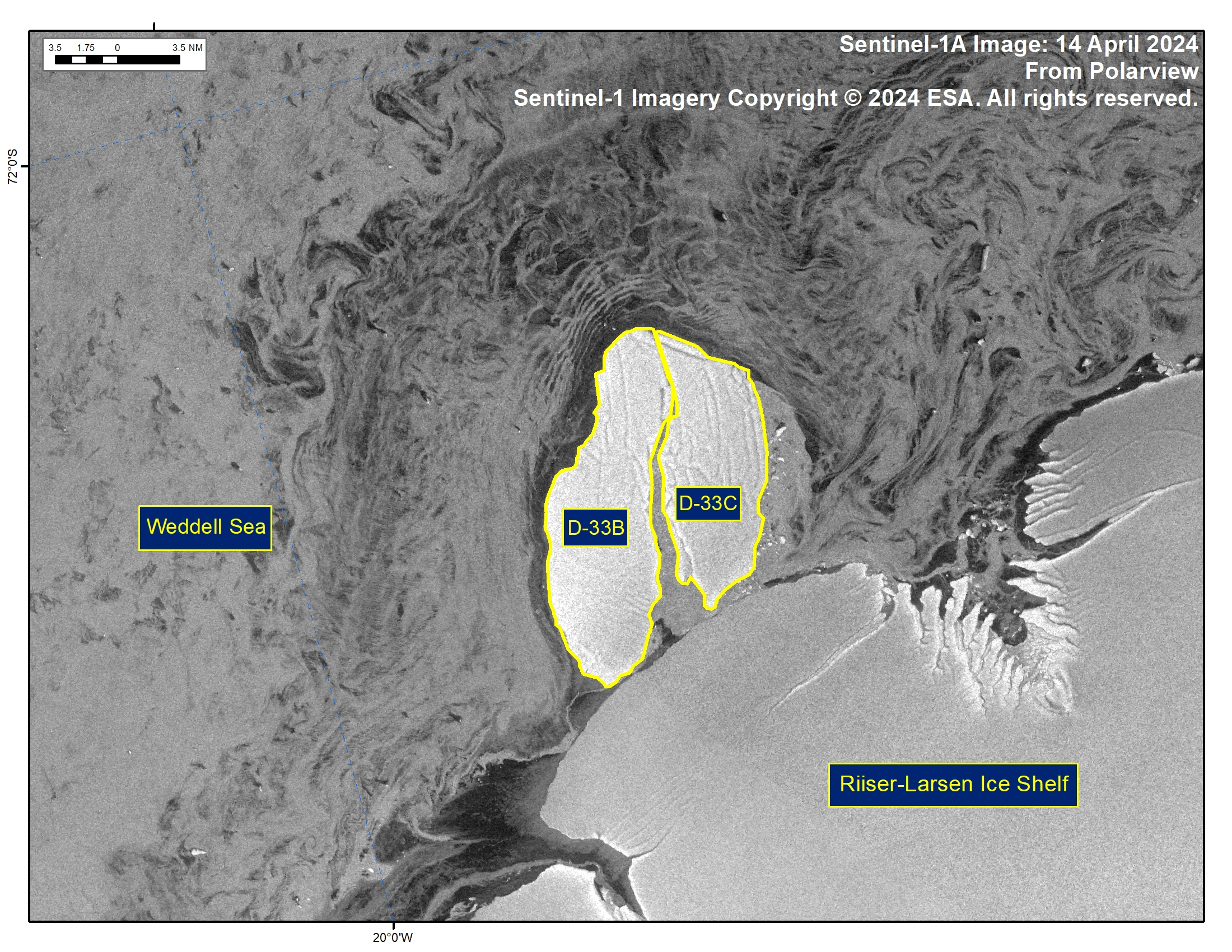
Press Release - Iceberg D-33C Has Calved from Iceberg D-33B in the Weddell Sea
18 April 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs D-33C calved from iceberg D-33B in the Weddell Sea. As of April 14, D-33B was centered at 72°28' South and 18°58' West and measured 20 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-33C was centered at 72°27' South and 18°36' West and measured 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. The break was first seen on satellite imagery on April 14. D-33B first calved from the Borchgrevink Ice Shelf in August 2023.
Go to Article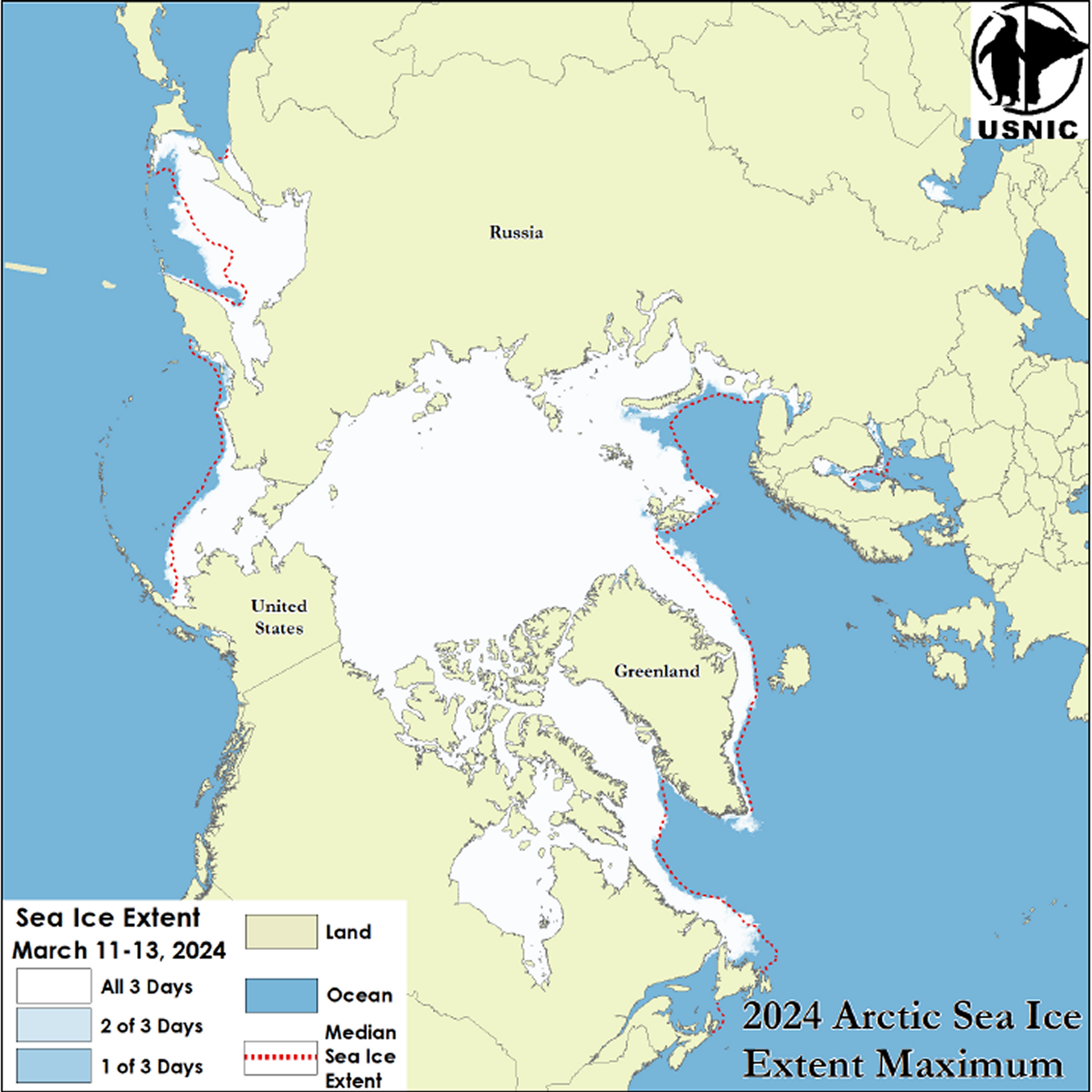
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Maximum Extent
25 March 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the 2024 maximum Arctic sea ice extent occurred in mid-March 2024 with an area of 15.14 million square kilometers. This estimate is based on analysis from the USNIC’s Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS), used in the Multisensor Analyzed Sea Ice Extent (MASIE) product, and is created jointly with the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Go to Article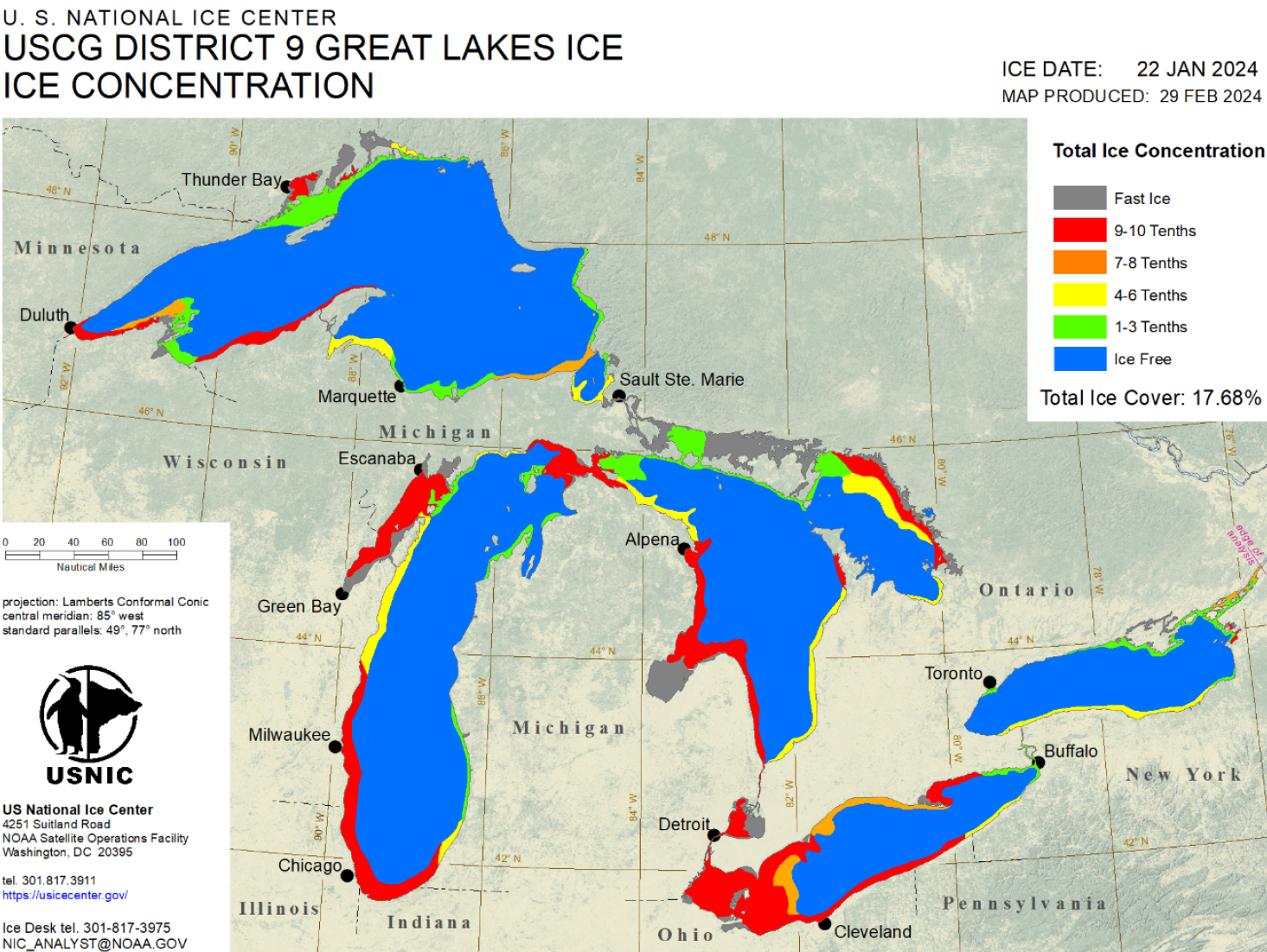
Press Release - Great Lakes Reaches Maximum Ice Coverage for 2023-2024 Season
29 February 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the Great Lakes experienced its annual maximum ice coverage for the 2023-2024 ice season on January 22, 2024. This annual maximum was estimated at 17.68% coverage, which is significantly lower than the average annual maximum of 53%¹ coverage; the 2023-2024 maximum was also observed to occur approximately one month earlier than the annual .
Go to Article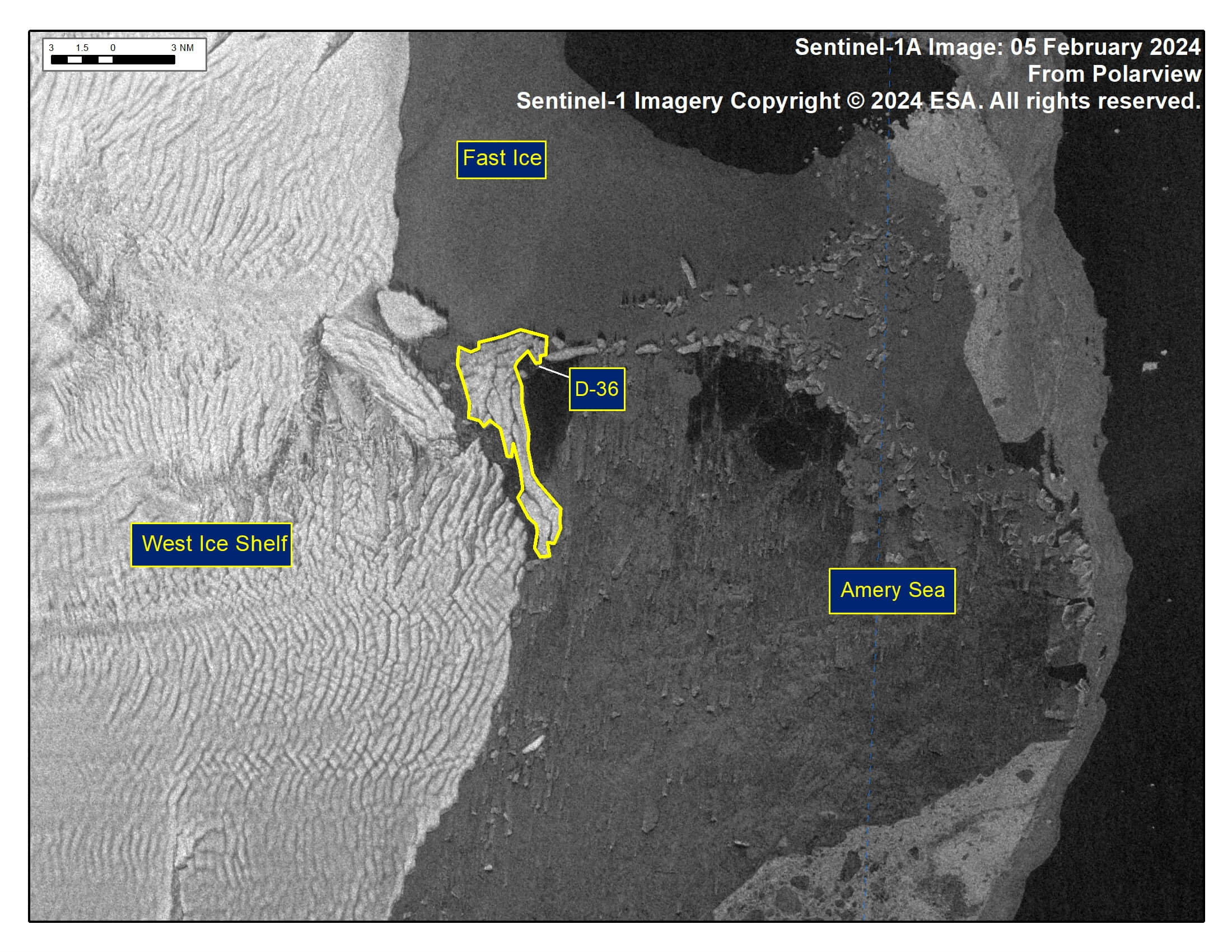
Press Release - Iceberg D-36 Has Calved From the West Ice Shelf
06 February 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-36 calved from the West Ice Shelf. As of February 05, D-36 was centered at 66°18' South and 86°37' East and measured 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article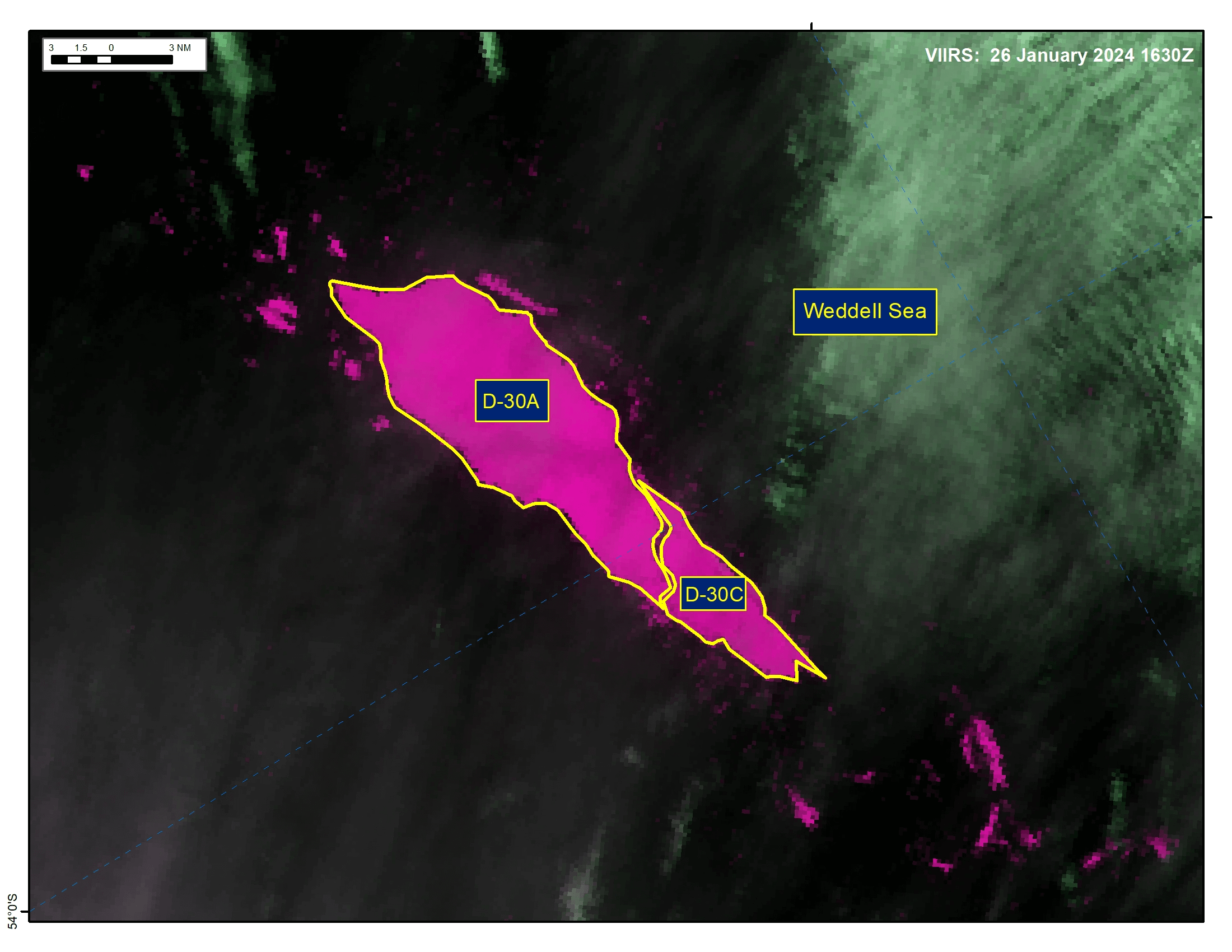
Press Release - Iceberg D-30C Has Calved from Iceberg D-30A in the Weddell Sea
02 February 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-30C calved from iceberg D-30A in the Weddell Sea. As of February 02, D-30A was centered at 53°16' South and 36°04' West and measured 23 nautical miles on its longest axis and 9 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-30C was centered at 54°04' South and 35°30' West and measured 13 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article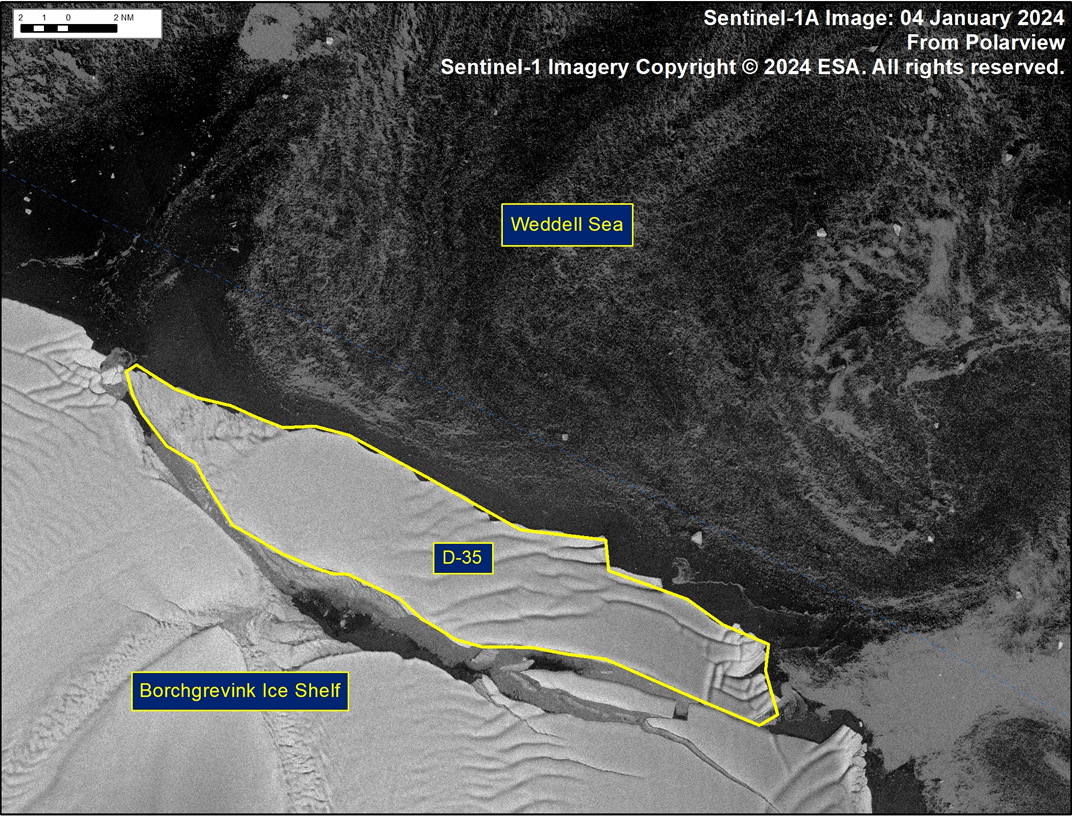
Press Release - Iceberg D-35 Has Calved From Borchgrevink Ice Shelf
08 January 2024 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-35 calved from Borchgrevink Ice Shelf. As of January 08, D-35 was centered at 70°01' South and 21°37' East and measured 29 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article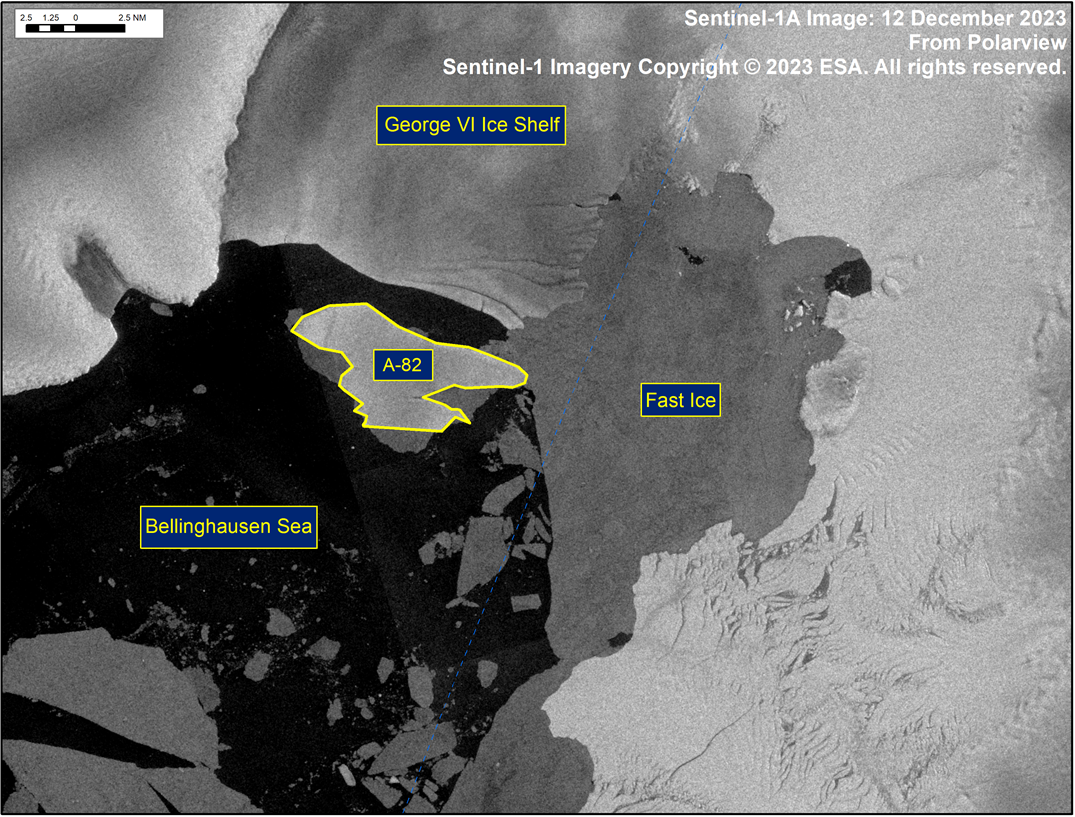
Press Release - Iceberg A-82 Has Calved From George VI Ice Shelf
13 December 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-82 calved from the George VI ice shelf. As of December 12, A-82 was centered at 72°51' South and 72°24' West and measured 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article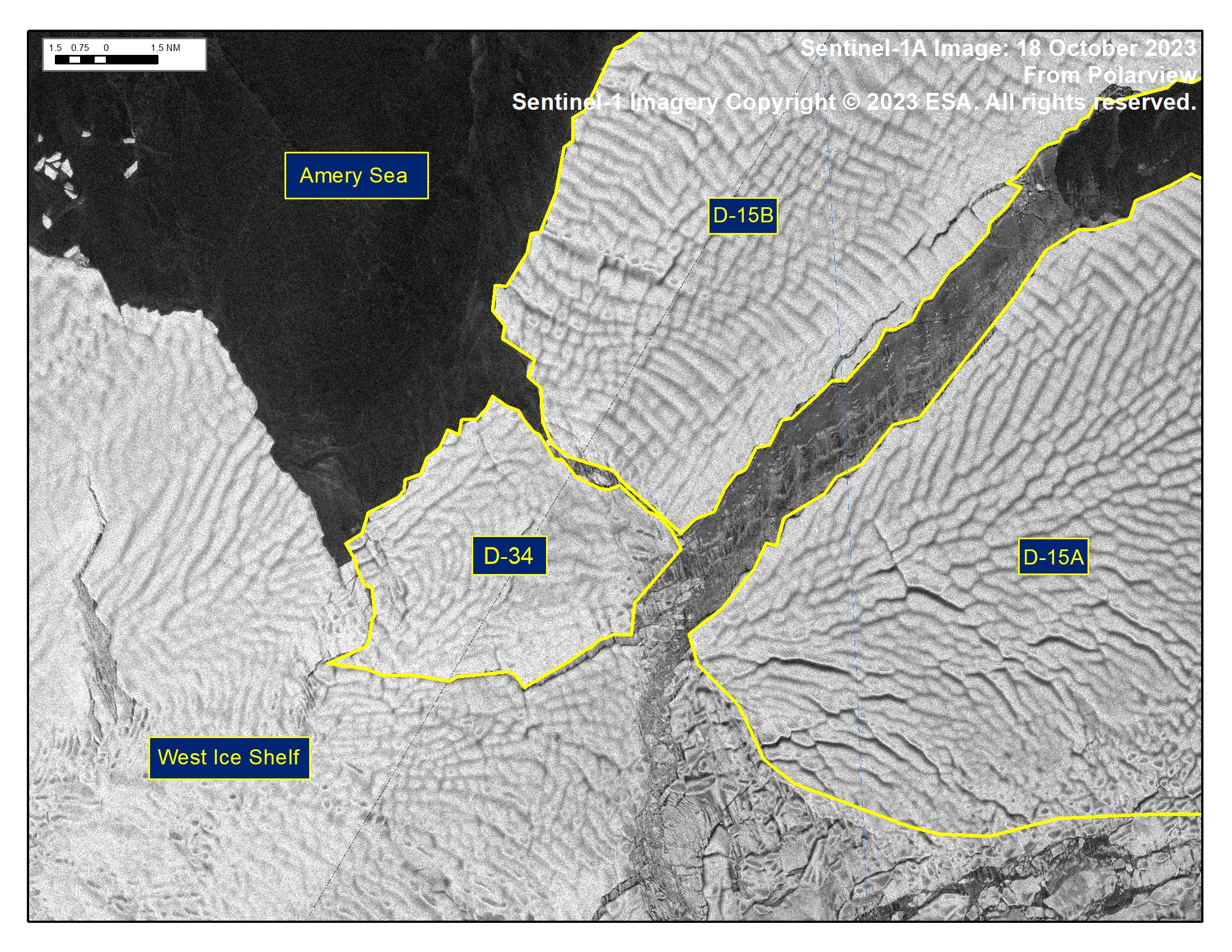
Press Release - Iceberg D-34 Has Calved From West Ice Shelf
19 October 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-34 calved from the West Ice Shelf. As of October 19, D-34 was centered at 67°11' South and 82°7' East and measured 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article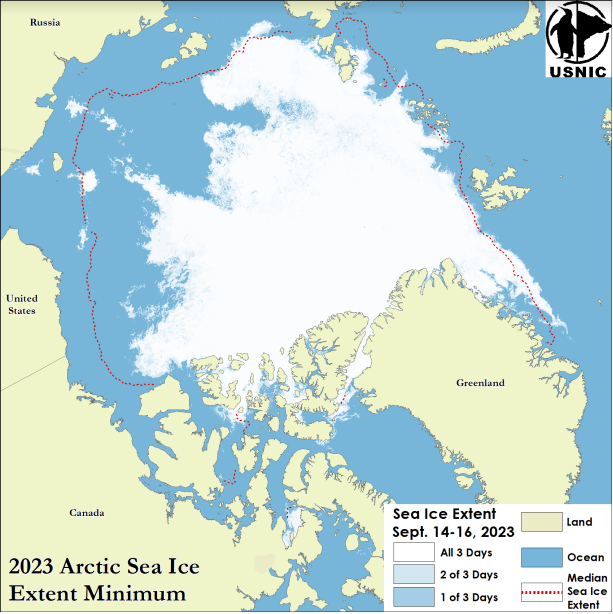
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Minimum Extent
26 Septemper 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the 2023 minimum Arctic sea ice extent occurred in mid-September 2023 with an area of 4.13 million square kilometers. This estimate is based on analysis from the USNIC’s Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS), used in the Multisensor Analyzed Sea Ice Extent (MASIE) product, and is created jointly with the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Go to Article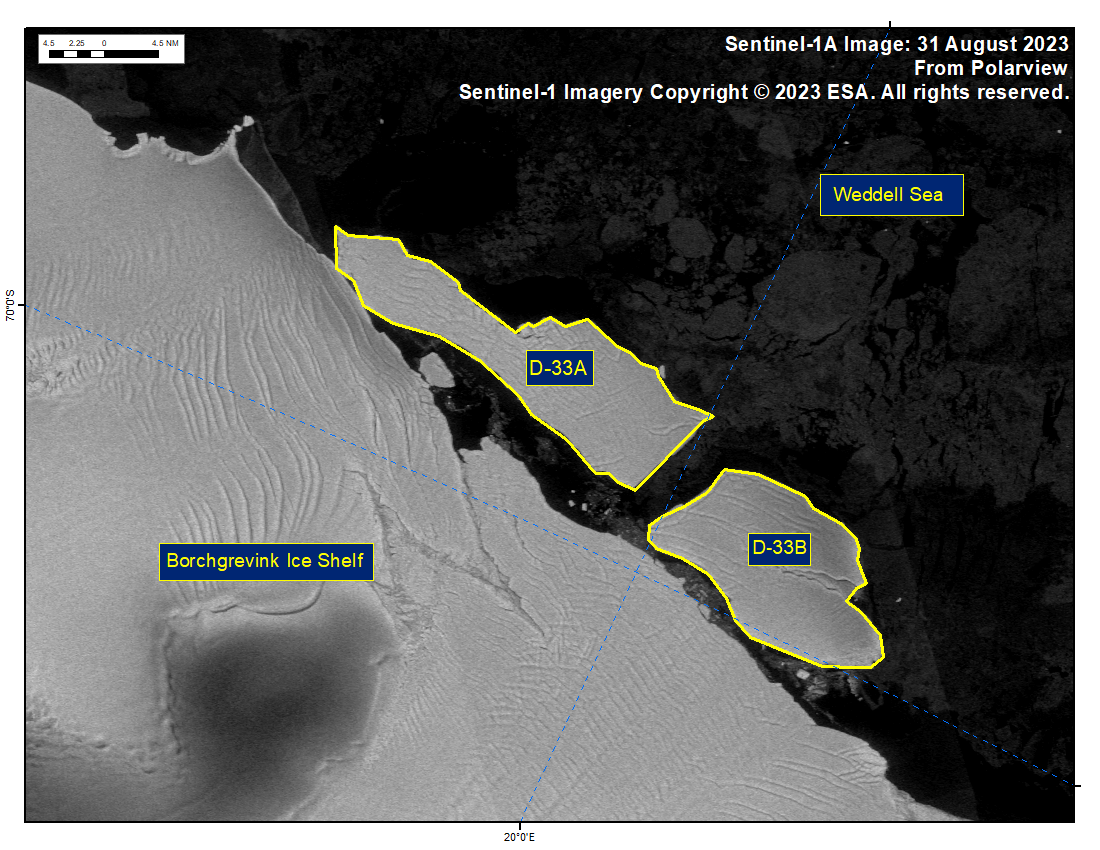
Press Release - Icebergs D-33A and D-33B Have Calved from Borchgrevink Ice Shelf
31 August 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs D-33A and D-33B calved from Borchgrevink Ice Shelf in the southern Weddell Sea. As of September 01, D-33A was centered at 69°47' South and 19°14' West and measured 34 nautical miles on its longest axis and 10 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-33B was centered at 69°54' South and 20°31' West and measured 21 nautical miles on its longest axis and 12 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article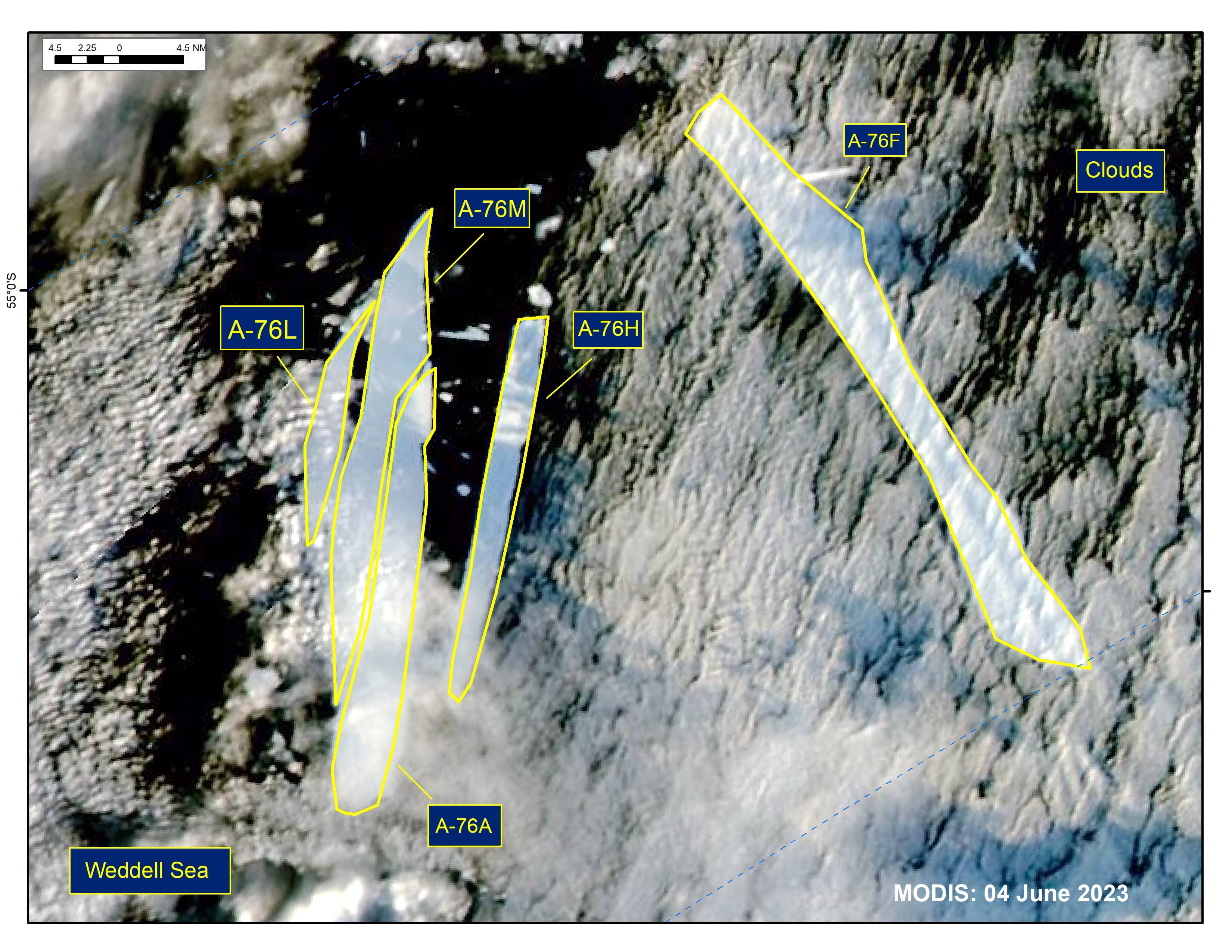
Press Release - Iceberg A-76A Split in Half, Creating A-76M
25 May 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-76A has split in half, creating A-76M in the northern Weddell Sea. The calving event was first spotted on MODIS imagery on June 03. As of June 04, A-76A was centered at 55° 32' S and 37° 22' W and measured 31 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-76M was centered at 55° 26' S and 37° 21' W and measured 35 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-76 first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in May 2021. The locations of A-76A through A-76L are still being tracked by the USNIC, while A-76I broke up and became too small to track on May 16.
Go to Article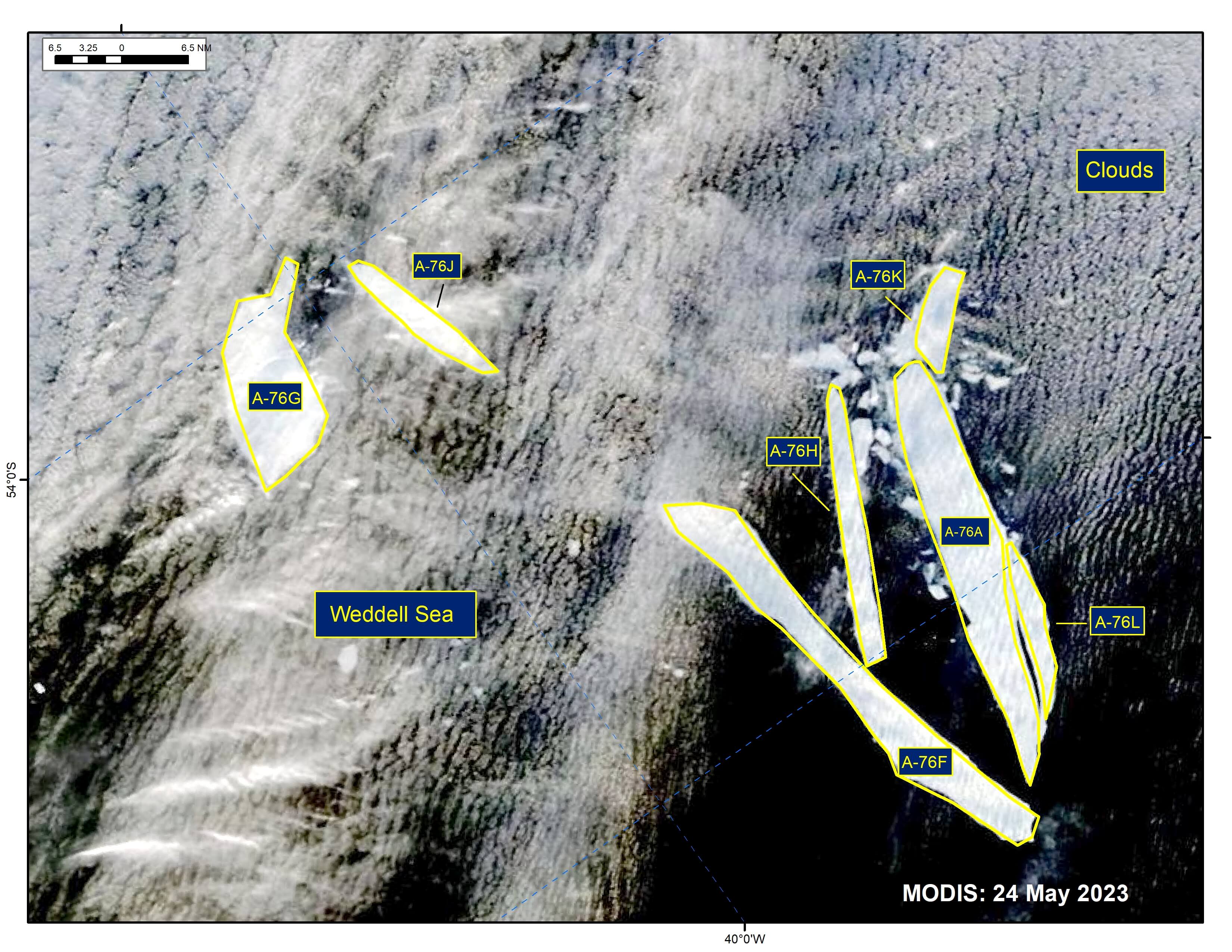
Press Release - The Breakup of A-76 Continues
25 May 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-76J calved from A-76F and icebergs A-76K and A-76L have calved from iceberg A-76A in the northern Weddell Sea. The calving event was first spotted on MODIS imagery as early as May 21.
Go to Article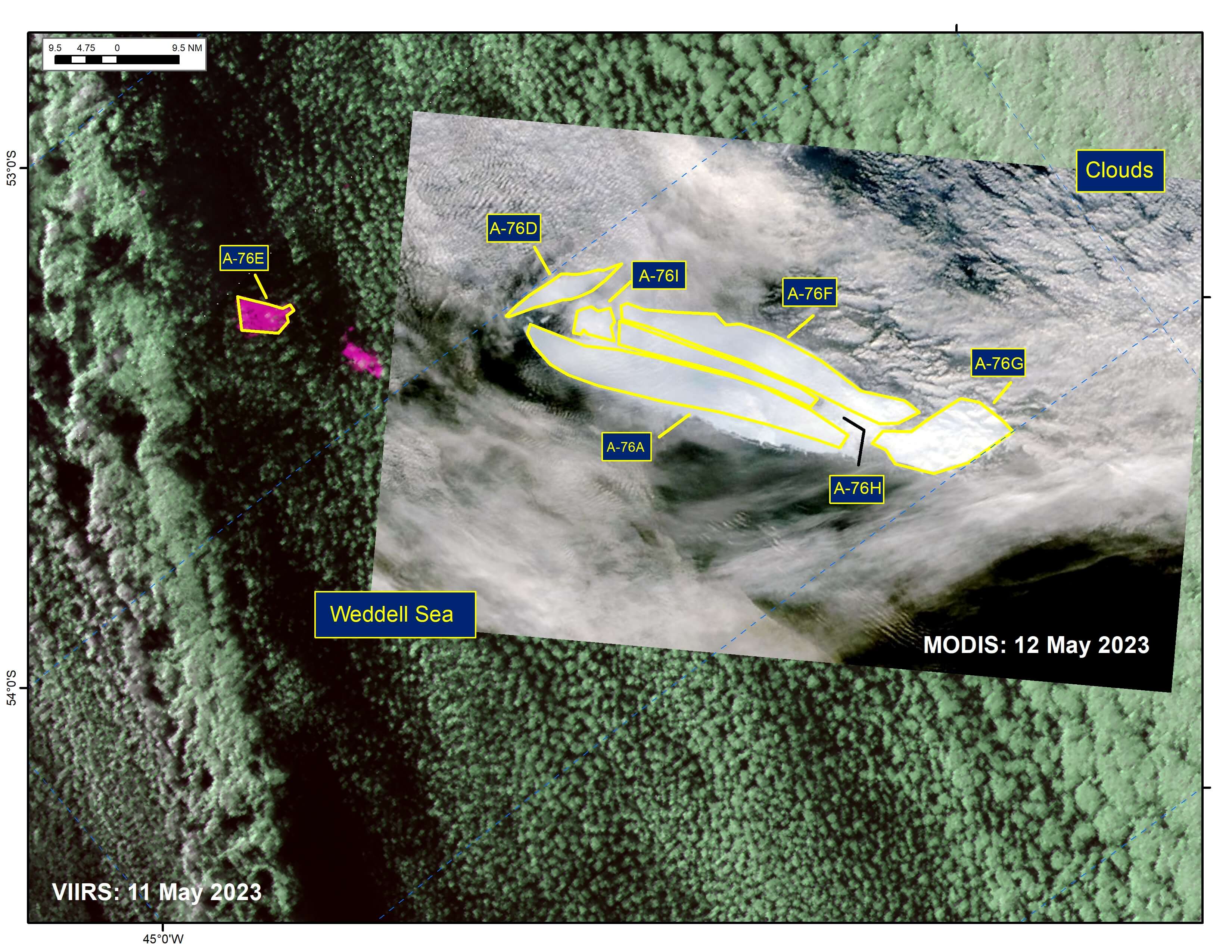
Press Release - Five New Icebergs Have Calved from Iceberg A-76A
12 May 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that icebergs A-76E, A76-F, A76-G, A76-H, and A76-I calved from iceberg A-76A in the northern Weddell Sea. The calving event was first spotted on MODIS imagery as early as May 08. A-76 first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in May 2021. A-76 calved into A-76A, A-76B, and A-76C later that month. A-76D calved on or about 28 April 2023.
Go to Article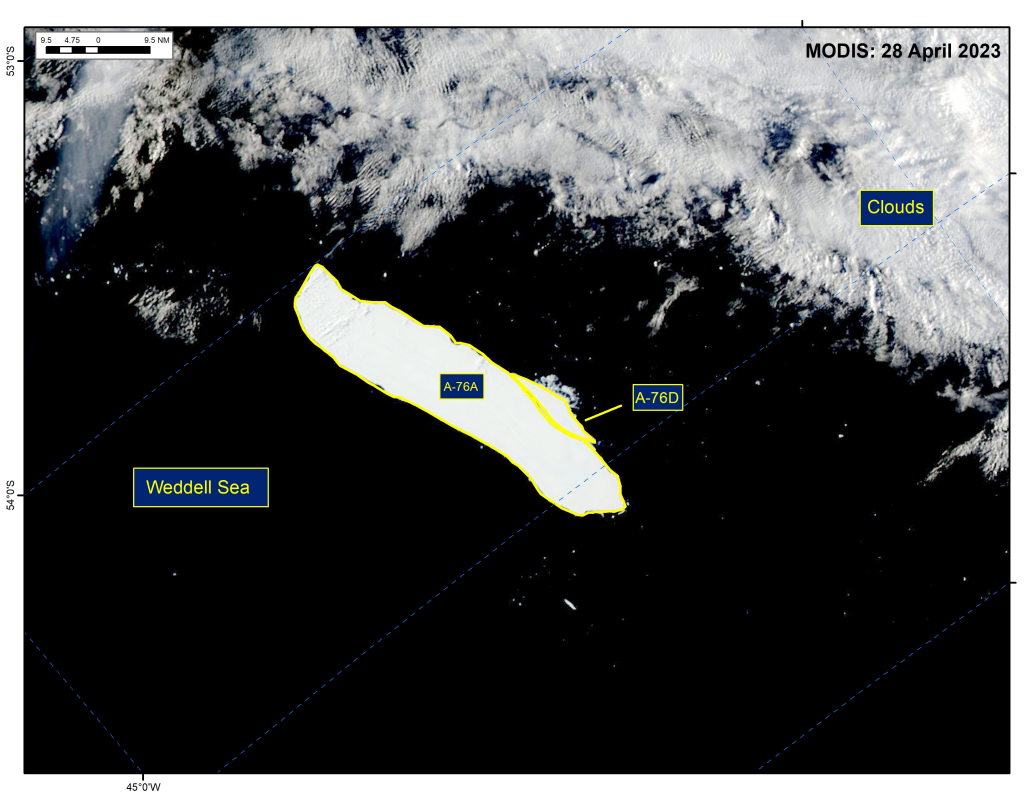
Press Release - Iceberg A-76D Has Calved from Iceberg A-76A
29 April 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-76D calved from iceberg A-76A in the northern Weddell Sea. As of April 28, A-76D was centered at 56°46' South and 42°10' West and measured 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-76 first calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf in May 2021 and subsequently calved into A-76A, A-76B and A-76C later that month.
Go to Article
Press Release - U.S. National Ice Center Welcomes New Director
28 April 2023 — Commander R. D. Travis Wendt, USN relieved Commander Casey J. Gon, USN as Commanding Officer of NAVICECEN during a change of command ceremony held at the NOAA Satellite Operations Facility in Suitland, MD on April 28, 2023 at 1000.
Go to Article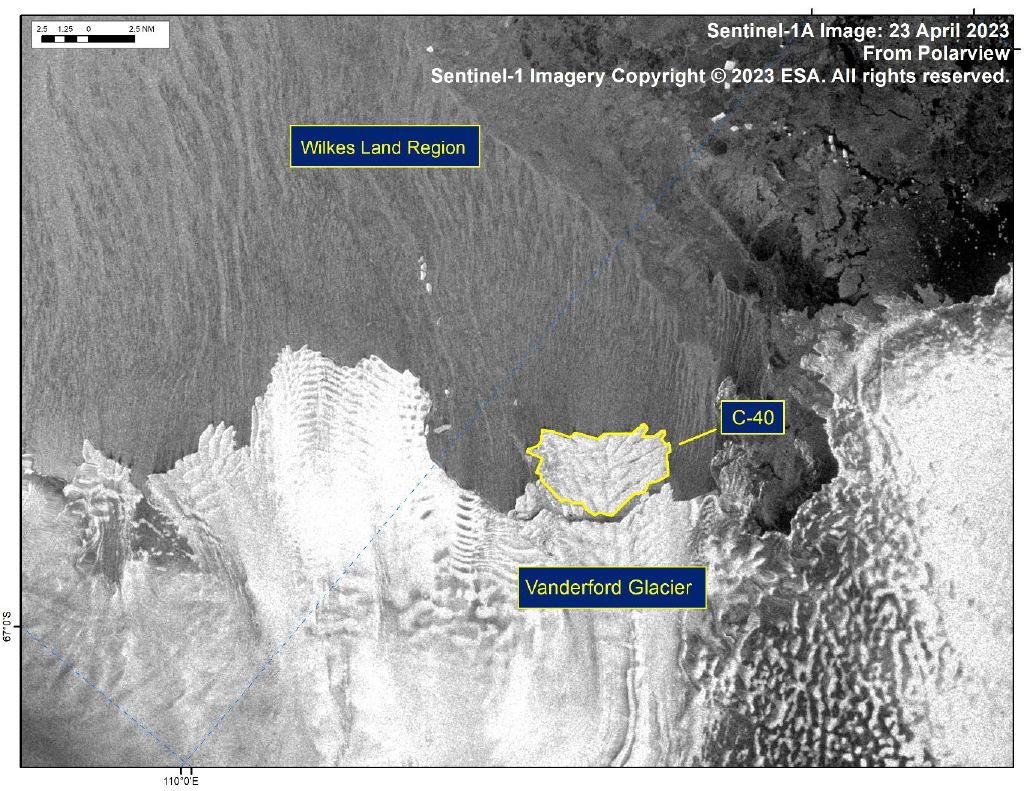
Press Release - Iceberg C-40 Has Calved from Vanderford Glacier
24 April 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg C-40 calved from the Vanderford Glacier in the Wilkes Land Region of Antarctica. As of April 23, C-40 was centered at 66°32' South and 110°17' East and measured 7 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis..
Go to Article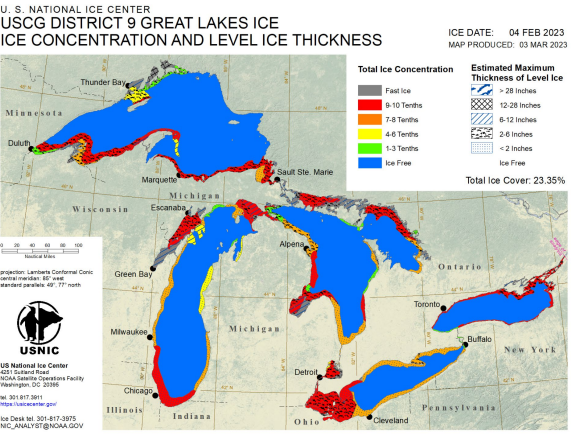
Press Release - Great Lakes Reaches Maximum Ice Coverage for 2022-2023 Season
03 March 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the Great Lakes experienced maximum ice coverage for the 2022-2023 ice season on February 04, 2023 at approximately 23.35% coverage. This maximum is significantly lower than the average maximum of 53%¹ and occurred approximately one month earlier than normal.
Go to Article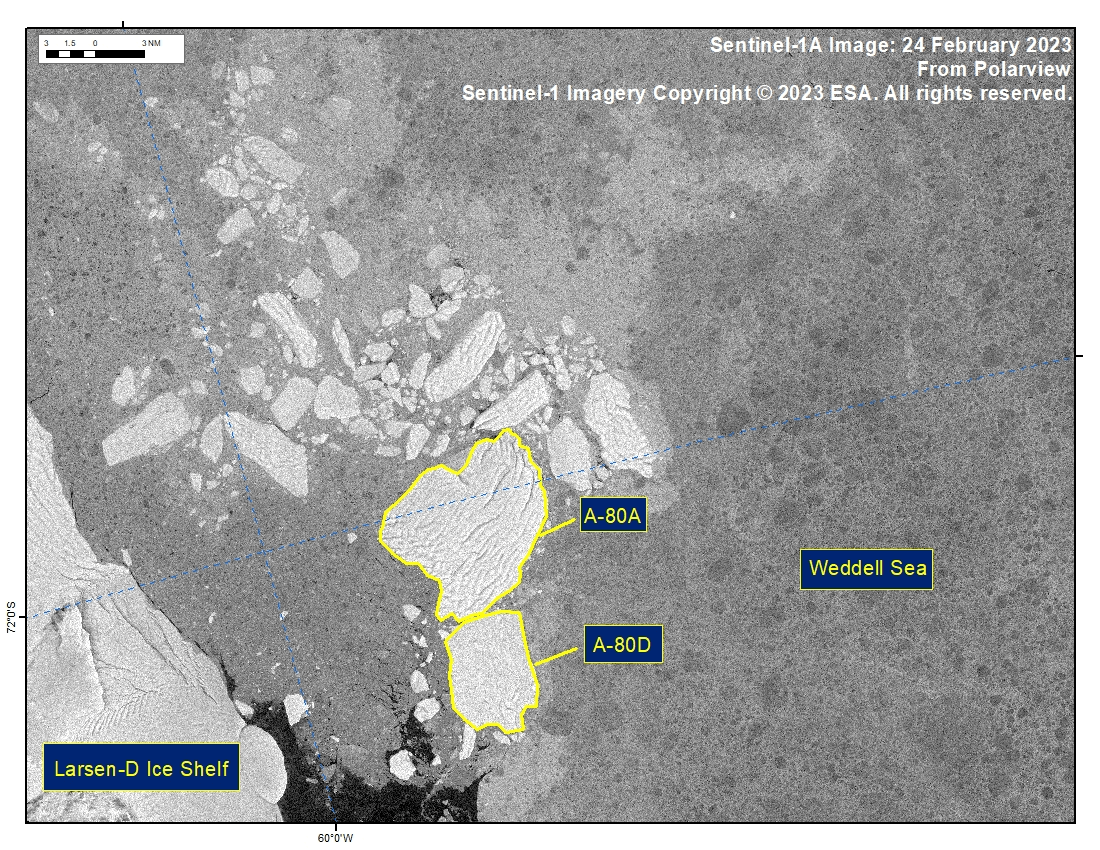
Press Release - Iceberg A-80D Has Calved from Iceberg A-80A in the Weddell Sea
24 February 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-80D (figure 1, below) calved from iceberg A-80A in the Weddell Sea. As of February 24, A-80A was centered at 72°02' South and 59°17' West and measured 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis. A-80D was centered at 72°11' South and 59°20' West and measured 7 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis. The initial break was seen in satellite imagery on 24 February. A-80A first calved from the Larsen-D Ice Shelf in November 2022 along with A-80B and A-80C. A-80B and A-80C are no longer large enough to track.
Go to Article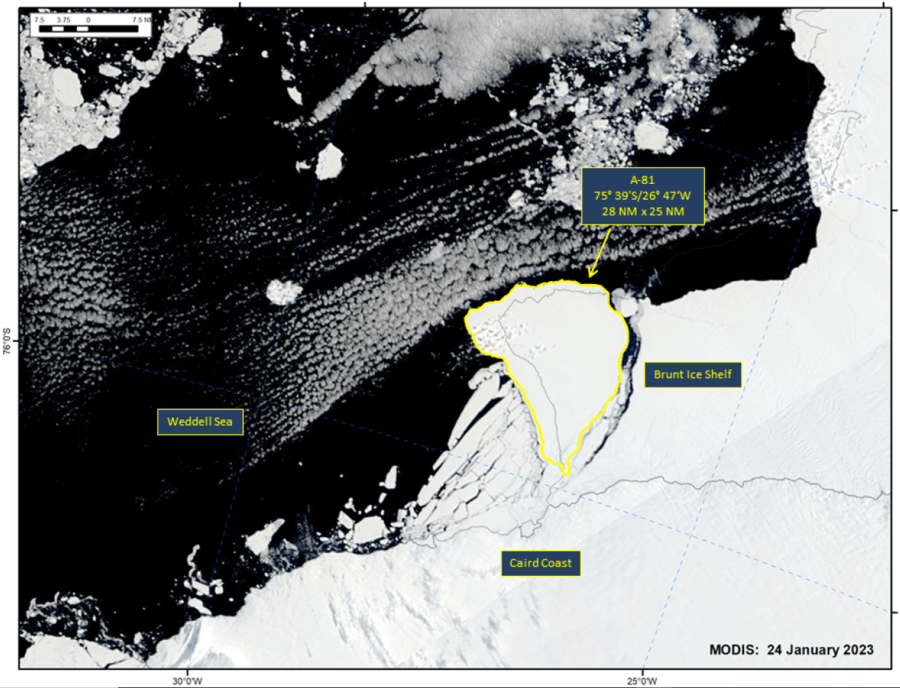
Press Release - Iceberg A-81 Has Calved from the Brunt Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea
24 January 2023 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg A-81 calved from the Brunt Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea. As of January 24, A-81 was centered at 75°39' South and 26°47' West and measured 28 nautical miles on its longest axis and 25 nautical miles on its widest axis. The initial break was seen in satellite imagery on 24 January.
Go to Article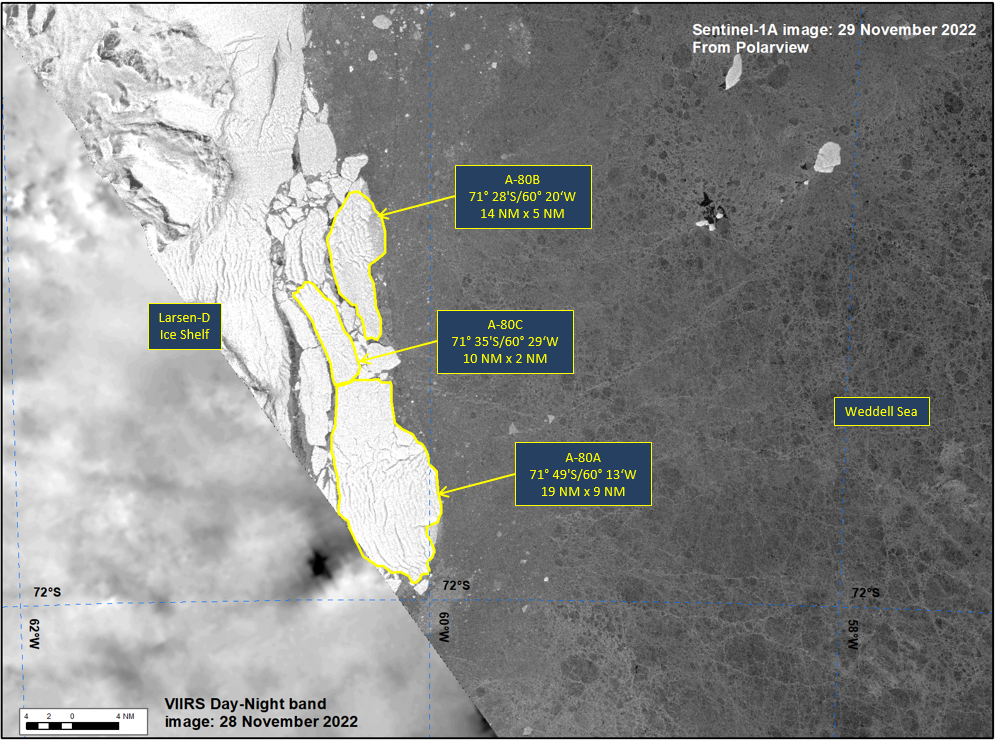
Press Release - Icebergs A-80A, A-80B, and A-80C Have Calved from the Southern End of the Larsen-D Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea
29 November 2022 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that the three new A-80 icebergs calved at the same time from a larger calving event of the Larsen-D Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea. As of November 29, A-80A was centered at 71°49' South and 60°13' West and measured 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 9 nautical miles on its widest axis, A-80B was centered at 71°28' South and 60°20' West and measured 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis, A-80C was centered at 71°35' South and 60°29' West and measured 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis. The initial break was seen in satellite imagery on 27 November..
Go to Article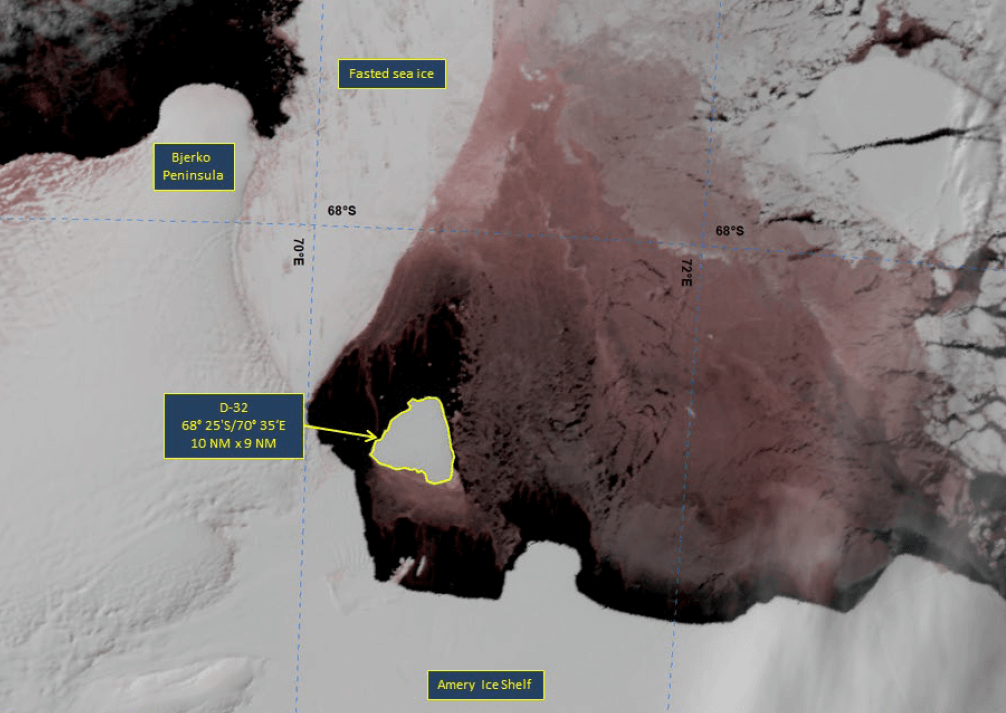
Press Release - Iceberg D-32 Has Calved from the Western Side of the Amery Ice Shelf
19 October 2022 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed that iceberg D-32 has calved from the Amery Ice Shelf in the Amery Region of Antarctica. As of October 19, D-32 was centered at 68° 25' South and 70° 35' East and measured 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 9 nautical miles on its widest axis. D-32 likely calved on or around October 14, and has drifted 14 nautical miles away from the shelf since then.
Go to Article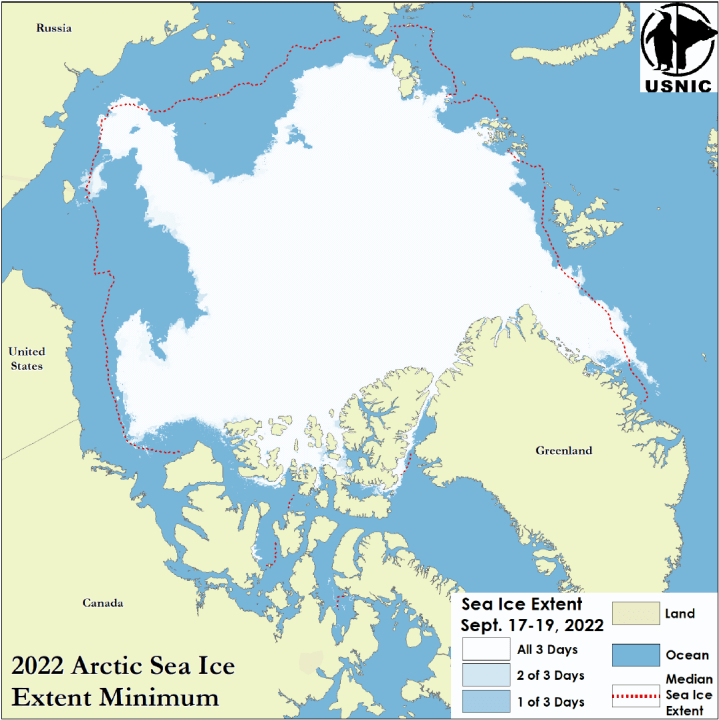
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Minimum Extent
26 Septemper 2022 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the 2022 minimum Arctic sea ice extent occurred in mid-September 2022 with an area of 4.72 million square kilometers based on analysis from the USNIC’s Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS), used in the Multisensor Analyzed Sea Ice Extent (MASIE) product, jointly created with the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Go to Article
Press Release - Call for Abstracts for AMS 2023 Session Topic: “Advancements in Operational and Scientific Sea Ice Applications”
U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) requests all cryosphere professionals to consider submitting an abstract to the USNIC’s session, “Advances in Operational and Scientific Sea Ice Applications,” at the American Meteorological Society (AMS) 2023 annual meeting, January 8-12, 2023 in Denver (and online). All are encouraged to consider an oral presentation.
Go to Article
Press Release - U.S. National Ice Center Deploys Buoy in Data-Sparse’d Arctic
15 August 2022 — U.S. Naval Meteorology and Oceanography (Naval Oceanography) representation from U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) were part of personnel aboard the USCGC Healy (WAGB-20) to successfully deploy Sofar Ocean spotter-buoys during its patrol to the North Pole, this Summer.
Go to Article
Press Release - USNIC Receives Esri Special Achievement Award
13 July 2022 — U.S. National Ice Center's(USNIC) Information Technology Department Head, Mr. George Wachira, accepted an Esri Special Achievement award in Geographic Information Systems(GIS) at the 2022 Esri User Conference on behalf of USNIC's workfore.
Go to Article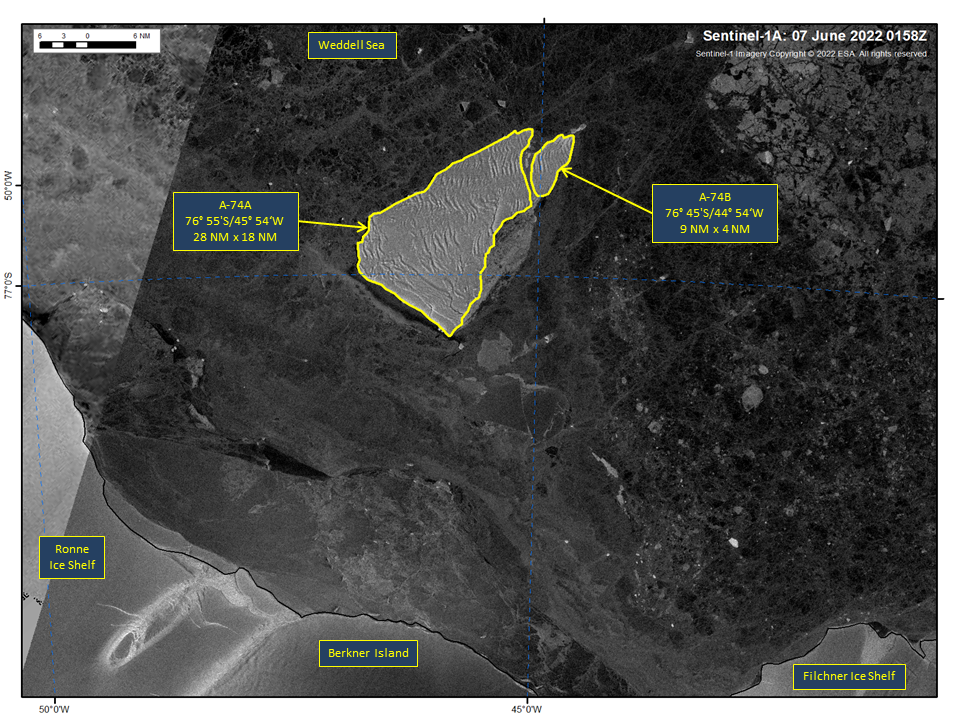
Press Release - Iceberg A-74 Has Calved into A-74A and A-74B
10 Jun 2022 — Iceberg A-74 has calved into two icebergs A-74A and A-74B near Berkner Island in the Weddell Sea. As of June 07, A-74A was centered at 76° 55' South and 45° 54' West and measured 28 nautical miles on its longest axis and 18 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article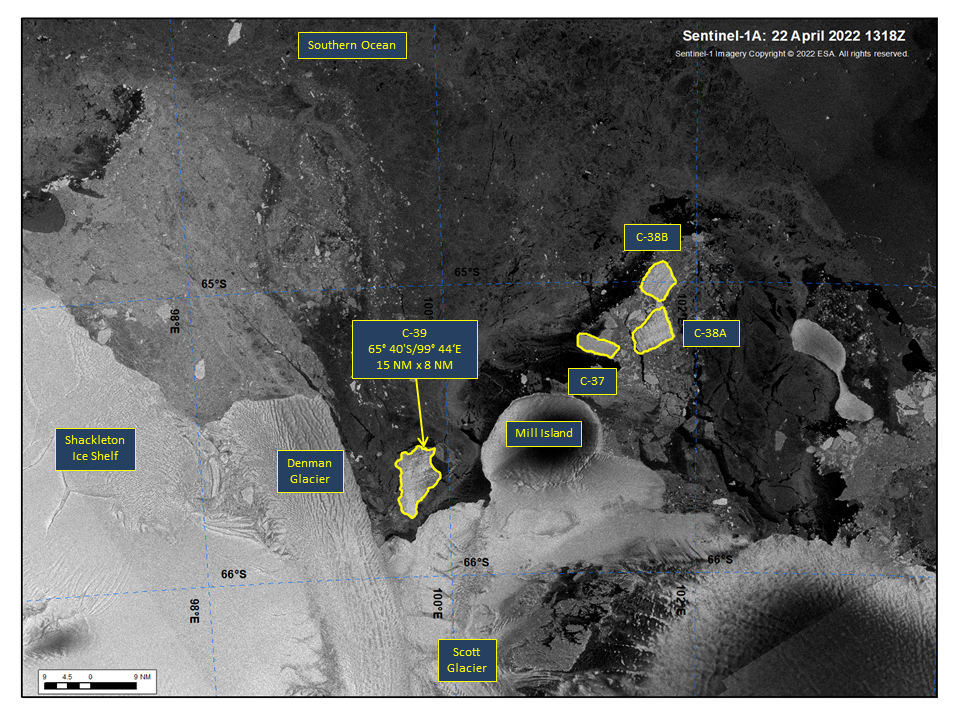
Press Release - Iceberg C-39 Has Calved From the Scott Glacier area of the Shackleton Ice Shelf
25 April 2022 — Iceberg C-39 has calved from the Scott Glacier area of the Shackleton Ice Shelf in the Wilkes Land Region of Antarctica. As of April 22, C-39 was centered at 65° 40' South and 99° 44' East and measured 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article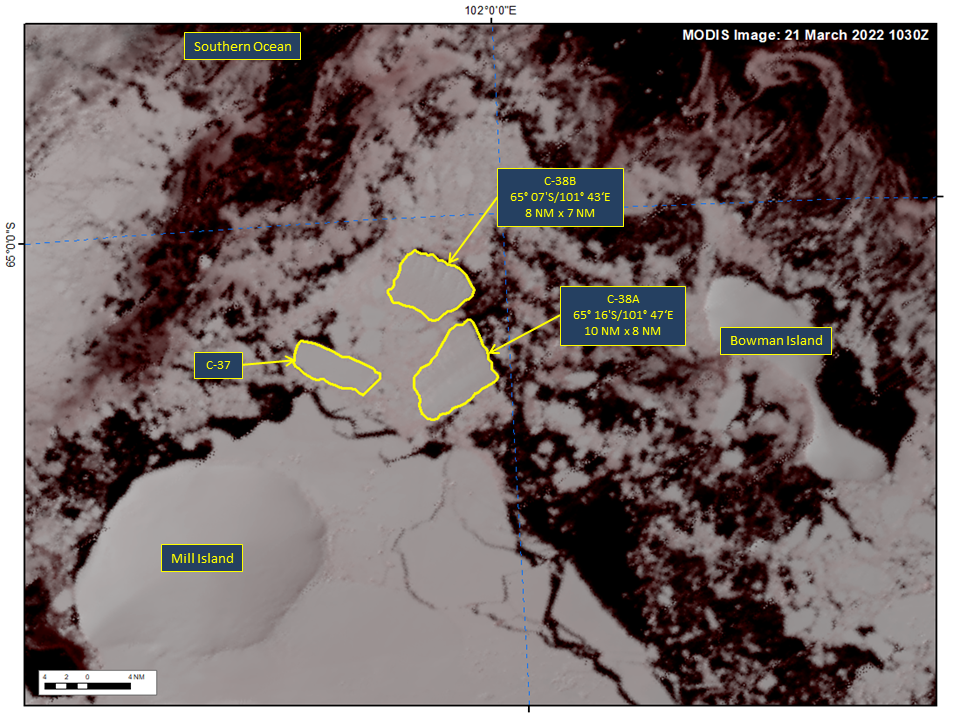
Press Release - Iceberg C-38 Has Calved into Two Smaller Icebergs named C-38A and C-38B
21 March 2022 — Iceberg C-38 Has Calved into two new icebergs named C-38A and C-38B. C-38A was centered at 65° 16' South and 101° 47' East and measured 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis. C-38B was centered at 65° 07' South and 101° 43' East and measured 8 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis. In the five days since calving from the Conger Ice Shelf, these icebergs have drifted approximately 40 nautical miles to the west northwest.
Go to Article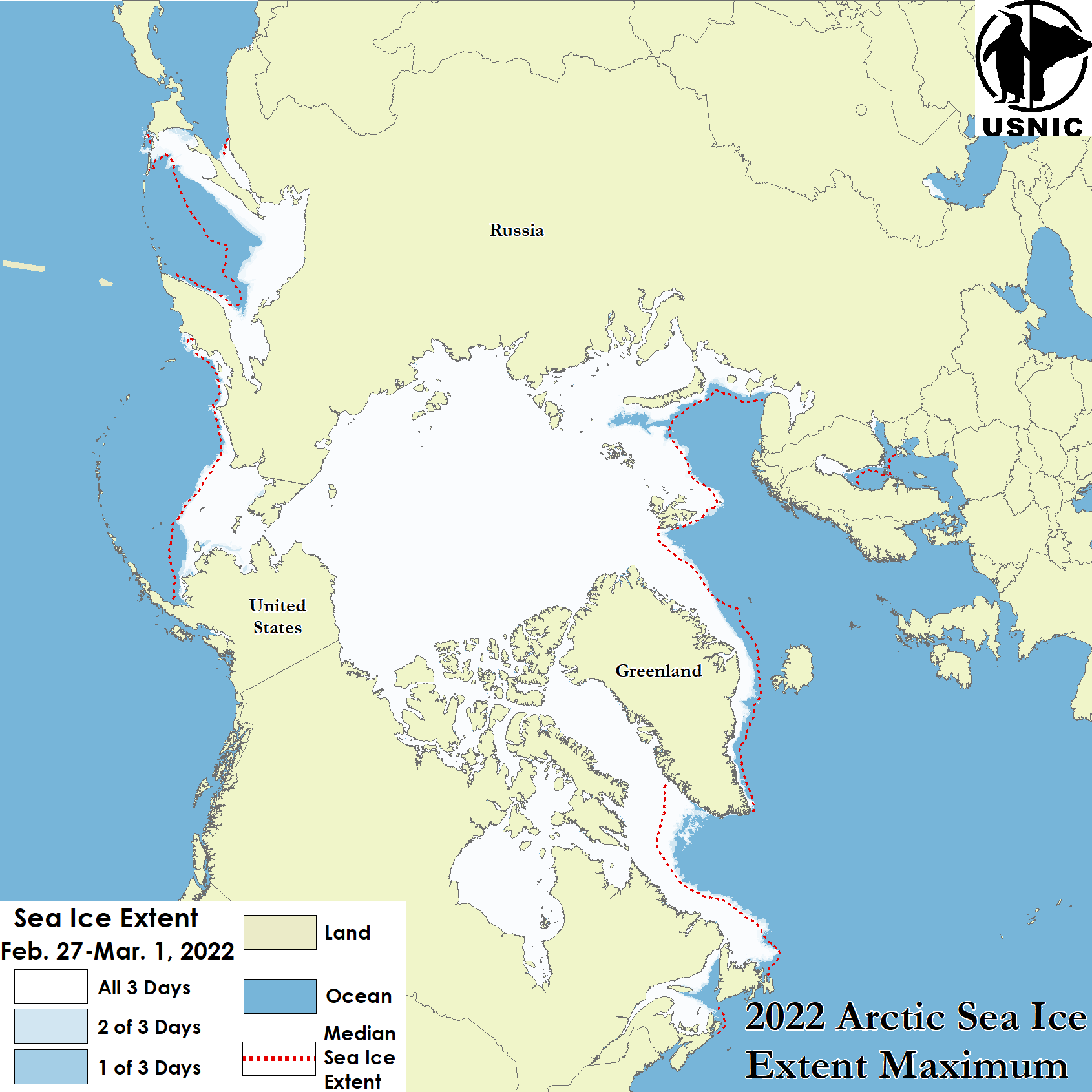
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Maximum Extent for Winter Season 2022
22 March 2022 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has determined the 2022 maximum Arctic sea ice extent occurred at the end of February 2022 with an area of 15.04 million square kilometers based on analysis from the USNIC’s Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS), used in the Multisensor Analyzed Sea Ice Extent (MASIE) product, jointly created with the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Go to Article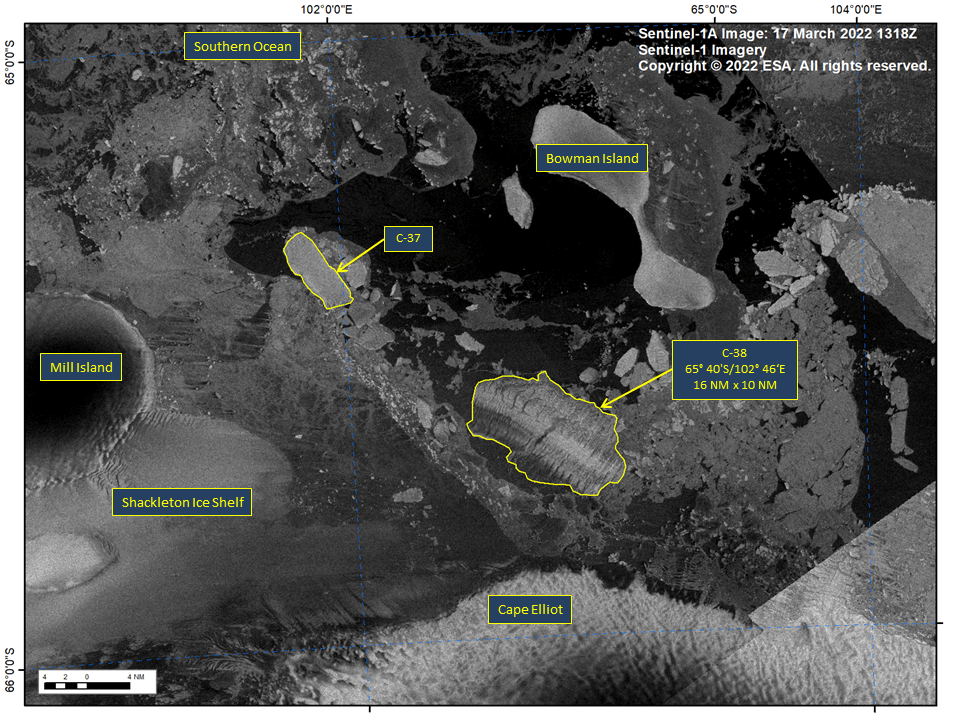
Press Release - Iceberg C-38 Has Calved as the Conger Ice Shelf Broke Free in the Wilkes Land Region
17 March 2022 — Iceberg C-38 has calved from the Conger Ice Shelf in the Wilkes Land Region of Antarctica. As of March 17, C-38 was centered at 65° 40' South and 102° 46' East and measured 16 nautical miles on its longest axis and 10 nautical miles on its widest axis. C-38 comprised virtually all that remained of the Conger ice shelf, which was adjacent to the Glenzer Ice Shelf which calved last week as iceberg C-37.
Go to Article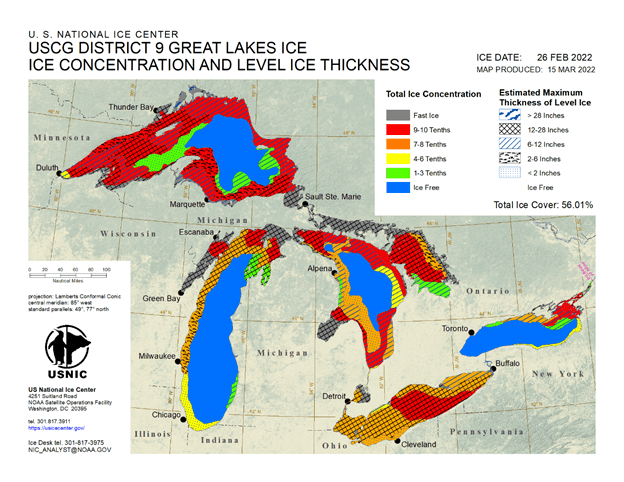
Press Release - Great Lakes Reaches Maximum Ice Coverage
15 March 2022 — The U.S. National Ice Center has determined that the Great Lakes experienced maximum ice coverage for the 2021-2022 ice season of approximately 56% on February 26, 2022.
Go to Article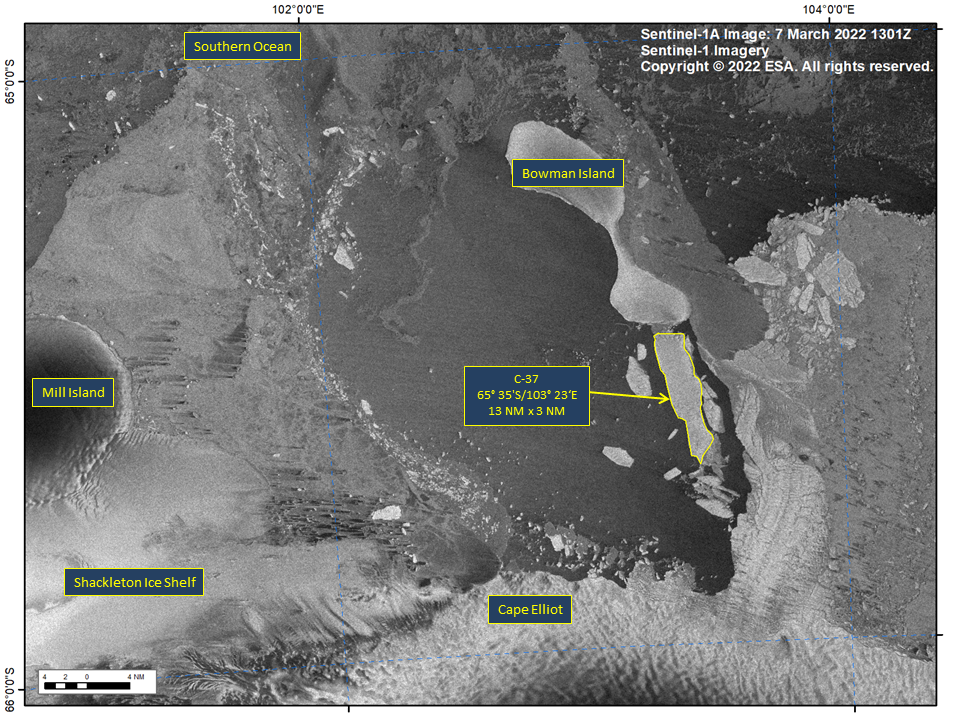
Press Release - Iceberg C-37 Broke Free from Bowman Island in the Wilkes Land Region
08 March 2022 — Iceberg C-37 has calved from the remnants of the Glenzer Ice Shelf. As of March 7, C-37 was centered at 65° 35' South and 103° 23' East and measured 13 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis
Go to Article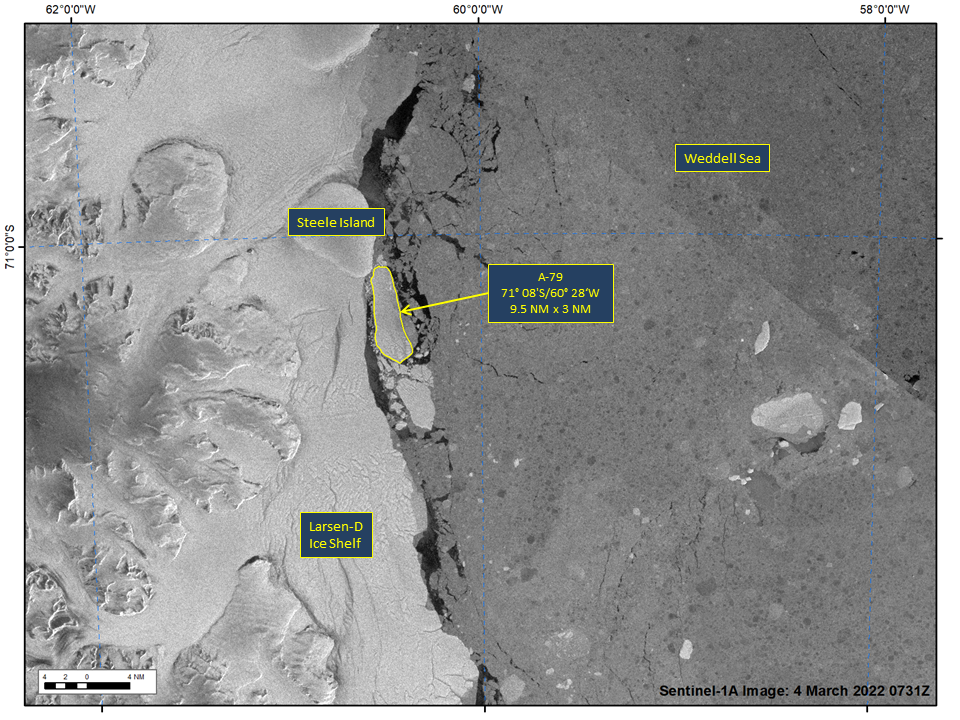
Press Release - Iceberg A-79 Calves from the Larsen-D Ice Shelf
04 March 2022 — Iceberg A-79 has calved from the Larsen-D Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea, continuing a years-long process of calving that has resulted in several named icebergs. As of March 4th, A-79 was centered at 71° 08' South and 60° 28' West and measured 9.5 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article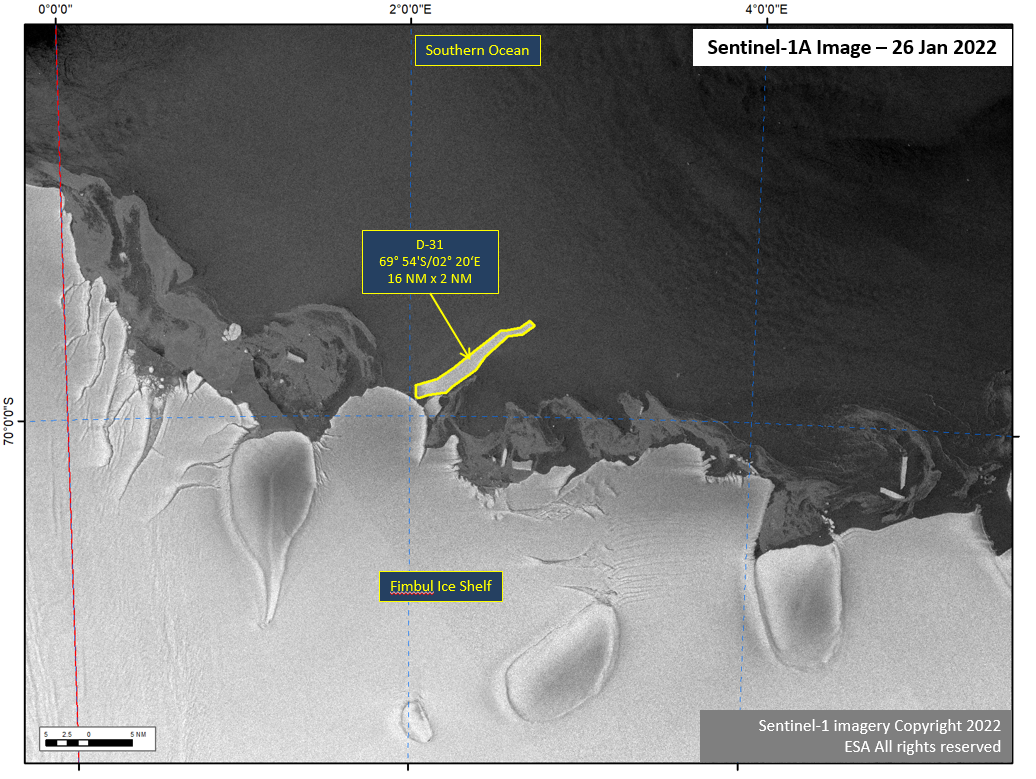
Press Release - Iceberg D-31 Calves from the Eastern Fimbul Ice Shelf.
26 January 2022 — Iceberg, D-31 has calved from the Fimbul Ice Shelf on the Princess Martha Coast of Antarctica, located at at 69°54’ South, 2°20’ East. It measures 16 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article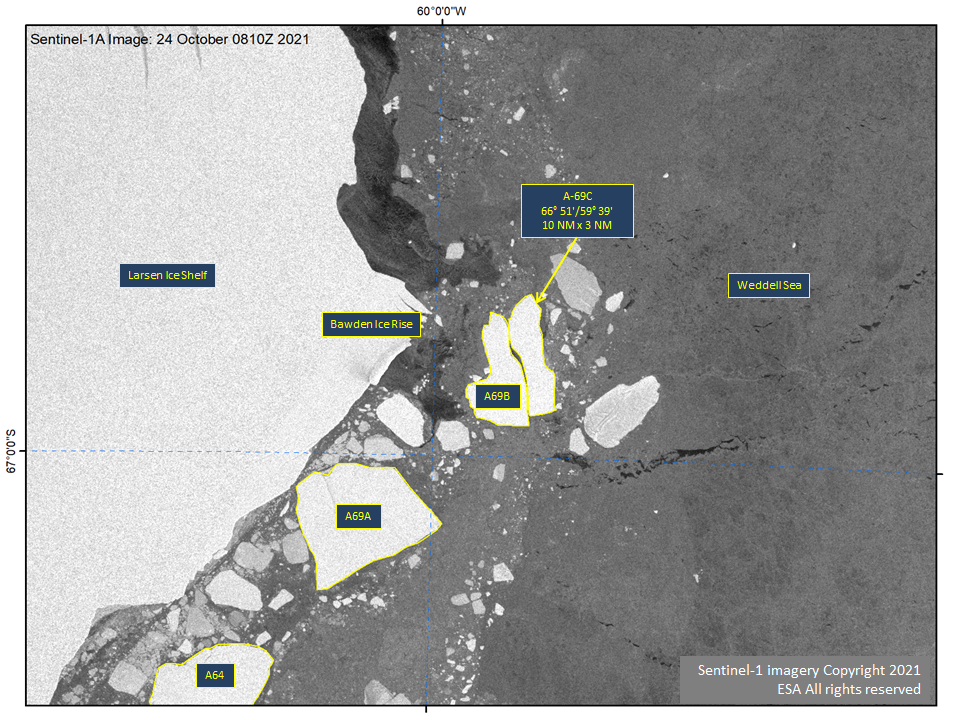
Press Release - Iceberg A-69B Has Broken in Half and Calved A-69C.
28 October 2021 — Iceberg, A-69C. A-69C is located at at 66°51’ South, 59°39’ West, in the Weddell Sea. It measures 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article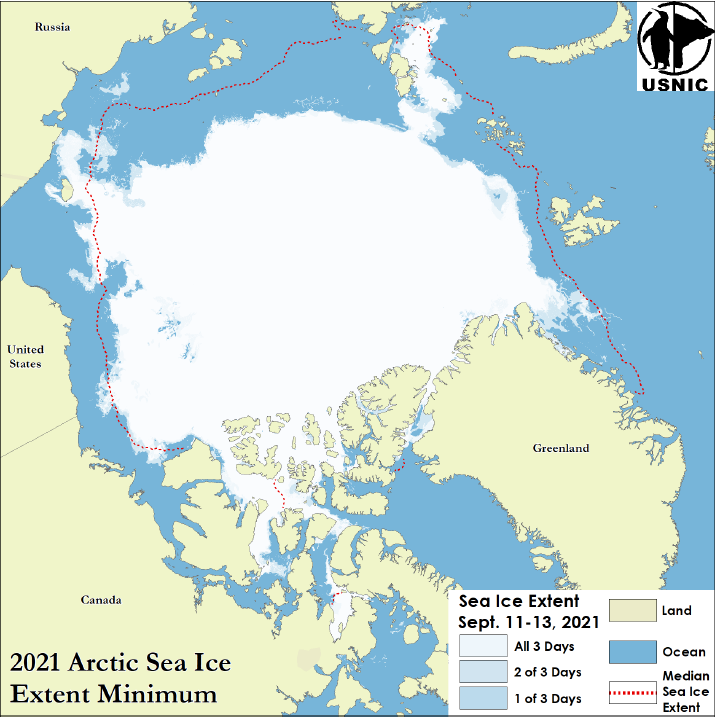
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Minimum Extent
22 September 2021 — U.S. National Ice Center determined the 2021 Arctic sea ice extent minimum was reached on September 12, 2021.
Go to Article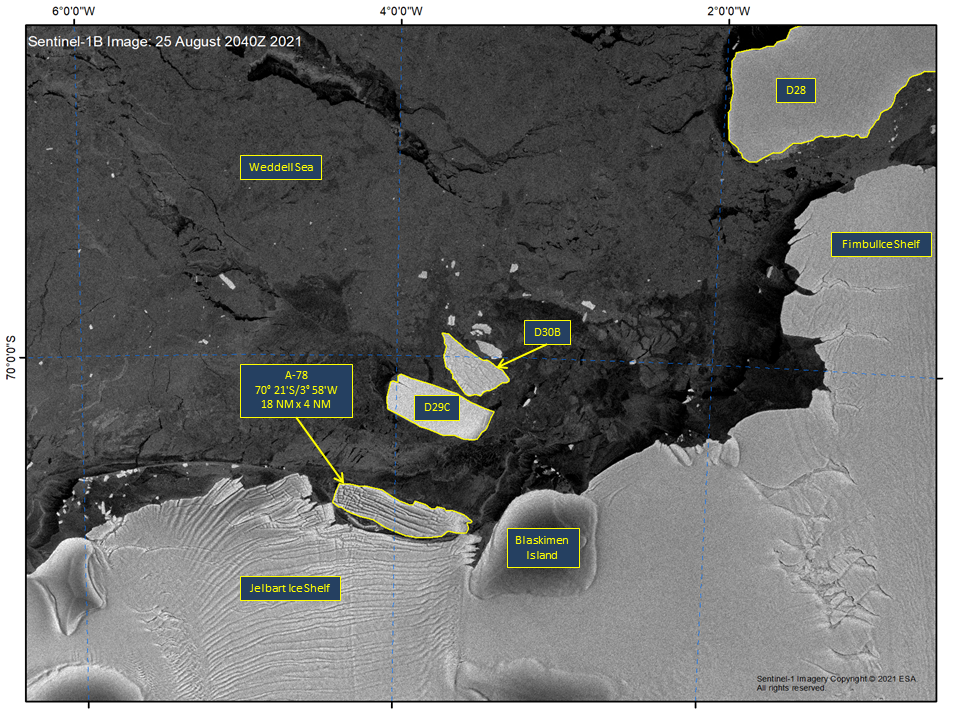
Press Release - Iceberg A-78 Calves from Jelbart Ice Shelf
26 August 2021 — Iceberg A-78 has calved from the Jelbart Ice Shelf on the Princess Martha Coast of Antarctica, located at 70° 21' South, 3° 58' West, measuring 18 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article
Press Release - IMS data will now be available in NetCDF format for 1km and 4km gridded data
18 August 2021 — The National Oceanic and Atmospheric (NOAA) team at the NSIDC (NOAA@NSIDC) and U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) announced Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS) data is now available in NetCDF file format for 1km and 4km gridded data.
Go to Article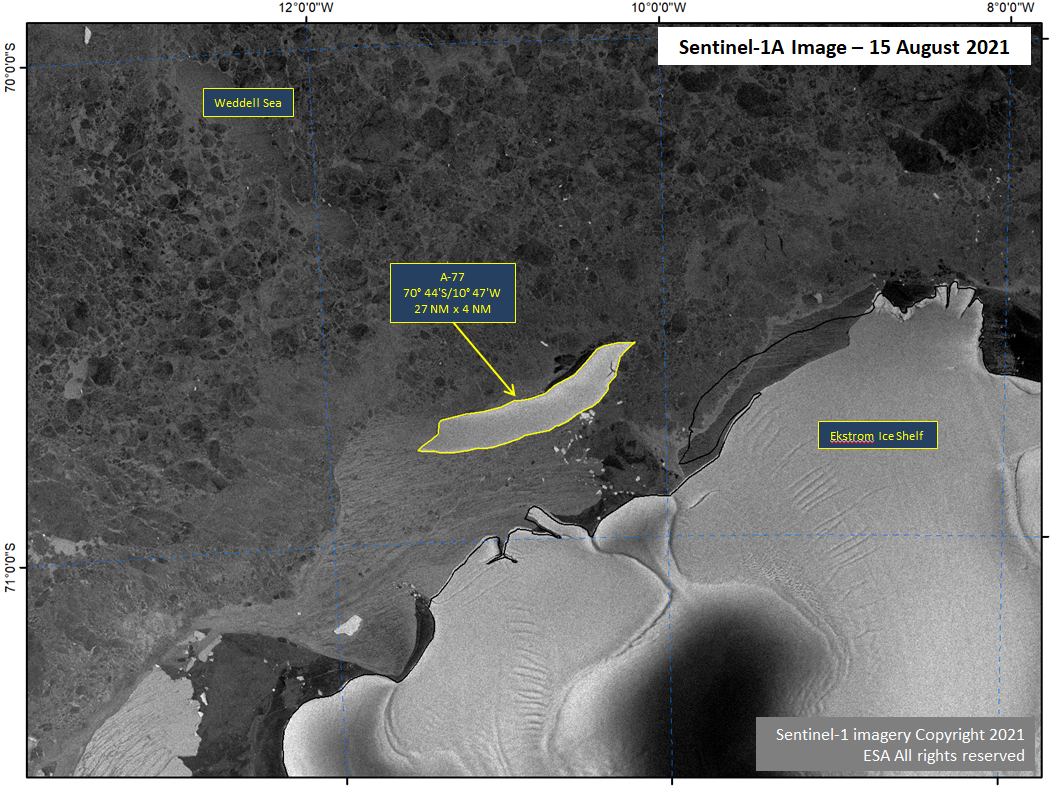
Press Release - Iceberg A-77 Calves from Ekstrom Ice Shelf
15 August 2021 — Iceberg A-77 has calved from the Ekstrom Ice Shelf on the Princess Martha Coast of Antarctica, located at 70° 44' South, 10° 47' West, measuring 27 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article
Press Release - U.S. National Ice Center Welcomes New Director
12 July 2021 — CDR Casey J. Gon relieved CDR Heather H. Quilenderino as Commanding Officer of NAVICEN during a change of command ceremony held at the NOAA Satellite Operations Facility (NSOF) in Suitland, MD on 08 July 2021 at 1000.
Go to Article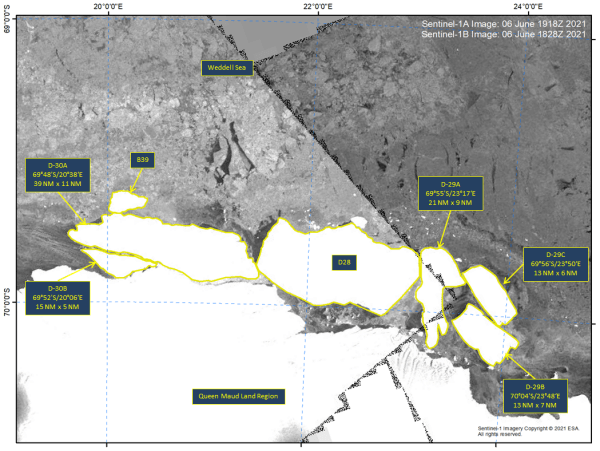
Press Release - Five New Icebergs in Queen Maud Land Region
07 June 2021 — Iceberg D-28 collided with ice shelves in the Queen Maud Land Region of Antarctica creating 5 new icebergs.
Go to Article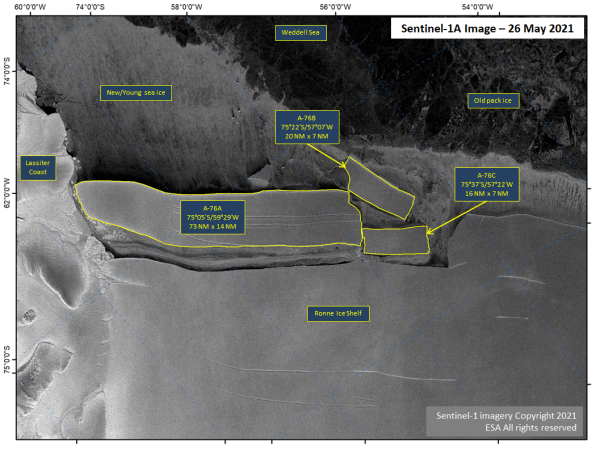
Press Release - Iceberg A-76 Calves into Icebergs A-76A, A-76B, and A-76C
26 May 2021 — Iceberg A-76 has calved two large icebergs. A-76 is now known as A-76A. The icebergs which formed are named A-76B, and A-76C.
Go to Article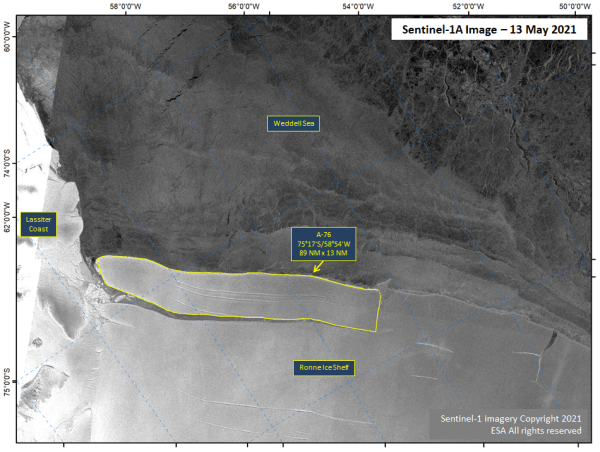
Press Release - Iceberg A-76 Calves from Ronne Ice Shelf
14 May 2021 — Iceberg A-76 has calved from the Ronne Ice Shelf, located at 75° 17' South, 58° 54' West, measuring 89 nautical miles on its longest axis and 14 nautical miles on its widest axis. This makes A-76 the largest iceberg in the world.
Go to Article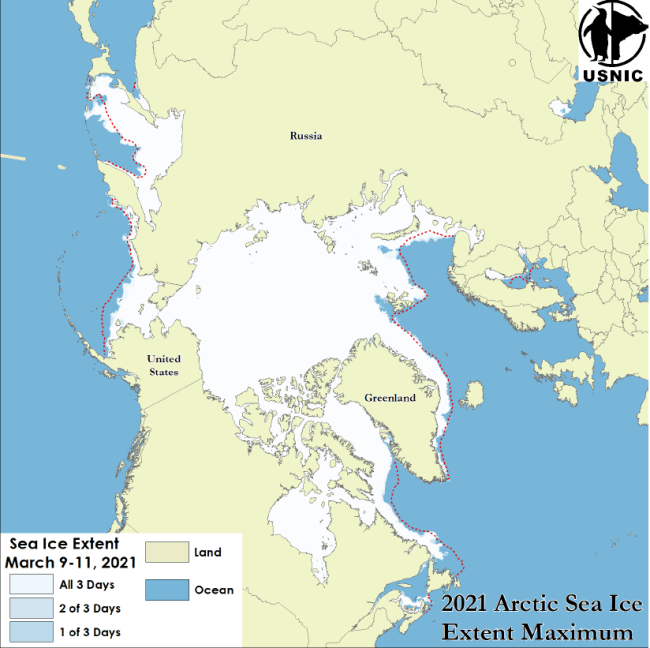
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Maximum Extent
02 April 2021 — The U.S. National Ice Center has determined that the 2021 maximum Arctic sea ice extent occurred on 10 March 2021 with an area of 14.87 million square km.
Go to Article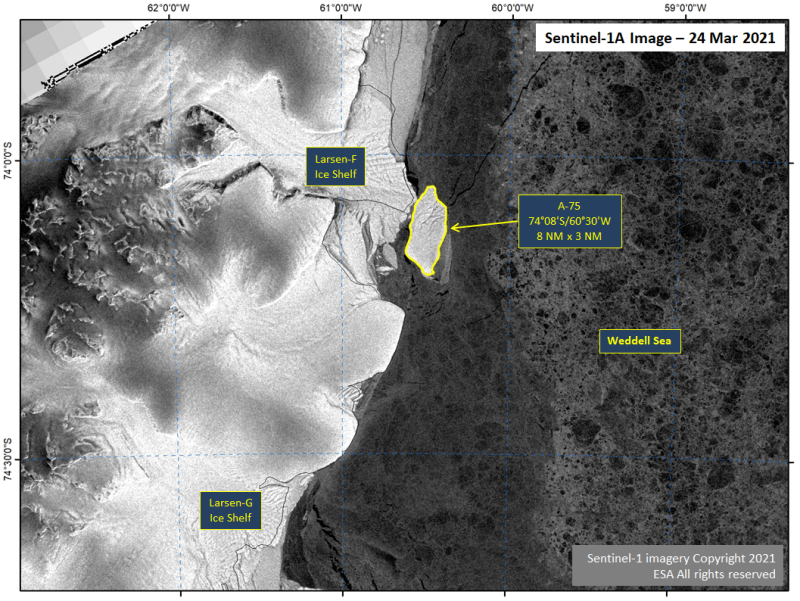
Press Release - Iceberg A-75 Calves from the Larsen-F Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea
26 March 2021 — A-75 has calved from the Larsen-F Ice Shelf, just north of Larsen-G and the Ronne Ice Shelves. Iceberg A-75 was located at 74° 08' South, 60° 30' West and measures eight nautical miles on its longest axis and three nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article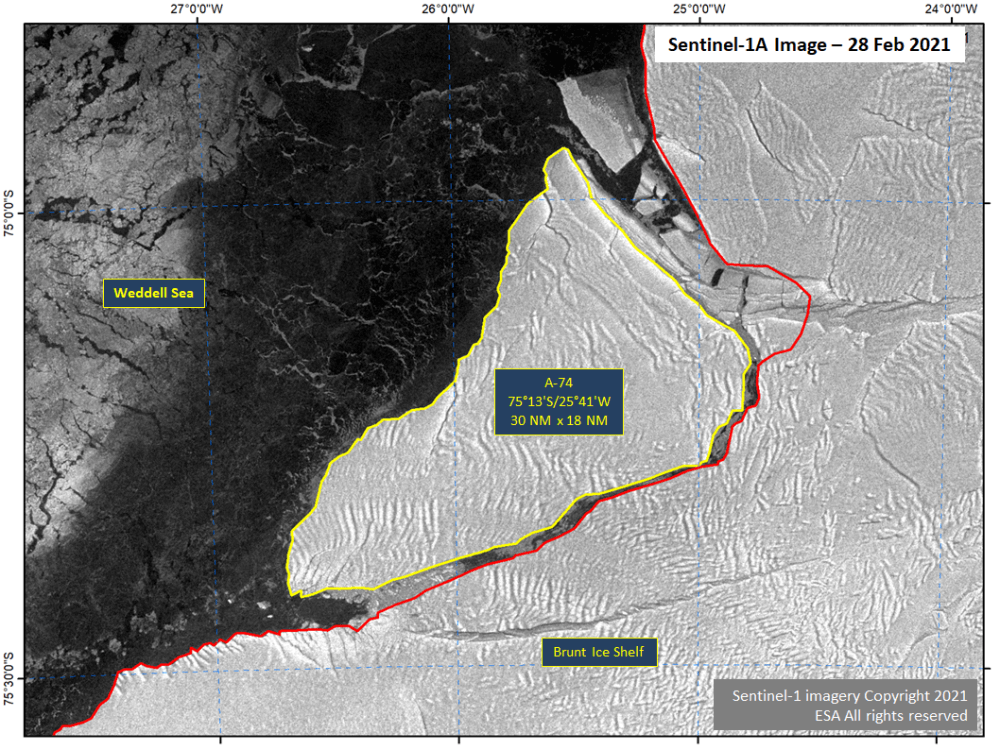
Press Release - Iceberg A-74 Calves from the Brunt Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea
01 March 2021 — A-74 has calved from the north facing side of the Brunt Ice Shelf. The new iceberg A-74 was located at 75° 13' South, 25° 41' West and measures 30 nautical miles on its longest axis and 18 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article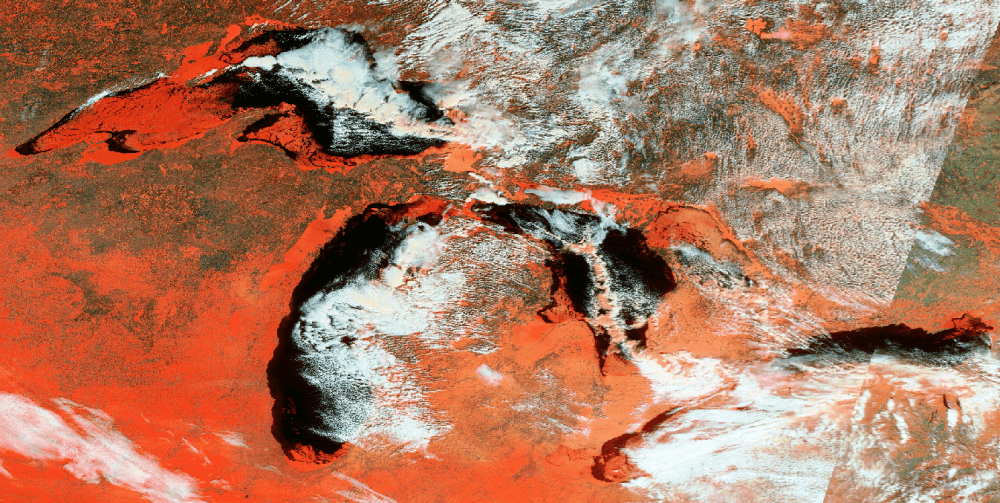
Press Release - Great Lakes Reaches Maximum Ice Coverage
01 March 2021 — The U.S. National Ice Center has determined that the Great Lakes experienced maximum ice coverage for the 2020-2021 ice season of approximately 46.5% on February 19, 2021.
Go to Article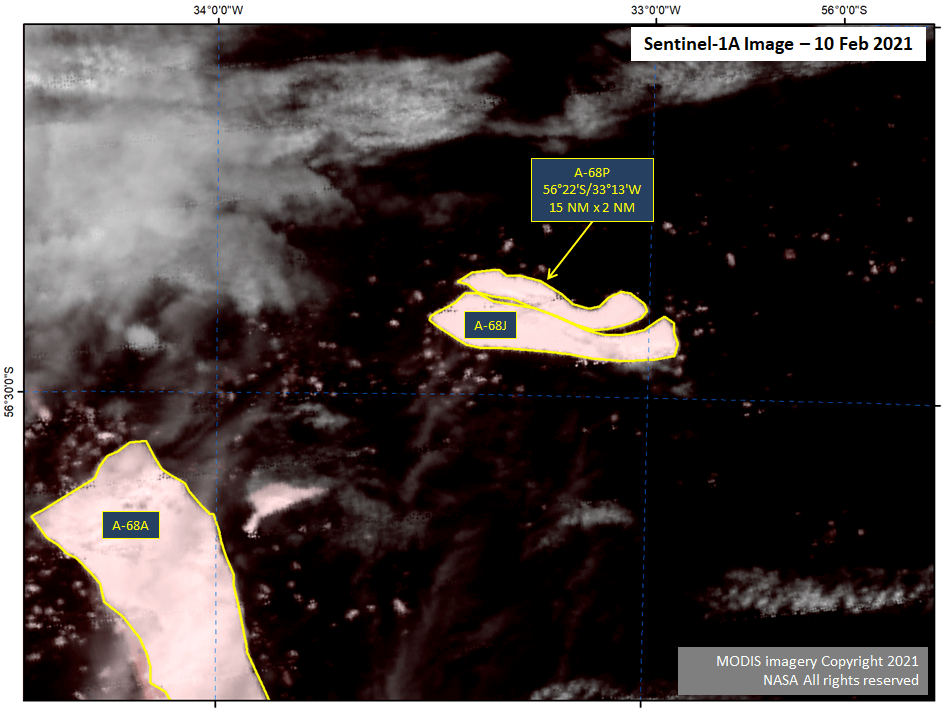
Press Release - Iceberg A-68P Calves from A-68J in the South Atlantic Ocean
10 February 2021 — A-68P has calved from A-68J. As of February 10th, the new iceberg A-68P was located at 56° 22' South, 33° 13' West, and measures 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and two nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article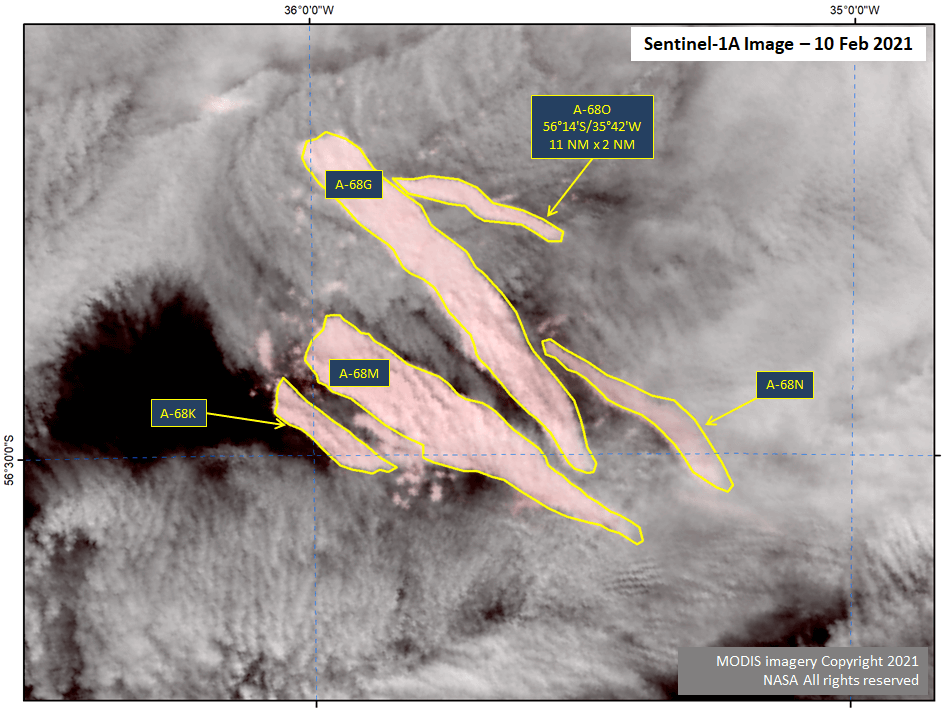
Press Release - Iceberg A-68N Calves from A-68G
10 February 2021 — A-68G has broken again prompting the naming of A-68O. As of February 10th, the new iceberg A-68O was located at 56° 14' South, 35° 42' West, and measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and two nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article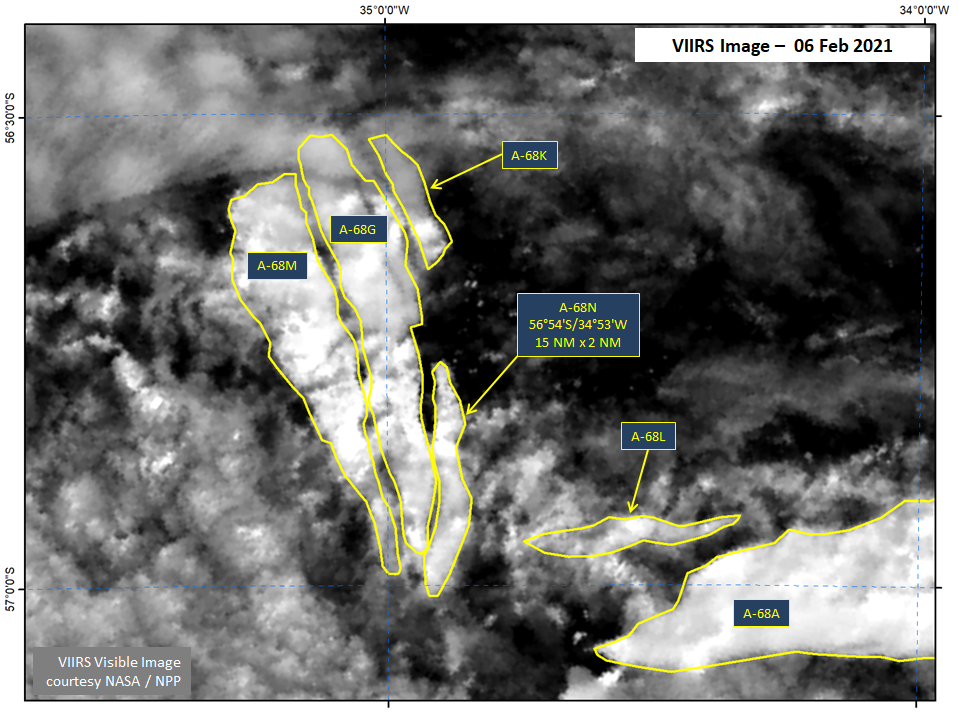
Press Release - Iceberg A-68N Calves from A-68G
08 February 2021 — A-68G has broken again prompting the naming of A-68N. As of February 6th, the new iceberg A-68N was located at 56° 54' South, 34° 53' West and measures 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and two nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article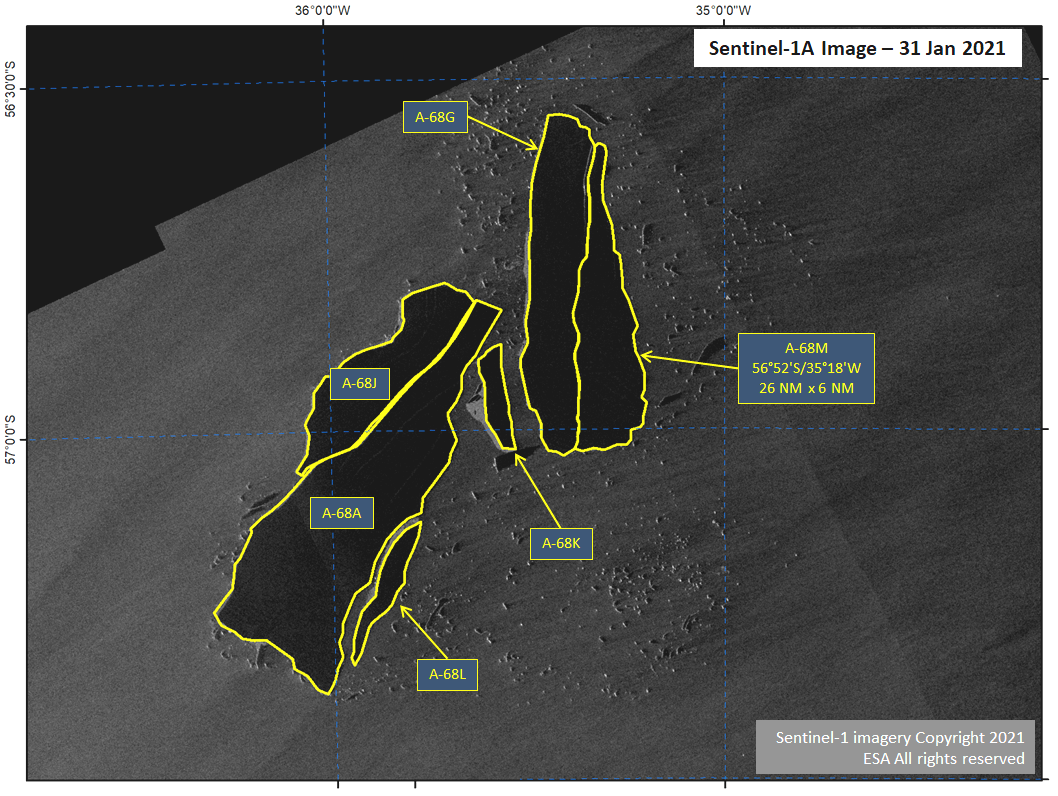
Press Release - Iceberg A-68M Calves from A-68G
31 January 2021 — A-68G has broken in half prompting the naming of A-68M in the continued rapid break-up of the A-68A family of icebergs.
Go to Article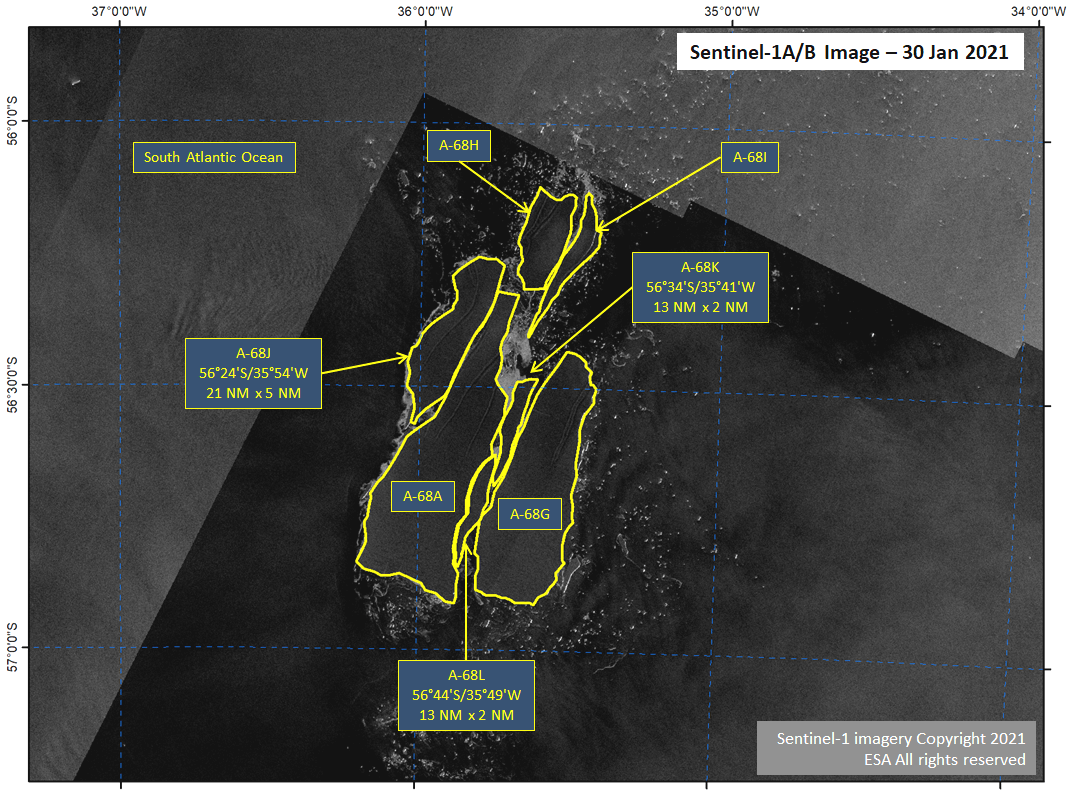
Press Release - Icebergs A-68J, A-68K, and A-68L Calve from Iceberg A-68A
30 January 2021 — Three new icebergs (A-68J, A-68K, and A-68L) calved from A-68A in the South Atlantic Ocean. For the third consecutive day, large icebergs have calved from the main iceberg, A-68A.
Go to Article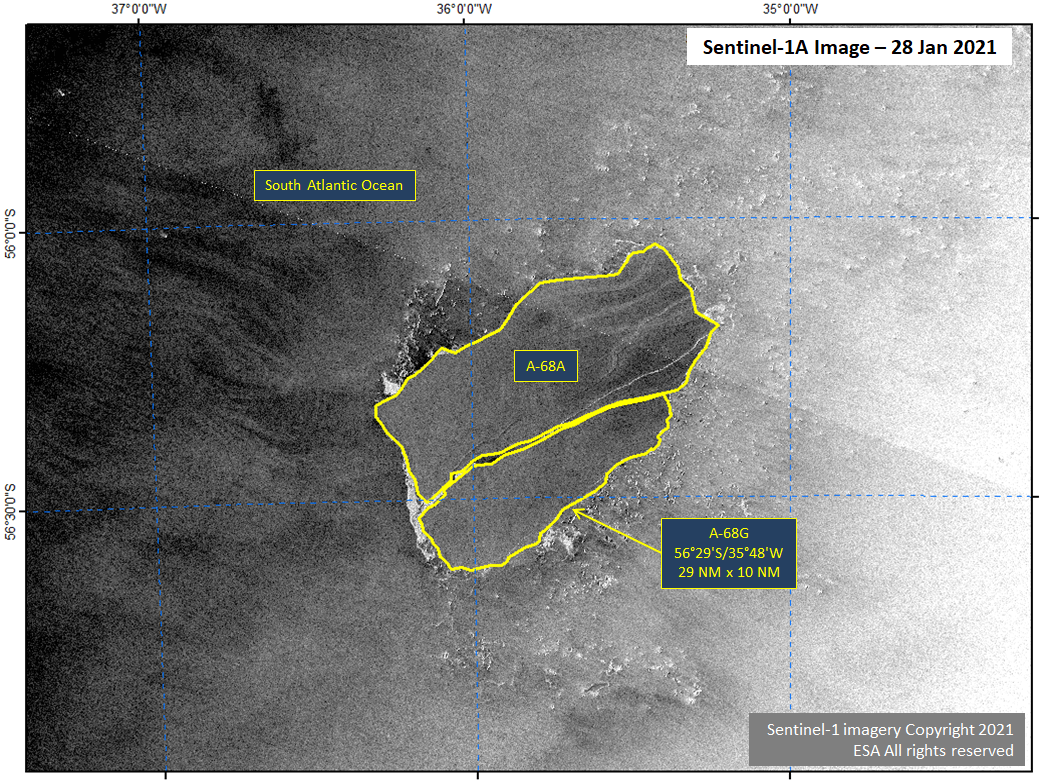
Press Release - Icebergs A-68G Calve from A-68A in South Atlantic Ocean
28 January 2021 — The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has confirmed a new iceberg calved from iceberg A-68A in the South Atlantic Ocean. The new iceberg A-68G is located at 56° 29' South, 35° 48' West. A-68G measures 29 nautical miles on its longest axis and 10 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article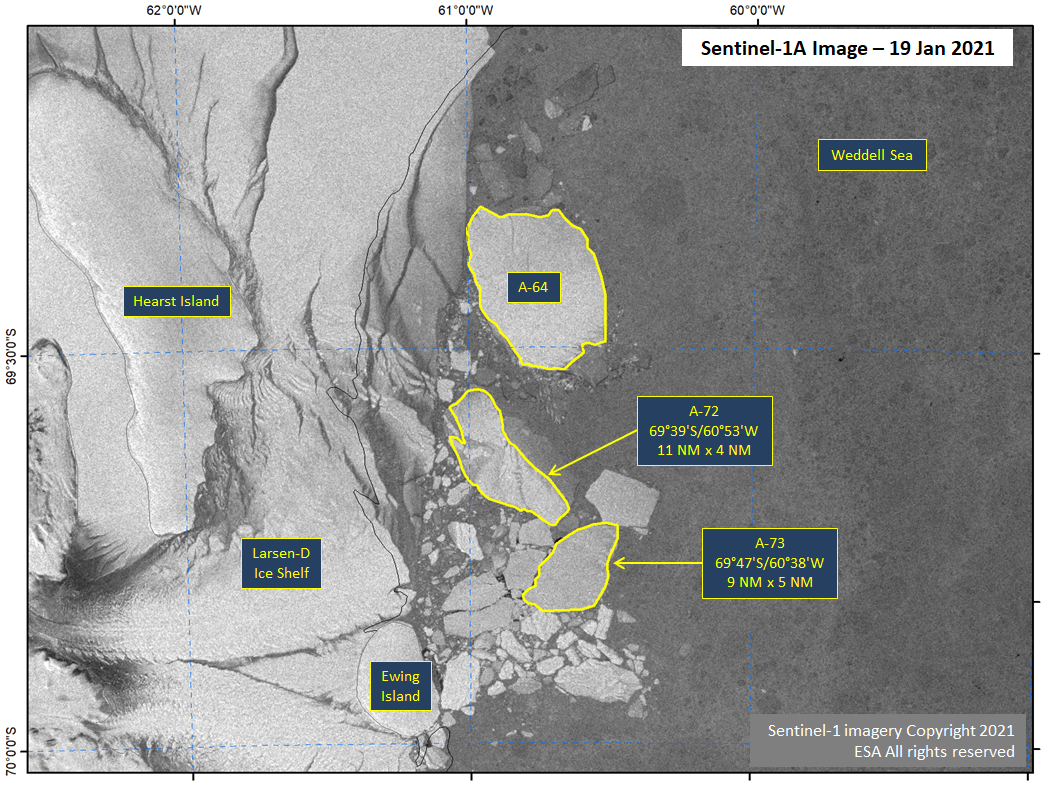
Press Release - Icebergs A-72 and A-73 Calve from Larsen-D Ice Shelf
19 January 2021 — The Larsen-D Ice Shelf calved two more icebergs which are large enough to be named. The breakup occurred in mid-December 2020 from the northern part of Larsen-D approximately 150 nautical miles north of the recently named A-70 and A-71 icebergs. Similar to the A-70 and A-71 calving, it had been difficult to confirm whether these were icebergs large enough to be named or extremely old sea ice that had fasted to the ice shelf. Recent imagery showing surface topography typical of icebergs has allowed us to confirm these are indeed icebergs. The new iceberg A-72 is located at 69° 39' South, 60° 53' West measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis. The new iceberg A-73 is located at 69° 47' South, 60° 38' West and measures 9 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article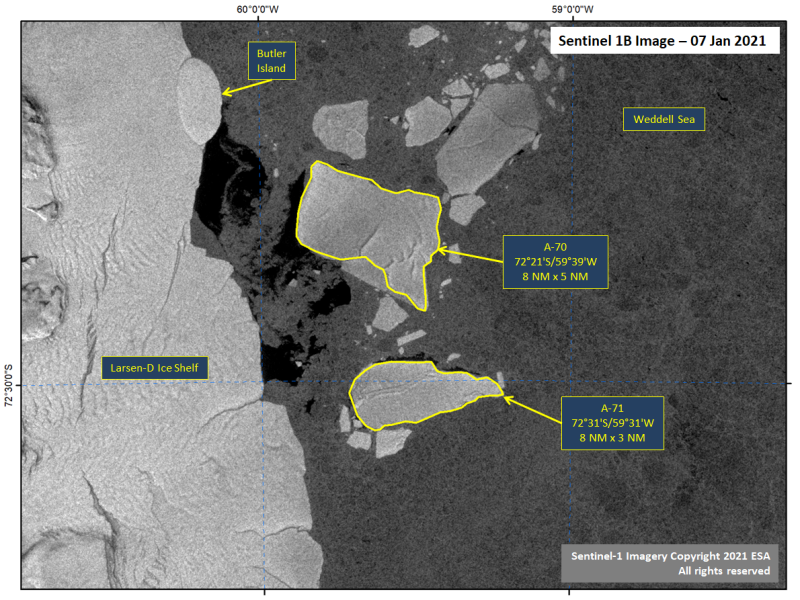
Press Release - Icebergs A-70 and A-71 Calve from Larsen-D Ice Shelf
08 January 2021 — The Larsen-D Ice Shelf calved several icebergs in a calving event, two of which are large enough to be named. The breakup occurred in early November 2020, but until now it had been impossible to confirm whether these were icebergs large enough to be named or extremely old sea ice that had fasted to the ice shelf. Recent imagery showing surface topography typical of icebergs has allowed us to confirm these are indeed icebergs. The new iceberg A-70 is located at 72° 21' South, 59° 39' West and measures 8 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis. The new iceberg A-71 is located at 72° 31' South, 59° 31' West and measures 8 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article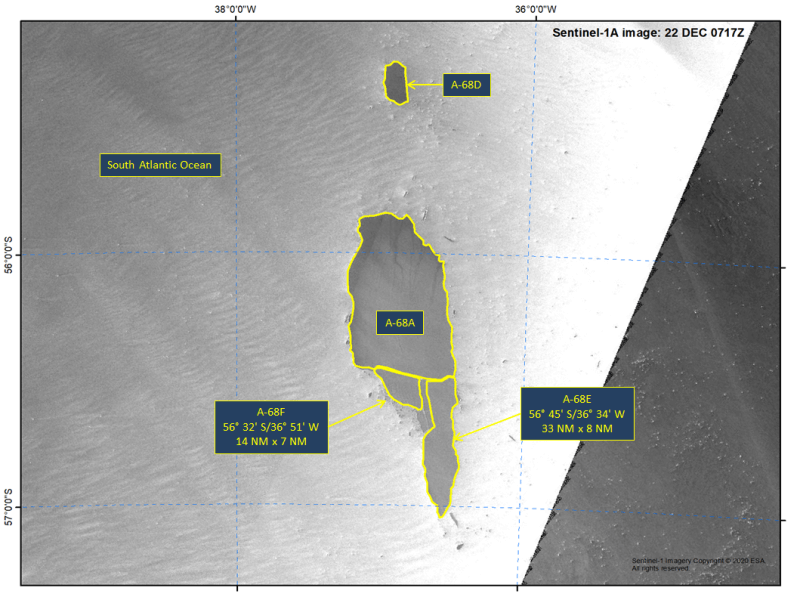
Press Release - Icebergs A-68E and A-68F Calve from Iceberg A-68A
22 December 2020 — Two new icebergs calved from A-68A in the South Atlantic Ocean. These new icebergs come just three days after A-68D was calved. The new iceberg named A-68E is located at 56° 45' South and 36° 34' West. A-68E measures 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles on its widest axis. The new iceberg A-68F is located at 56° 32' South and 36° 51' West. A-68F measures 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article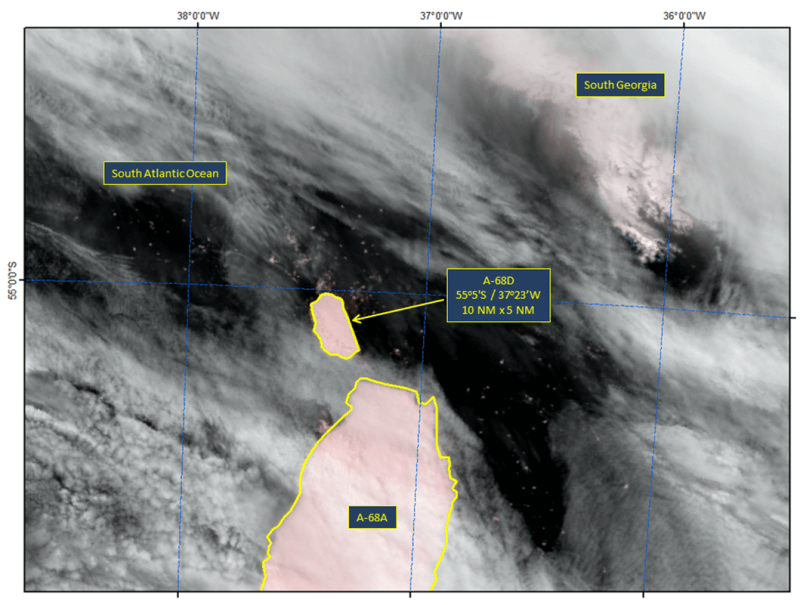
Press Release - Iceberg A-68D Calves from Iceberg A-68A
18 December 2020 — A new iceberg has calved from the A-68A iceberg in the South Atlantic Ocean. This iceberg, named A-68D, is located at 55°5’ South, 37°23’ West. The iceberg measures 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article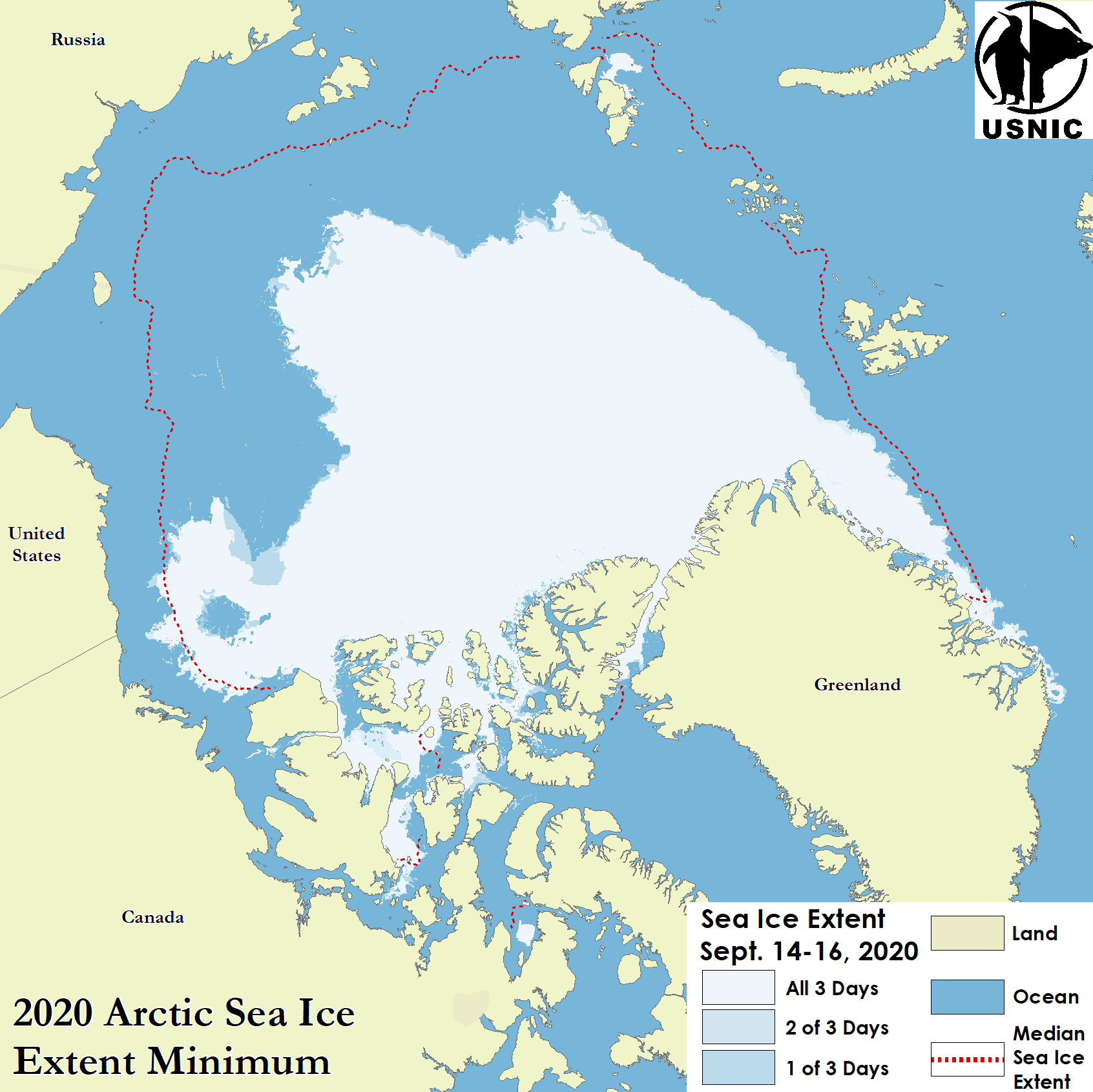
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Minimum Extent
24 September 2020 — U.S. National Ice Center determined the 2020 Arctic sea ice extent minimum was reached on September 15, 2020.
Go to Article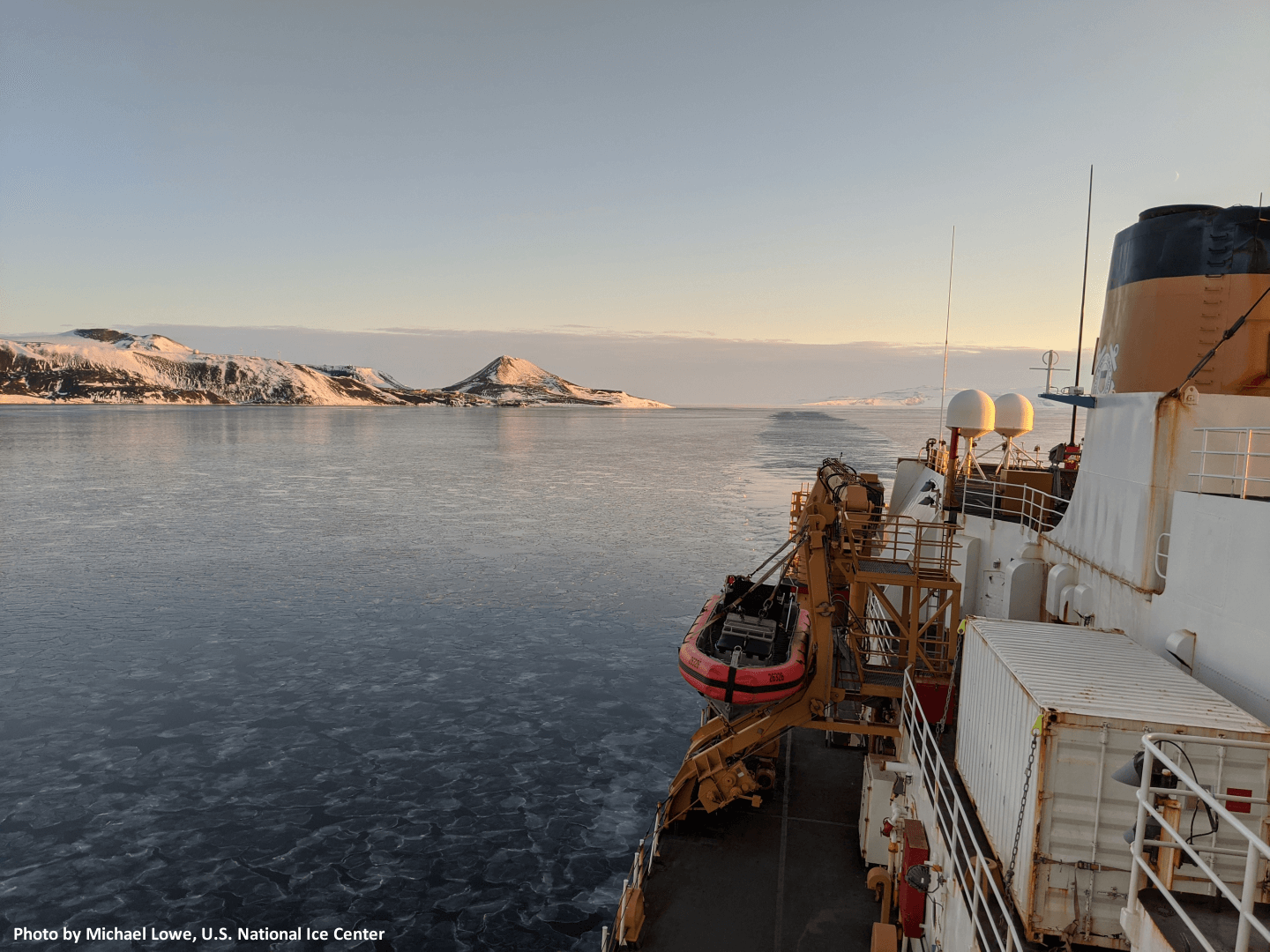
Feature - Operation Deep Freeze Support 2019-2020
31 July 2020 — Senior Ice Analyst Michael Lowe, U.S. National Ice Center, was tasked with deploying on U.S. Coast Guard’s Cutter Polar Star in support of Operation Deep Freeze season 2019-2020. Mr. Lowe provided ice and environmental support for its Antarctic transit to support the resupply of McMurdo Station.
Go to Article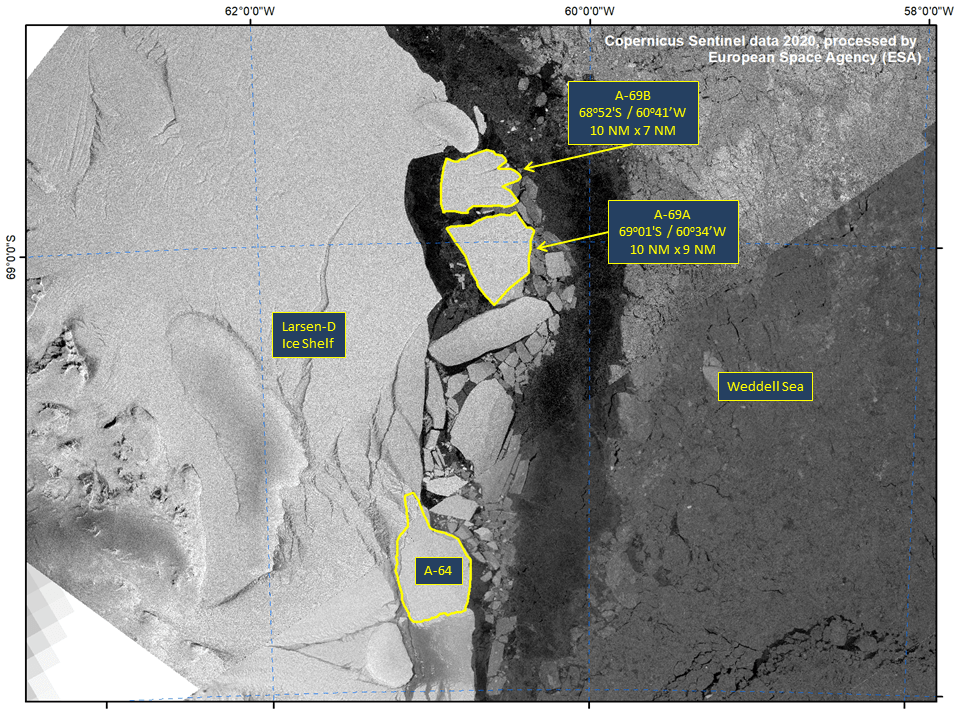
Press Release - Iceberg A69 Calves Becoming Icebergs A-69A and A-69B
09 July 2020 — The newly named iceberg A-69 has broken into two nameable icebergs. A-69A is located at 69°01’ South, 60°34’ West, in the Weddell Sea, it measures 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 9 nautical miles on its widest axis. Iceberg A-69B is located at 68°52’ South, 60°41’ West, in the Weddell Sea, it measures 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article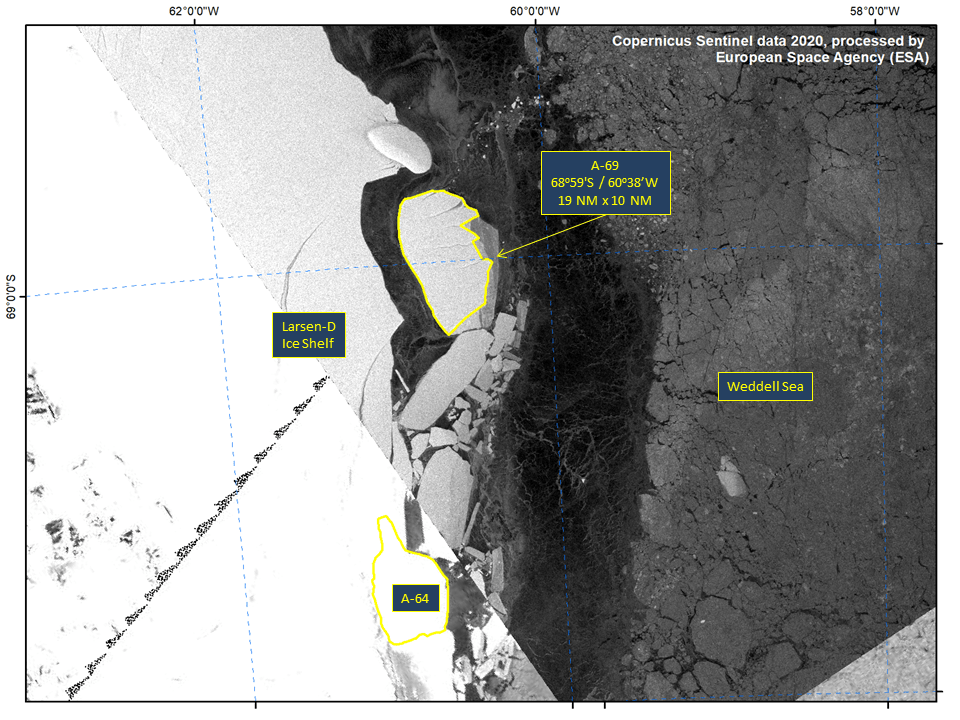
Press Release - Iceberg A-69 Calves from Larsen-D Ice Shelf
26 June 2020 — A new iceberg has calved from the Larsen-D Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea. A-69 is located at 68°59’ South, 60°38’ West in the Weddell Sea. The iceberg measures 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 10 nautical miles on its widest axis with an area of approximately 135 square nautical miles.
Go to Article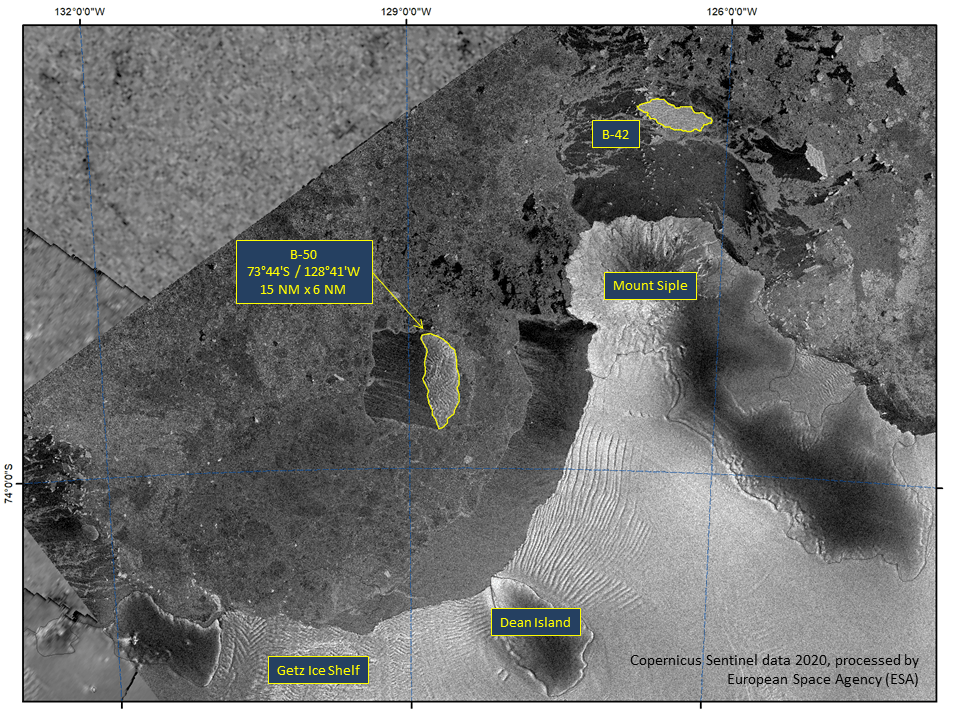
Press Release - Iceberg B-50 Calves from Getz Ice Shelf
24 April 2020 — Iceberg B-50 calved from the eastern edge of the Getz Ice Shelf in the Amundsen Sea. B-50 is located at 73°44' South, 128°41' West and measures 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis with an area of approximately 62 square nautical miles.
Go to Article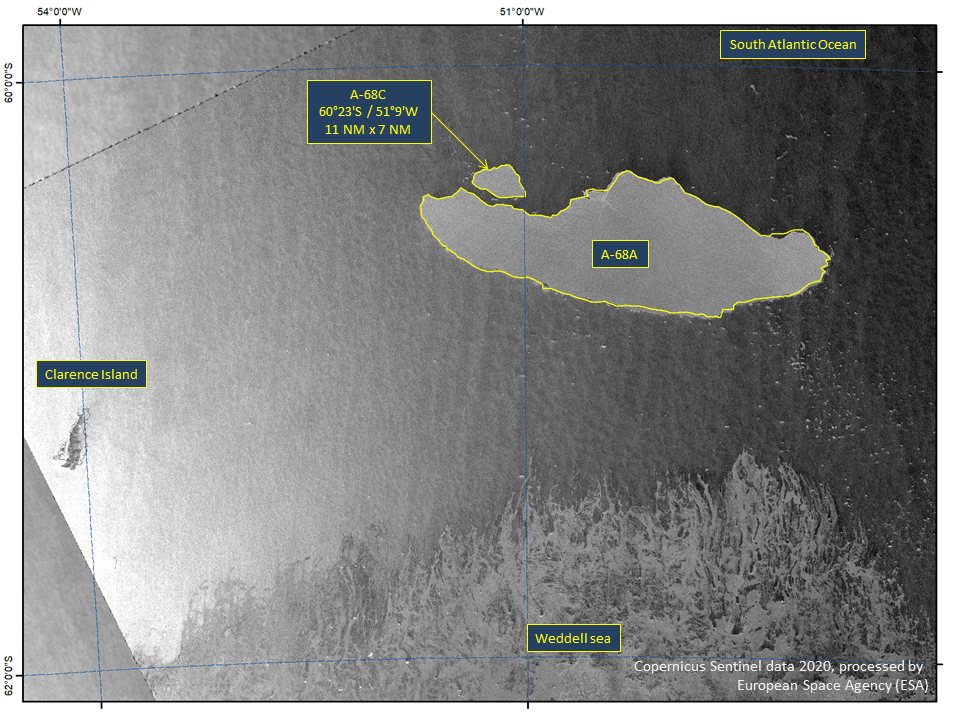
Press Release - Iceberg A-68C Calves from A-68A
24 April 2020 — The U.S. National Ice Center has confirmed that a new iceberg calved from parent iceberg A-68A, currently the world’s largest iceberg. The new iceberg A-68C is the second to calve from origin iceberg A-68.
Go to Article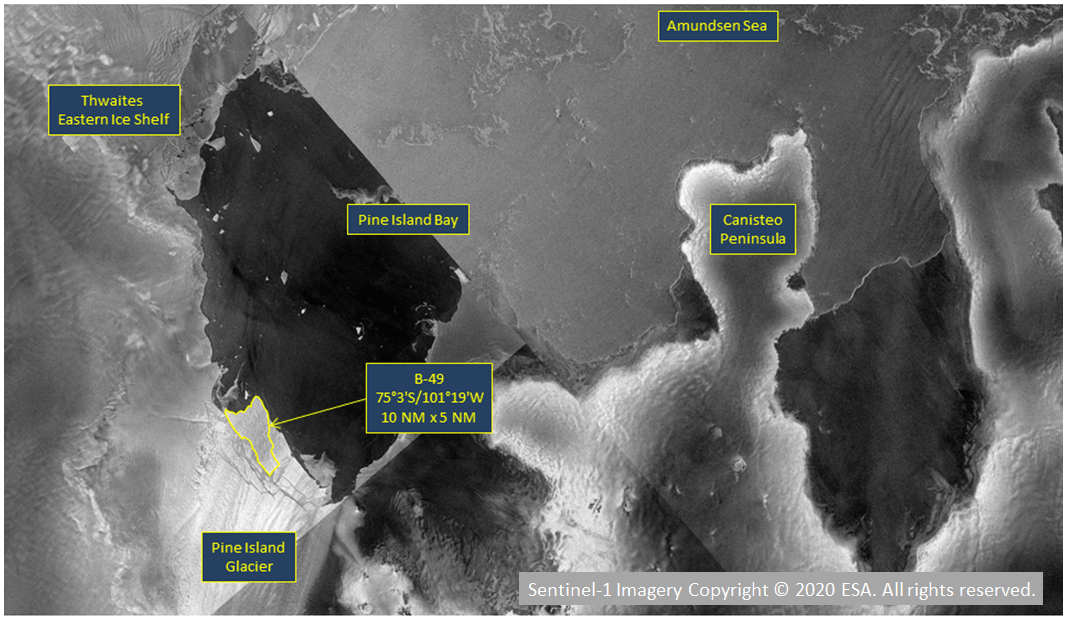
Press Release - Pine Island Glacier Calves New Iceberg (B-49)
10 February 2020 - The National Ice Center named a new iceberg that meets the criteria for tracking by the USNIC. This iceberg from Pine Island Glacier is part of a larger calving event that mostly broke apart into smaller pieces.
Go to Article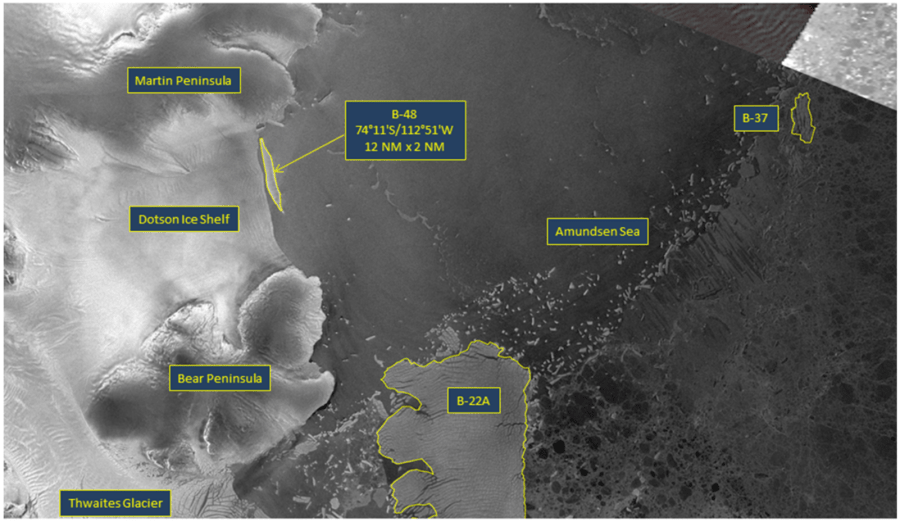
Press Release - Dotson Ice Shelf Calves New Iceberg (B-48)
06 February 2020 - The U.S. National Ice Center named a new iceberg that meets the criteria for tracking by the USNIC. This particular iceberg calved from the Dotson Ice Shelf in the Amundsen Sea just west of Thwaites Glacier.
Go to Article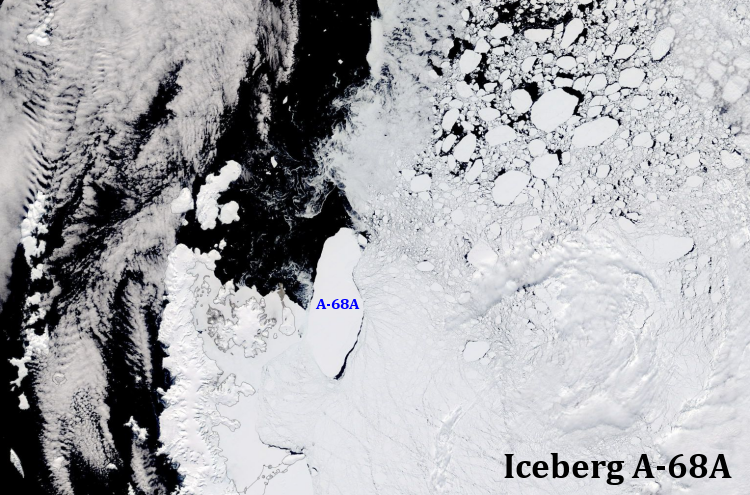
Feature: Iceberg A-68A on the move
27 January 2020 - Over the last two months Antarctica's largest iceberg, A-68A, has been moving off the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. This feature product shows the movement over the last 2 months in an animated graphic.
Go to Article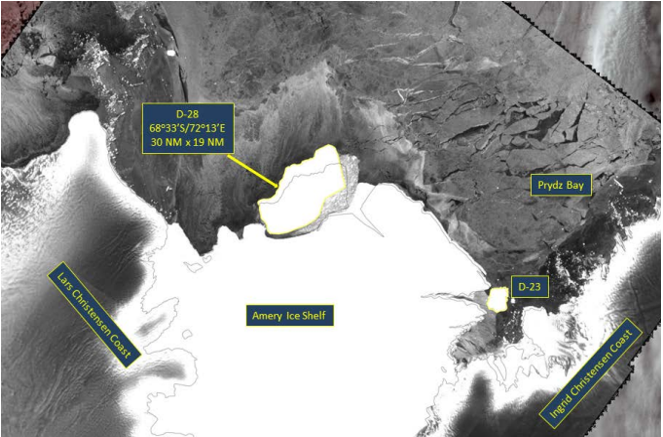
Press Release - Amery Ice Shelf Calves a New Iceberg (D-28)
04 October 2019 - The U.S. National Ice Center named a new iceberg when it calved from the western half of the Amery Ice Shelf
Go to Article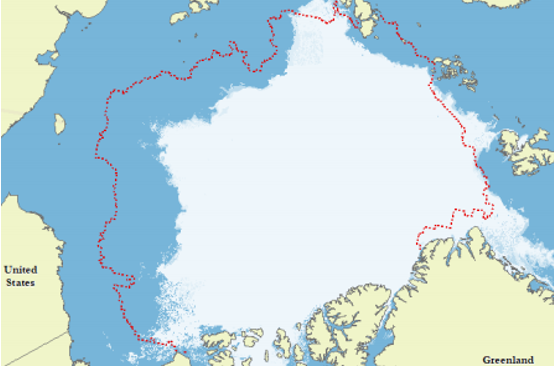
Press Release - Arctic Sea Ice at Minimum Extent 2019
04 October 2019 - U.S. National Ice Center determined the 2019 Arctic sea ice extent minimum was reached on September 17, 2019. This year’s analysis indicated a minimum 3-day average of 3.916 million square kilometers.
Go to Article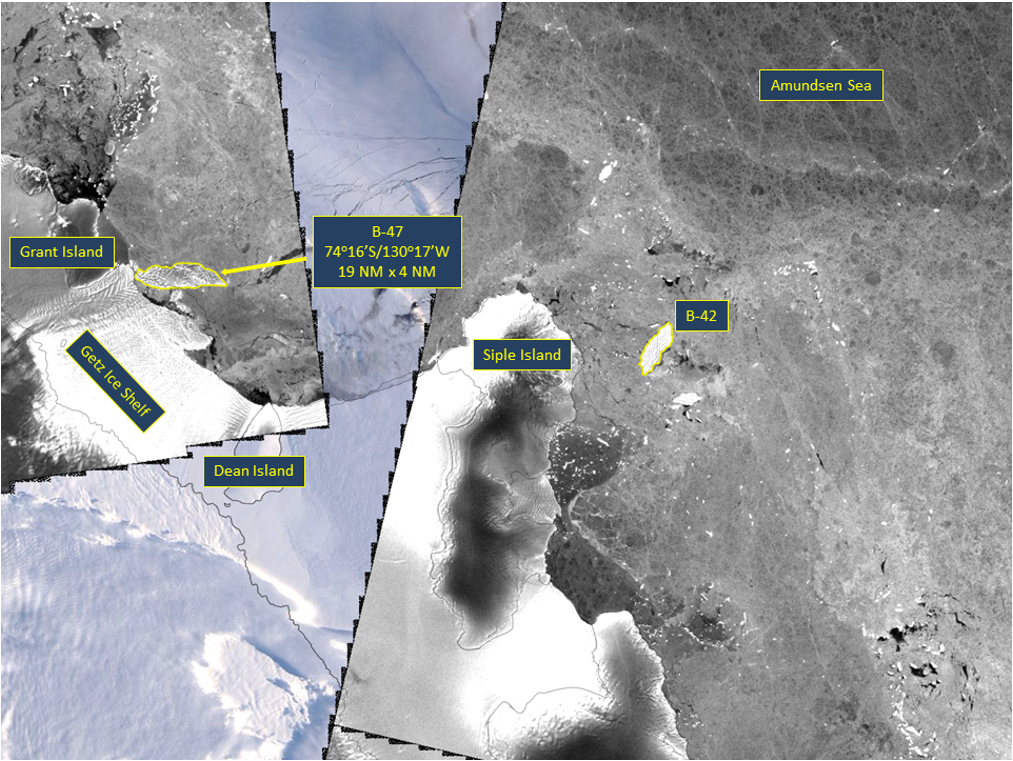
Press Release - Icebeg B-47 calved from the Getz Ice Shelf in the Amundsen Sea
18 September 2019 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the Getz Ice Shelf, West of Siple Island, on September 6, 2019. B-47 is located at 74° 16' South, 130° 17' West in the South Pacific Ocean, specifically the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 19 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article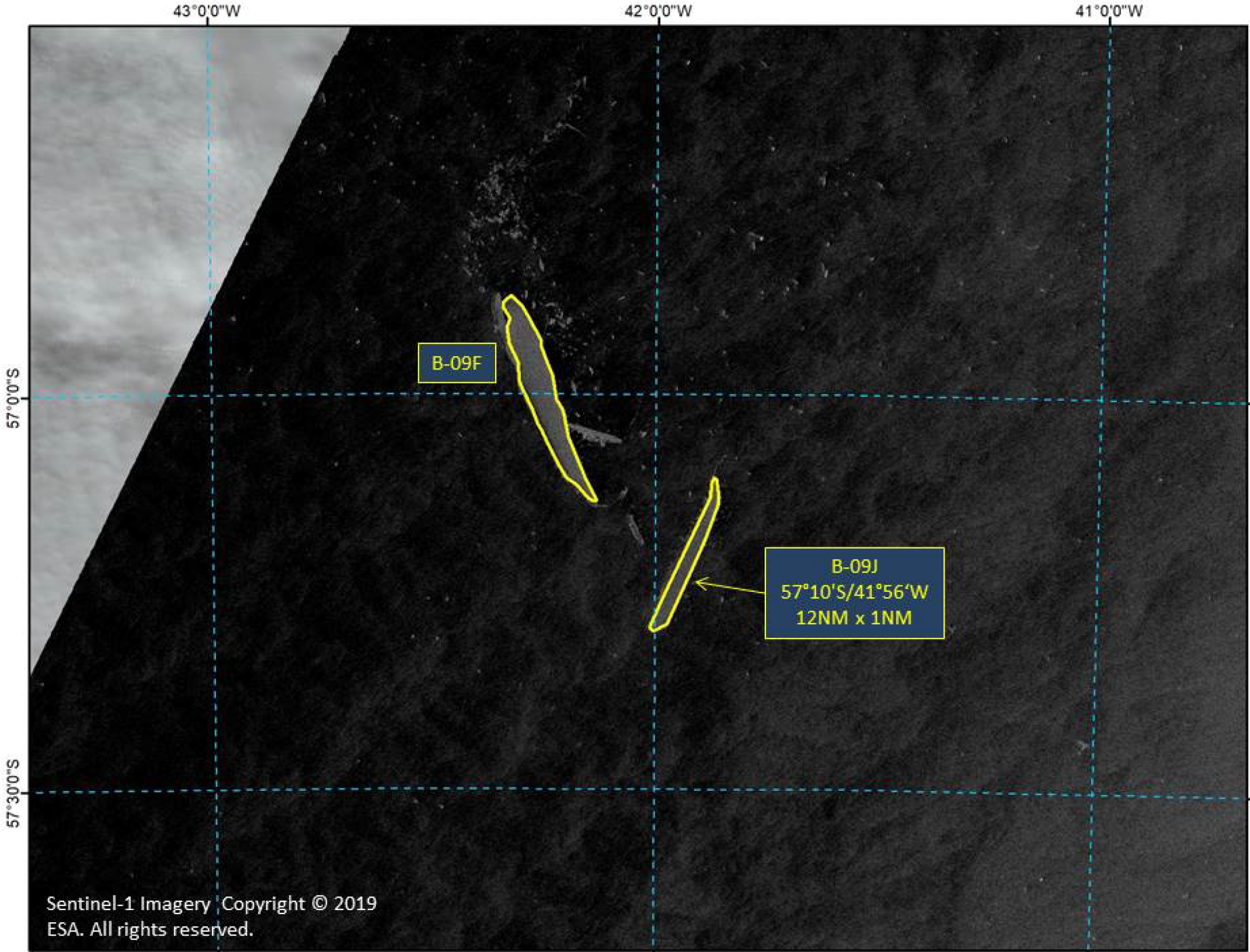
Press Release - Icebeg B-09J calved from iceberg B-09F in the South Atlantic Ocean
25 April 2019 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from iceberg B-09F between the South Orkney Islands and South Georgia Island. B-09J is located at 57° 10' South, 41° 56' West in the South Atlantic Ocean. The iceberg measures 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 1 nautical mile on its widest axis.
Go to Article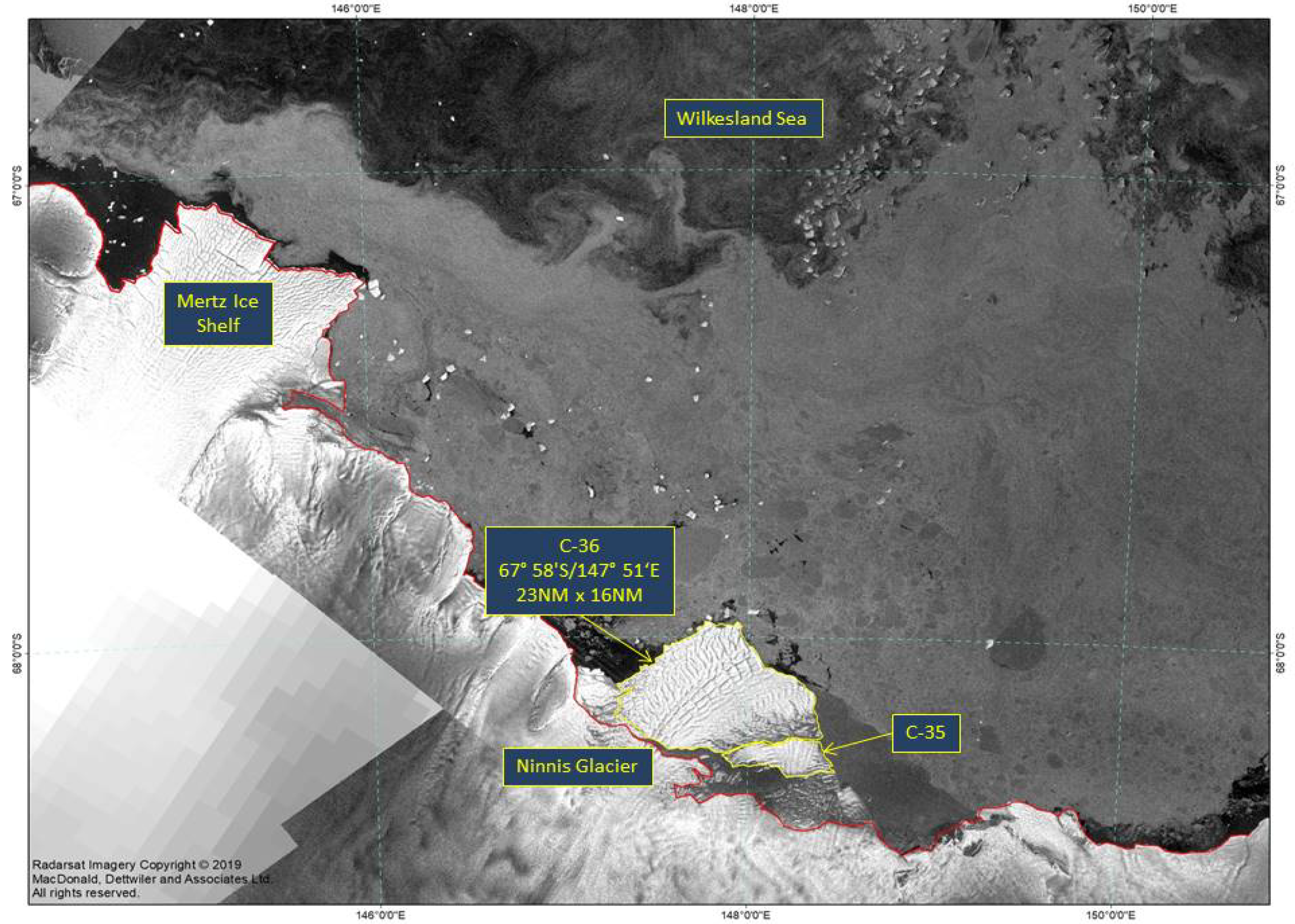
Press Release - Icebeg C-36 calved from Ninnis Ice Shelf in the Eastern Wilkesland Sea
31 January 2019 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has named a new iceberg that calved from the Ninnis Ice Shelf in Antarctica. C-36 is located at 67°58' South, 147°51' East, in the eastern Wilkesland Sea. The iceberg measures 23 nautical miles on its longest axis and 16 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article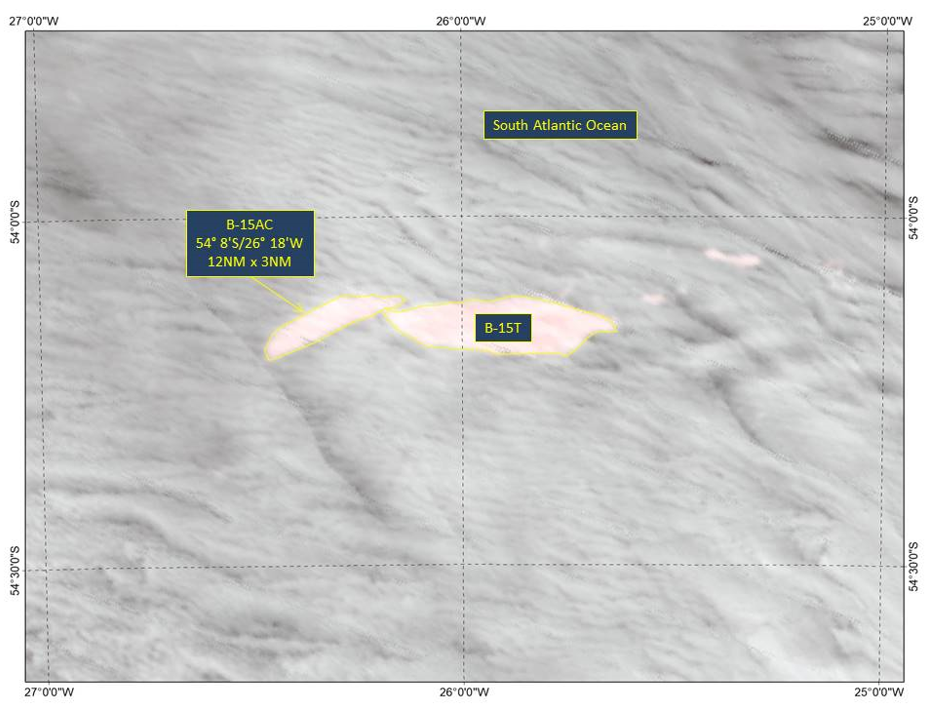
Press Release - Icebeg B-15AC Calved off of B-15T as it drifts in the warmer Southern Ocean
25 January 2019 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the previously named B-15T iceberg in the south Atlantic Ocean 340 NM east of South Georgia Island. Over the past few months as B-15T has drifted in warmer ocean water it is breaking up causing this calving event. B-15AC is located at 548’South, 2618’West in the south Atlantic Ocean. The iceberg measures 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 3 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article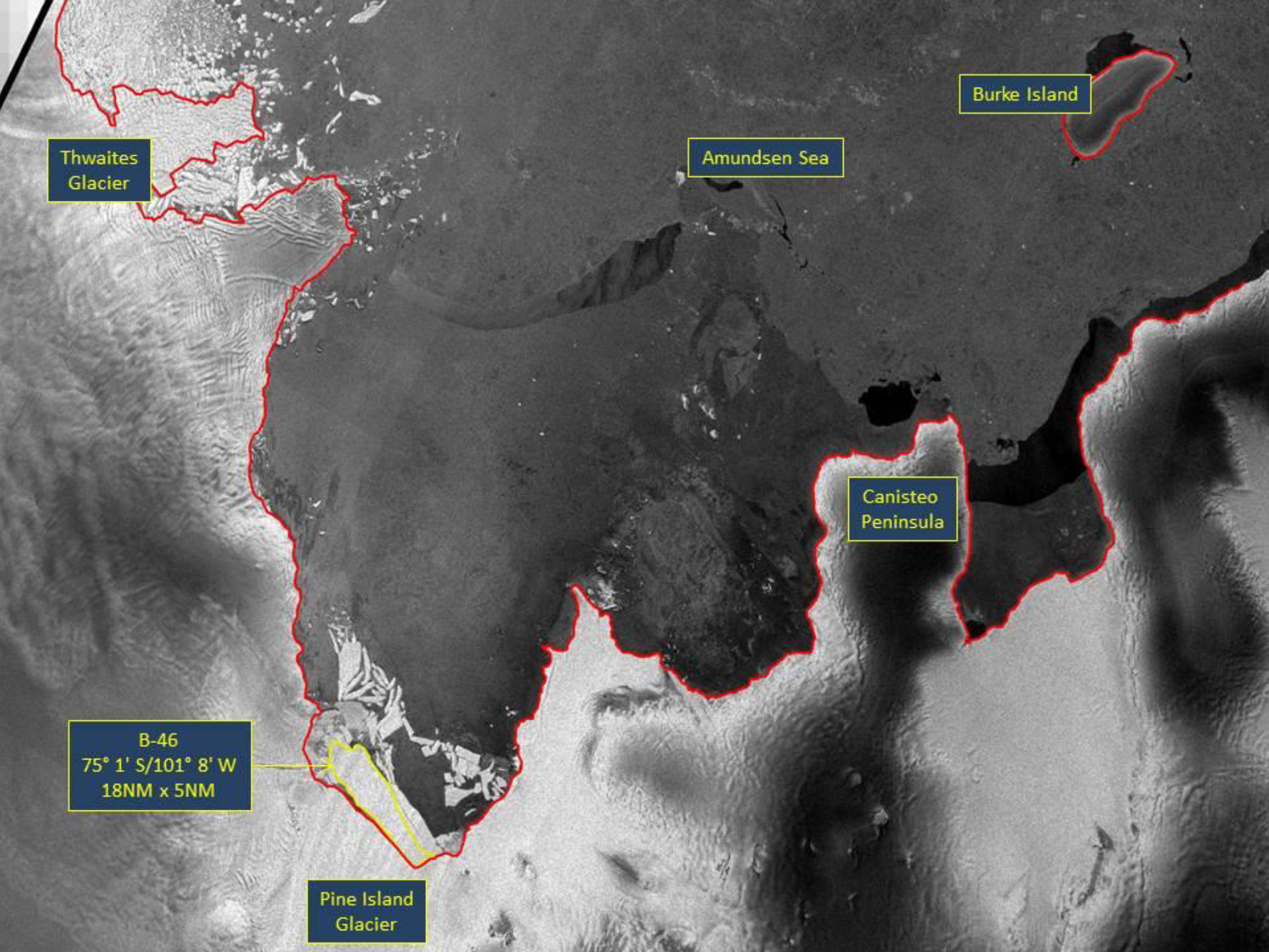
Press Release - Icebeg B-46 Calved off Pine Island Glacier in the Amundsen Sea
29 October 2018 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has named a new iceberg that calved from Pine Island Glacier (PIG) in the Amundsen Sea and is another in a set of recent calvings from PIG. B-46 is located at 75°1' South, 101°8' West and measures 18 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis with an area of 66 square nautical miles.
Go to Article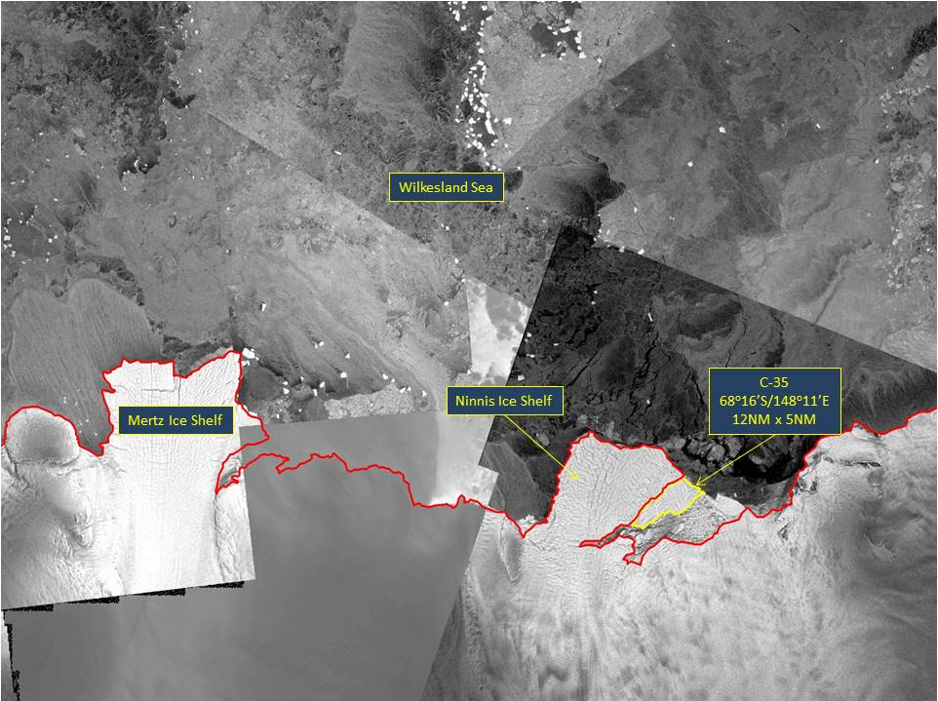
Press Release - Icebeg C-35 Calves off Ninnis Ice Shelf in the D’Urville Sea
30 August 2018 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) has named a new iceberg that calved from the Ninnis Ice Shelf in Antarctica. C-35 is located at 68° 16' South, 148° 11' East, in the D’Urville Sea. The iceberg measures 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article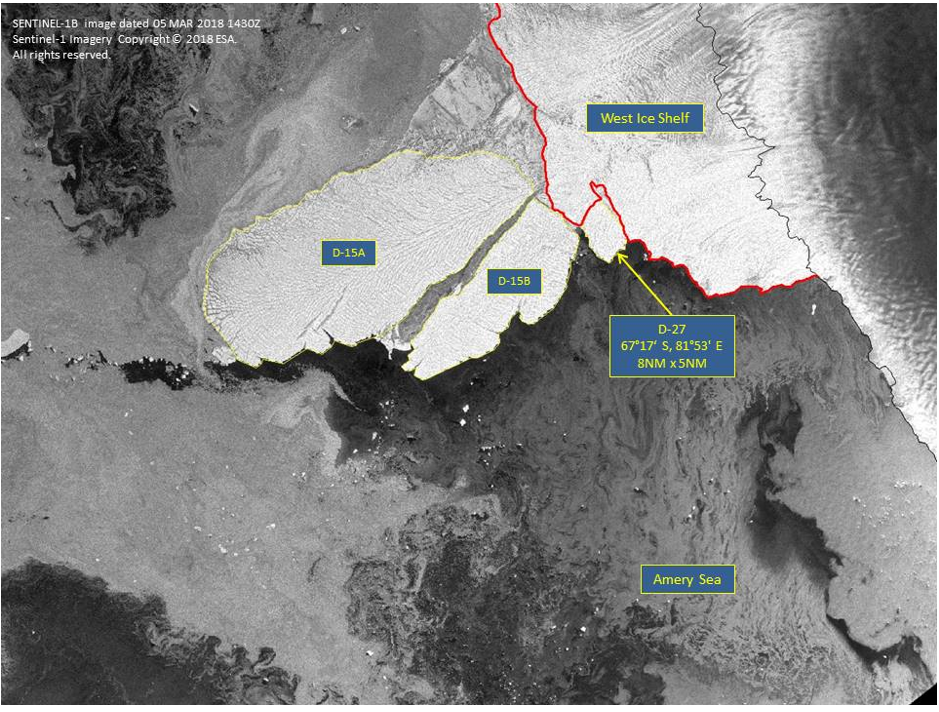
Press Release - Icebeg D-27 Calves off the Western Antarctic Ice Sheet
26 February 2018 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new Antarctic iceberg, D-27. D-27 is located in the Amery Sea at 67°17' South, 81°53' East, just south of the much larger iceberg D-15B. D-27 measures eight nautical miles on its longest axis and five nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article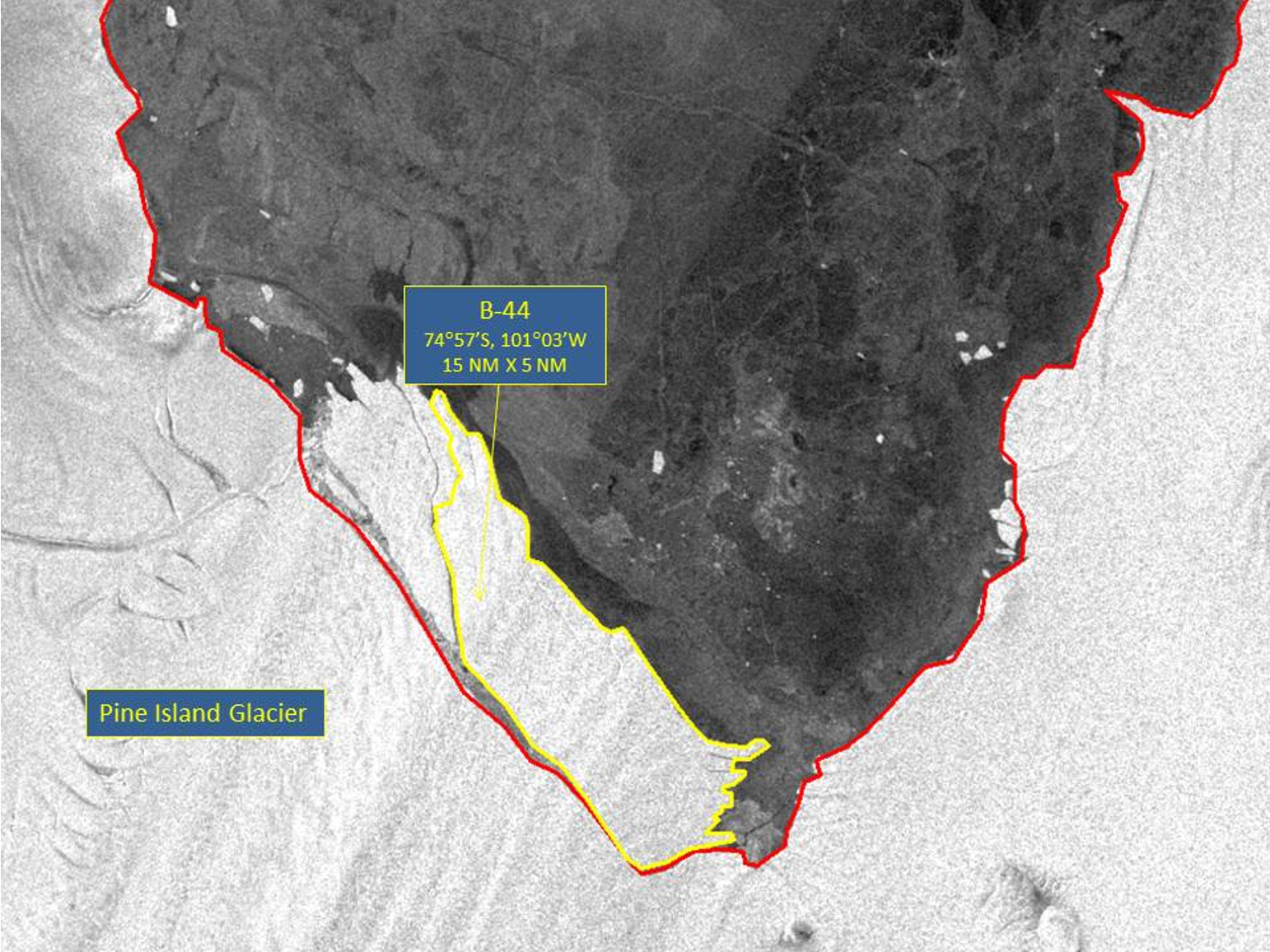
Press Release - Iceberg B-44 Have Calved from Pine Island Glacier
25 September 2017 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) discovered a new iceberg that meets the criteria for naming and tracking by the NIC. This particular iceberg is believed to have calved from the Pine Island Glacier. B-44 is located at 74°57' South, 101°03' West, in the Amundsen Sea. Iceberg B-44 measures 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis, with an area of 54 square nautical miles.
Go to Article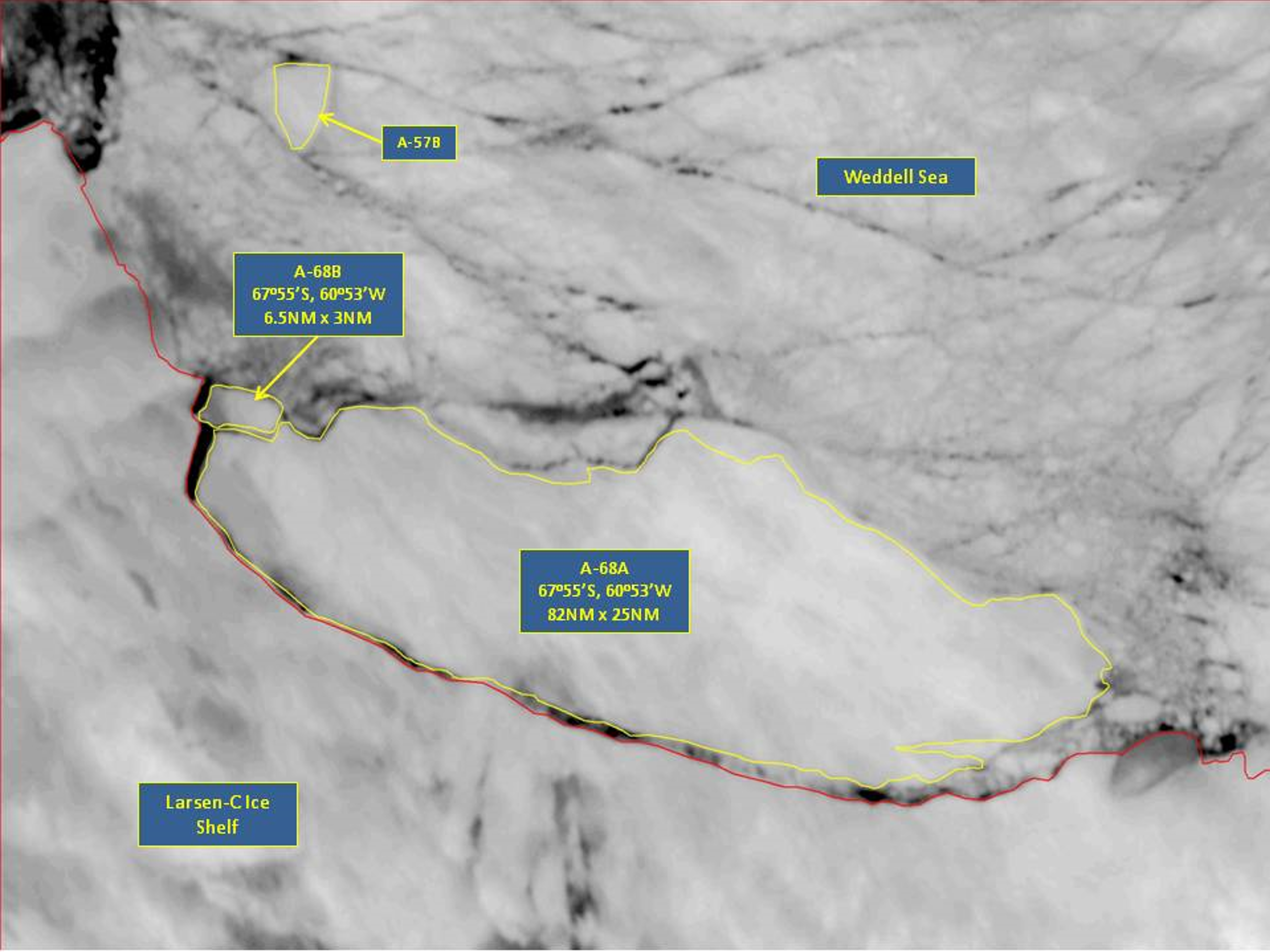
Press Release - Icebergs A-68A and A-68B Calve from Iceberg A-68 in the Larsen-C Ice Shelf
17 July 2017 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) confirmed that iceberg A-68 has broken into two smaller icebergs. A-68 calved off of the Larsen-C Ice Shelf on July 13th and has remained within a few miles of the ice shelf on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula. The larger iceberg, A-68A, measures 82 nautical miles on its longest axis, 25 nautical miles on its widest axis and is located at 67° 56' South and 60° 55' West. The smaller iceberg, A-68B, measures 6.5 nautical miles by 3 nautical miles and is located at 67° 15' South and 60° 49' West.
Go to Article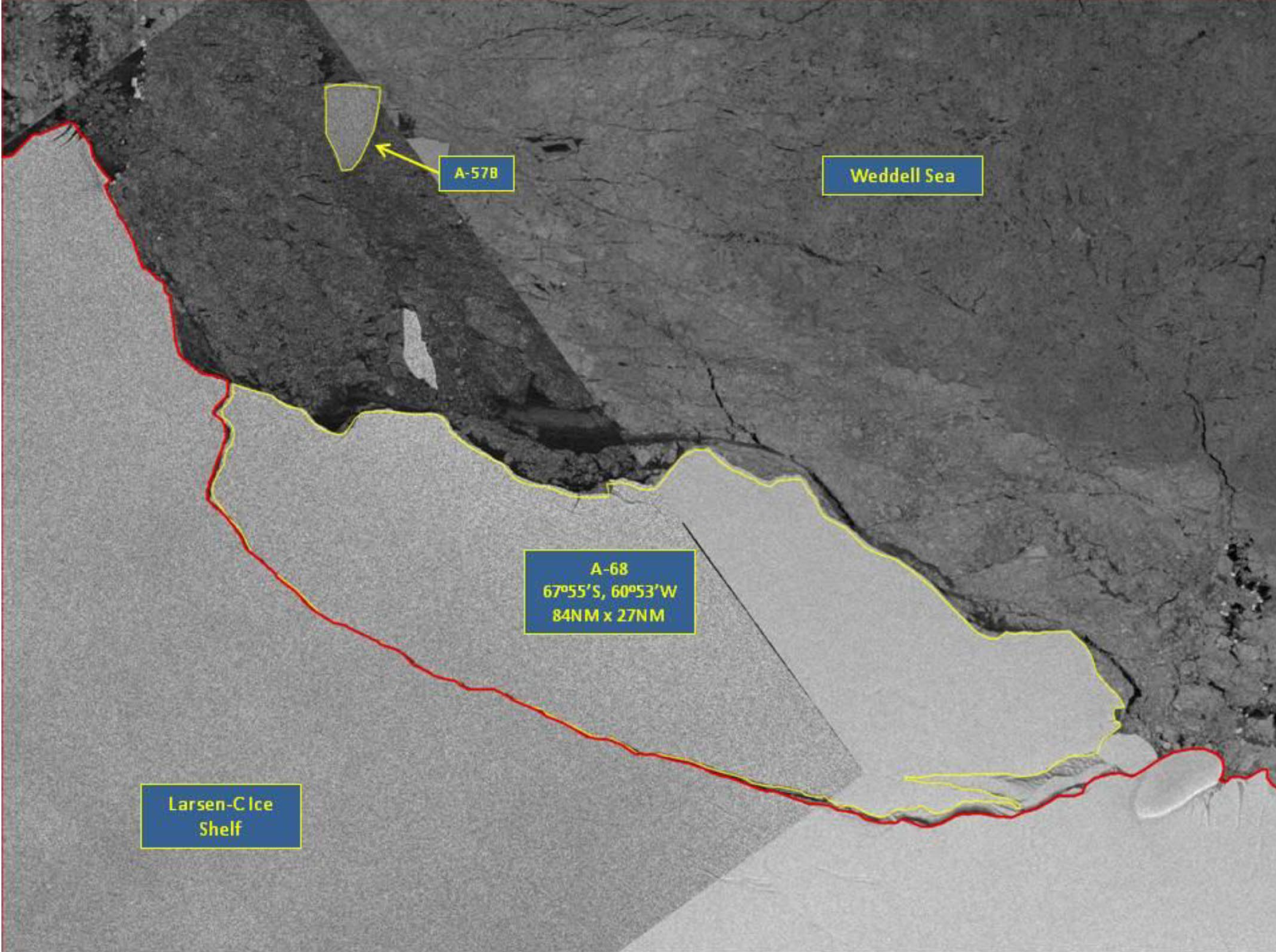
Press Release - Iceberg A-68 Calves off Larsen-C Ice Shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula
13 July 2017 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) discovered a new iceberg has calved from the Larsen-C ice shelf on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula. This iceberg, name A-68, is located at 67°55’ South, 60°35’ West, in the Weddell Sea. The iceberg measures 84 nautical miles on its longest axis and 25 nautical miles on its widest axis, and is slightly smaller than the state of Delaware.
Go to Article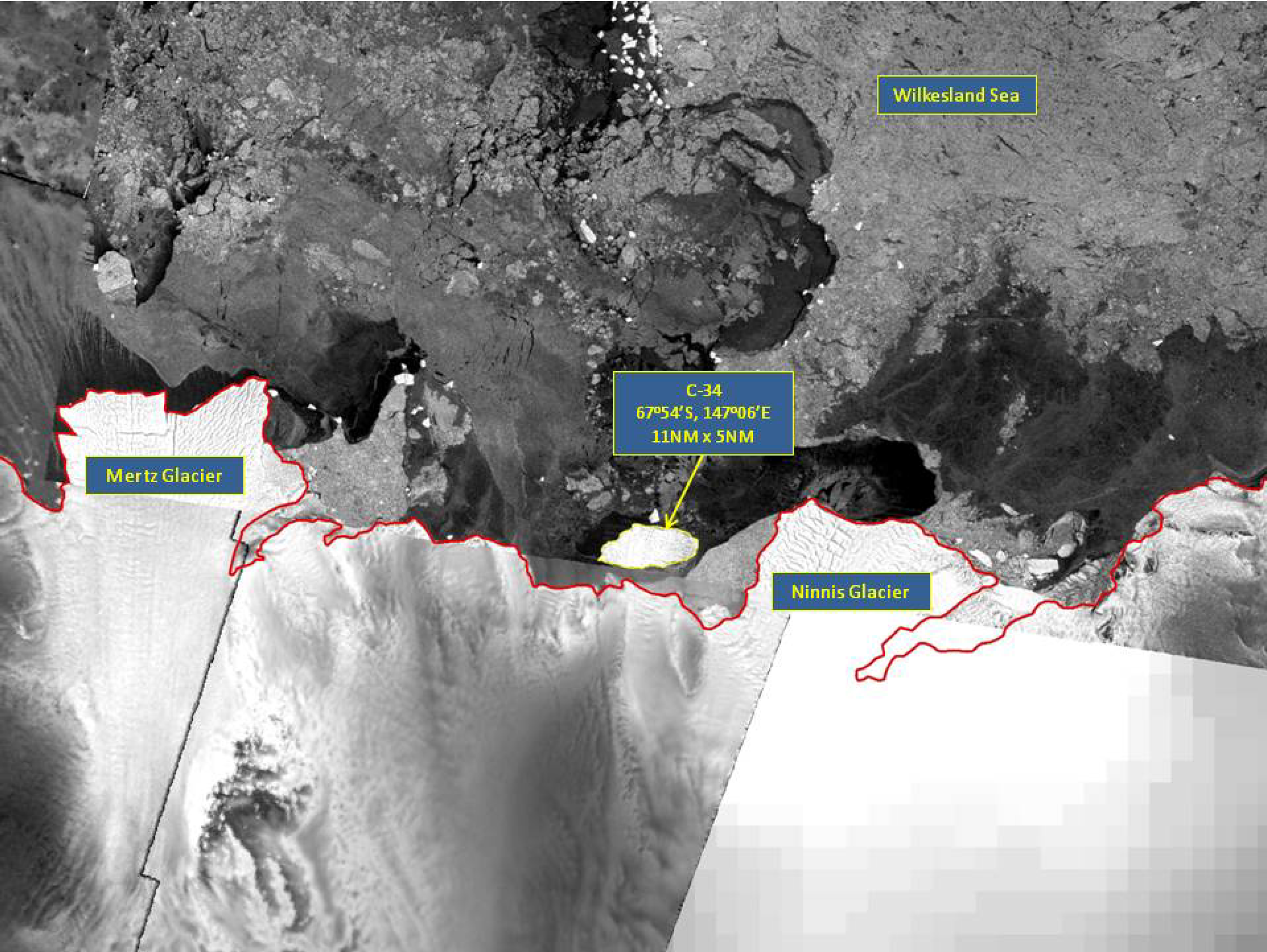
Press Release - Iceberg C-34 Calves off the Ninnis ice shelf in the eastern Wilkesland Sea
27 April 2017 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) identified a new iceberg that calved from the Ninnis Ice Shelf in Antarctica. C-34 is located at 67°54’ South, 147°06’ East, in the eastern Wilkesland Sea. The iceberg measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article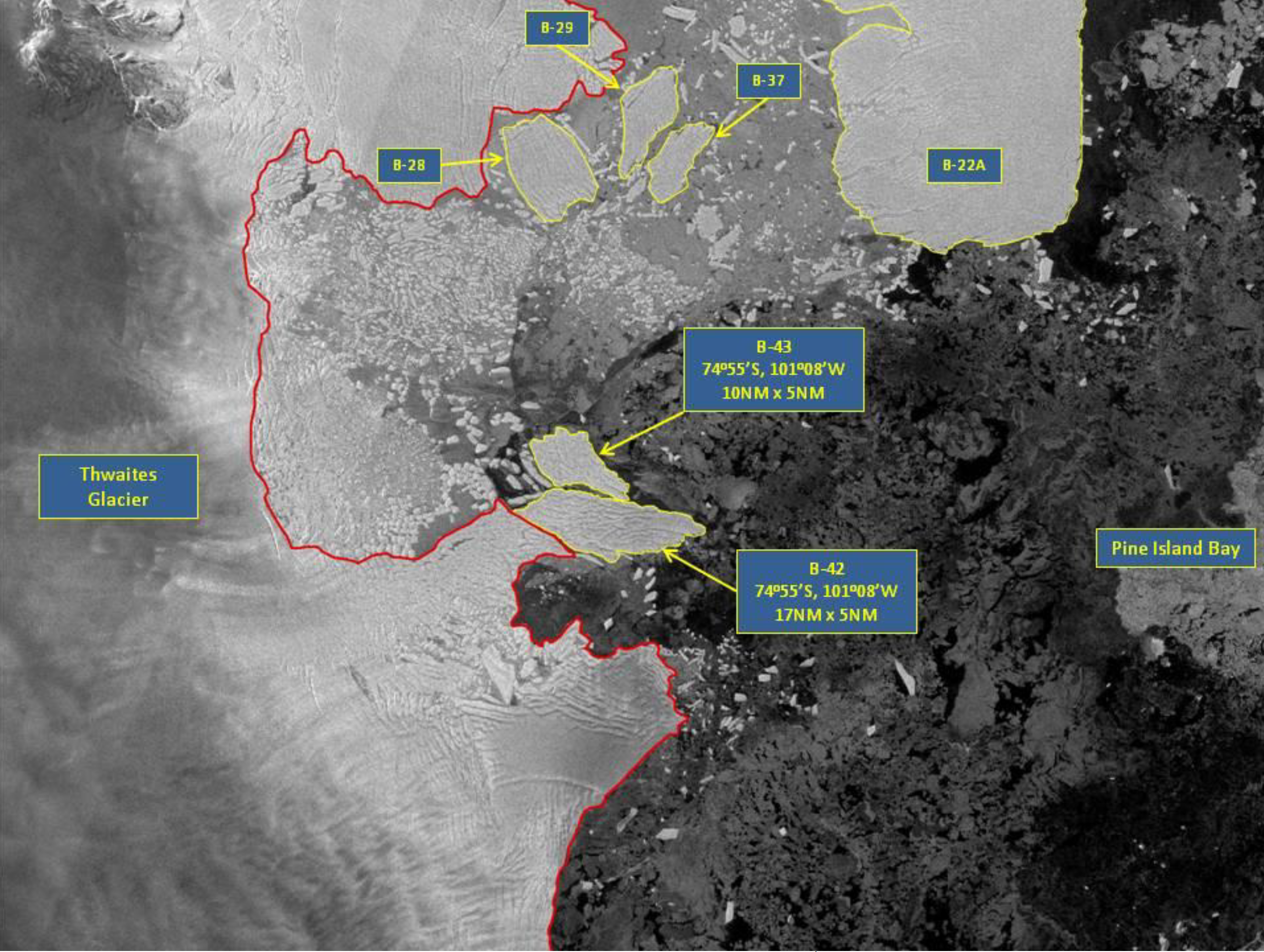
Press Release - Icebergs B-42 and B-43 Icebergs Separate from Thwaites Glacier Calving Front
11 April 2017 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) identified two new icebergs that calved from Thwaites Glacier in the Amundsen Sea. The icebergs had been perched on the edge of Thwaites glacier for a few years, but finally began to separate from the ice shelf. B-42 is located at 74°50’ South, 106°48’ West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 17 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis. B-43 is located at 74°51’ South, 107°10’ West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 10 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article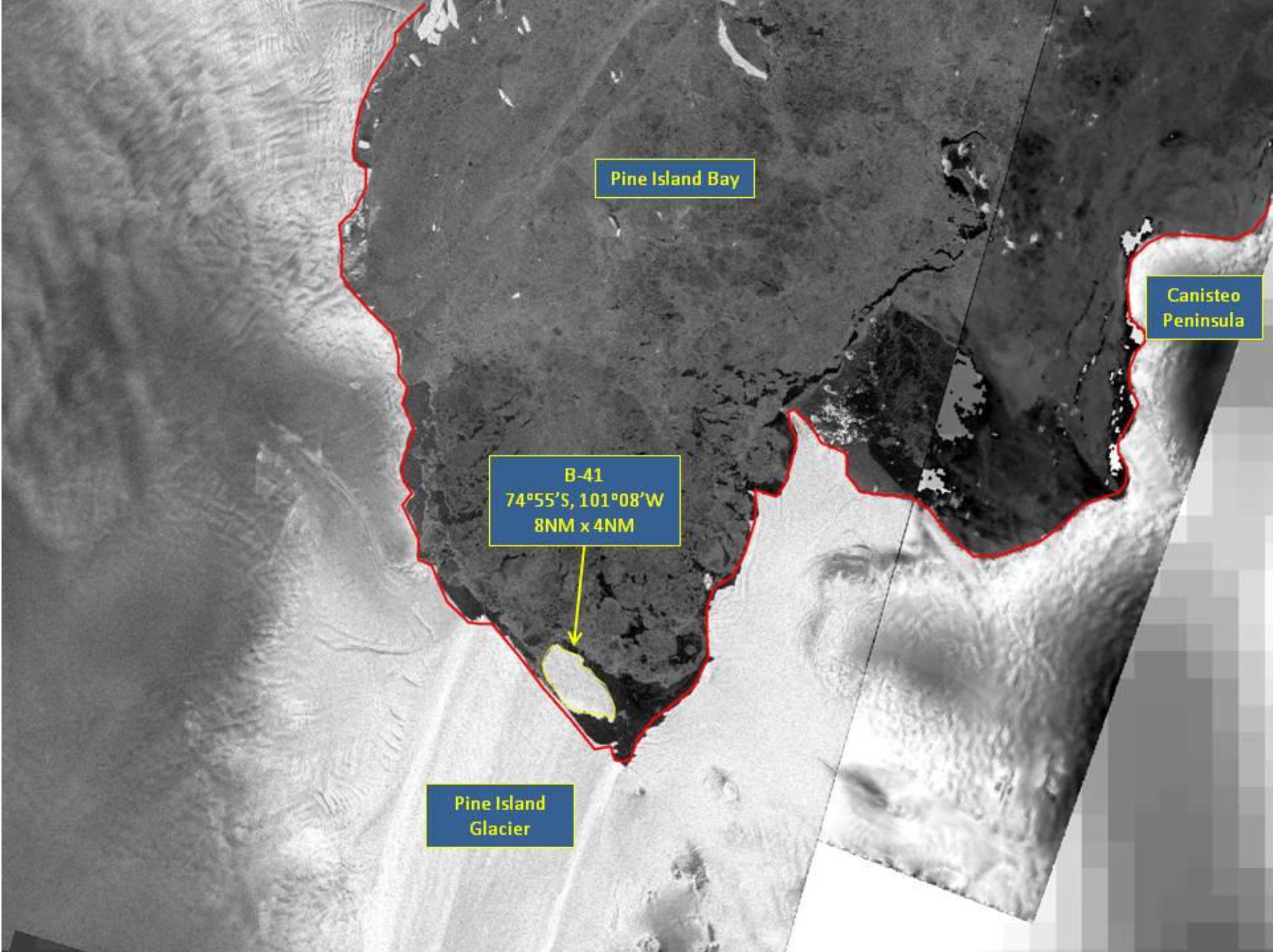
Press Release - Iceberg B-41 Have Calved from Pine Island Glacier
6 September 2016 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from Pine Island Glacier in Pine Island Bay. Since the last calving event in 2015, iceberg B-41 has been perched against the shelf seemingly still attached. In the past week however, B-41 has broken free and is now drifting into Pine Island Bay. B-41 is located at 74°55' South, 101°08' West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article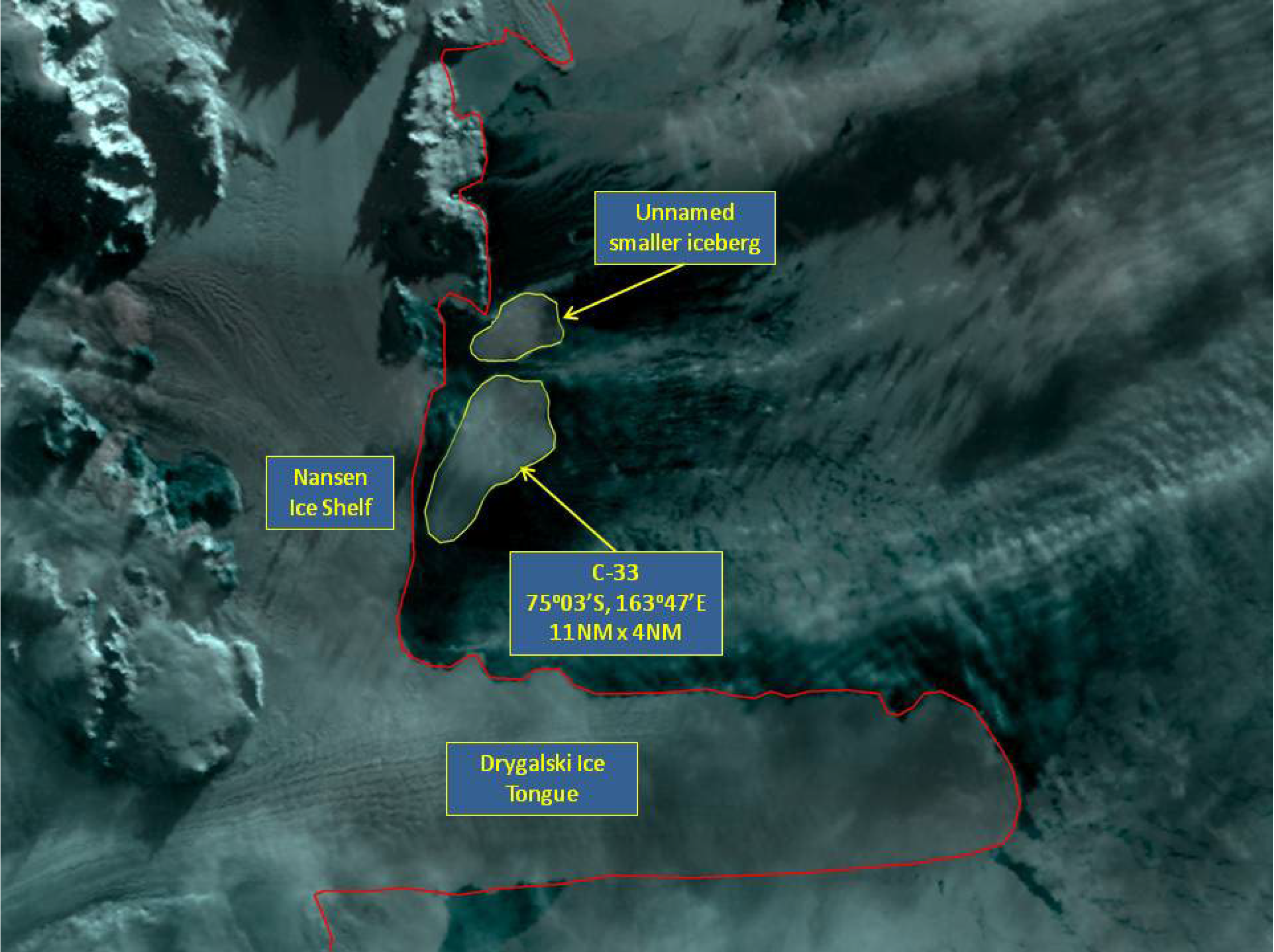
Press Release - Iceberg C-33 Calves off of the Nansen ice shelf in Ross Sea
12 April 2016 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the Nansen Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The NASA Earth Observatory published images showing the shelf's crack in March. C-33 is located at 75°03’ South, 163°47’ East, in the Ross Sea. The iceberg measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 4 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article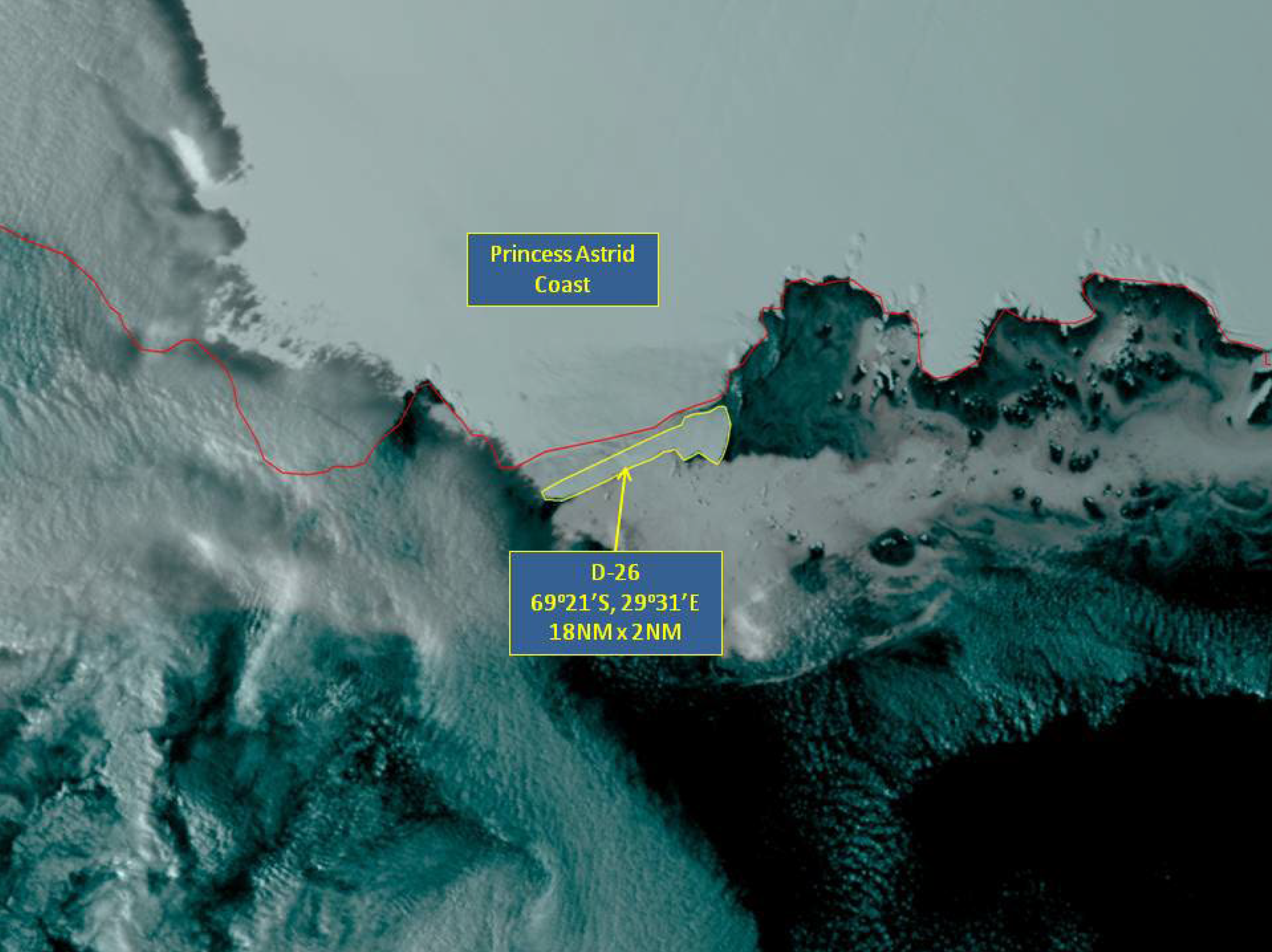
Press Release - Iceberg D-26 Calves off an ice shelf along the Princess Astrid Coast
8 April 2016 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the Princess Astrid Coast in Antarctica. D-26 is located at 69°21’ South, 29°31’ East, in the Amery Sea. The iceberg measures 18 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article
Press Release - Iceberg D-25 Calves into the Amery Sea
29 January 2016 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the ice shelf near the Kemp Coast. D25 measures 13 nautical miles on its longest axis and 8 nautical miles wide and is located at 69°20’ South, 37°57’ East in the Amery Sea.
Go to Article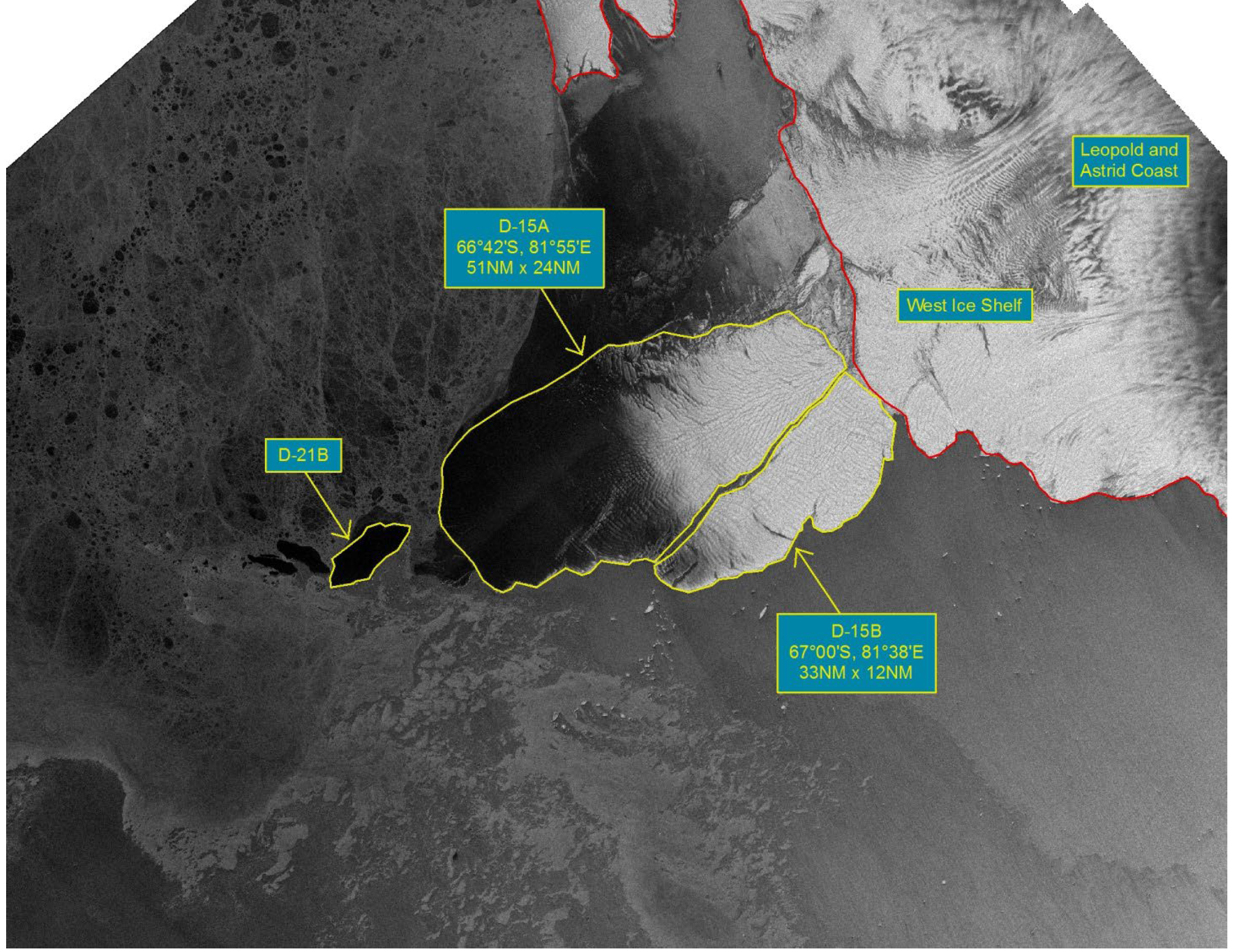
Press Release - Iceberg D-15 Breaks into D15A and D15B in the Amery Sea
27 January 2016 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) confirmed the iceberg D15 broke into two pieces. Both the larger remainder, named D15A, and the smaller piece, named D15B. D15A measures 51 nautical miles on its longest axis and 24 nautical miles wide and is located at 66°42’ South, 81°55’ East in the Amery Sea. D15B measures 33 nautical miles on its longest axis and 12 nautical miles wide and is located at 67°00’ South, 81°38’ East in the Amery Sea. Before breaking, D15 was the largest current iceberg in the world and had remained grounded in the same location for many years. D15A has now been demoted to the second largest iceberg, while D15B ranks in as fourth largest.
Go to Article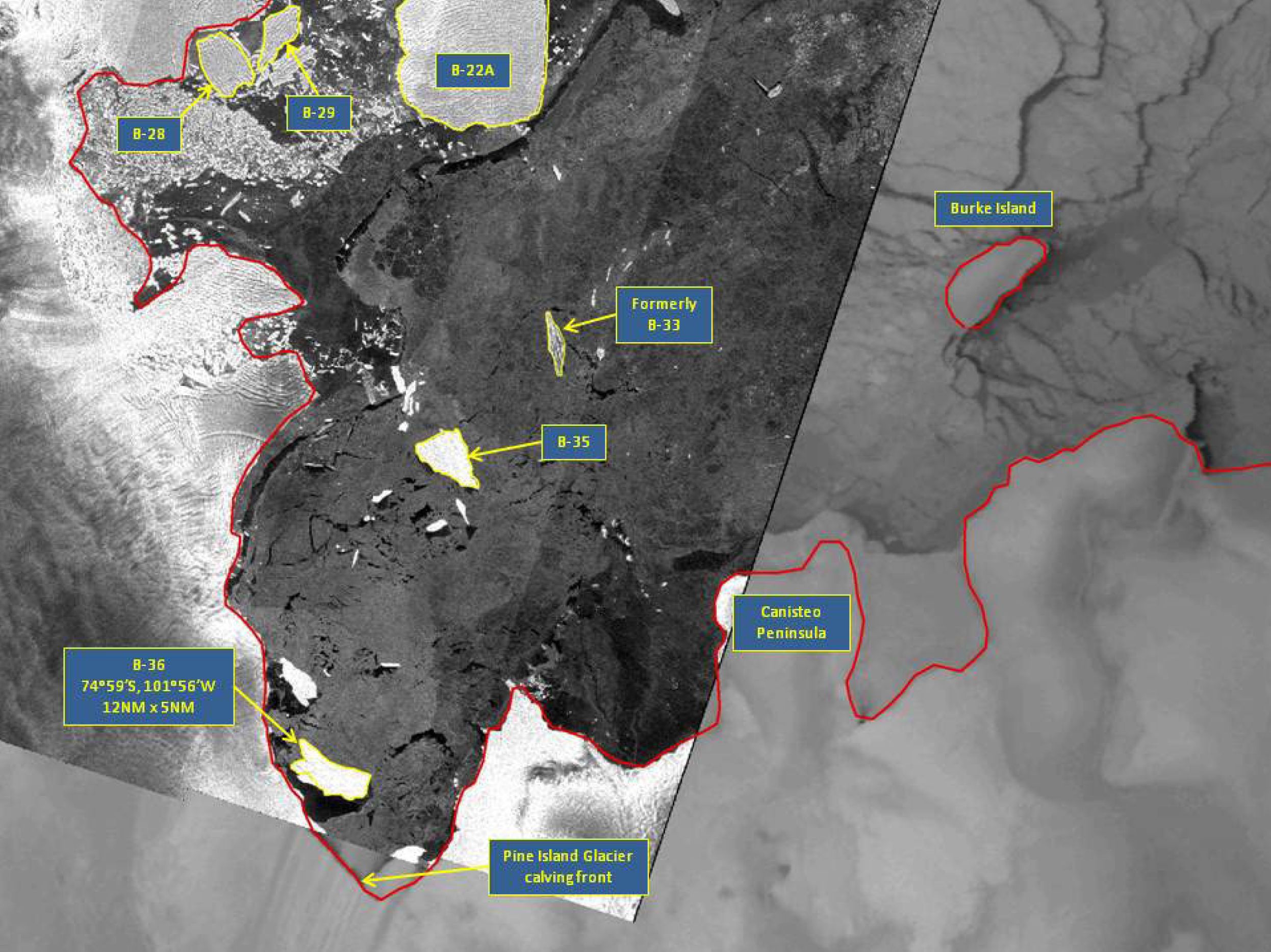
Press Release - Iceberg B-36 Calves off of Pine Island Glacier
23 October 2015 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from Pine Island Glacier in Pine Island Bay. In the span of 2 weeks, the NIC has named two new icebergs that have calved from Pine Island Glacier, the newest being B-36. B-36 is located at 74°59’34” South, 101°55’52” West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 12 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article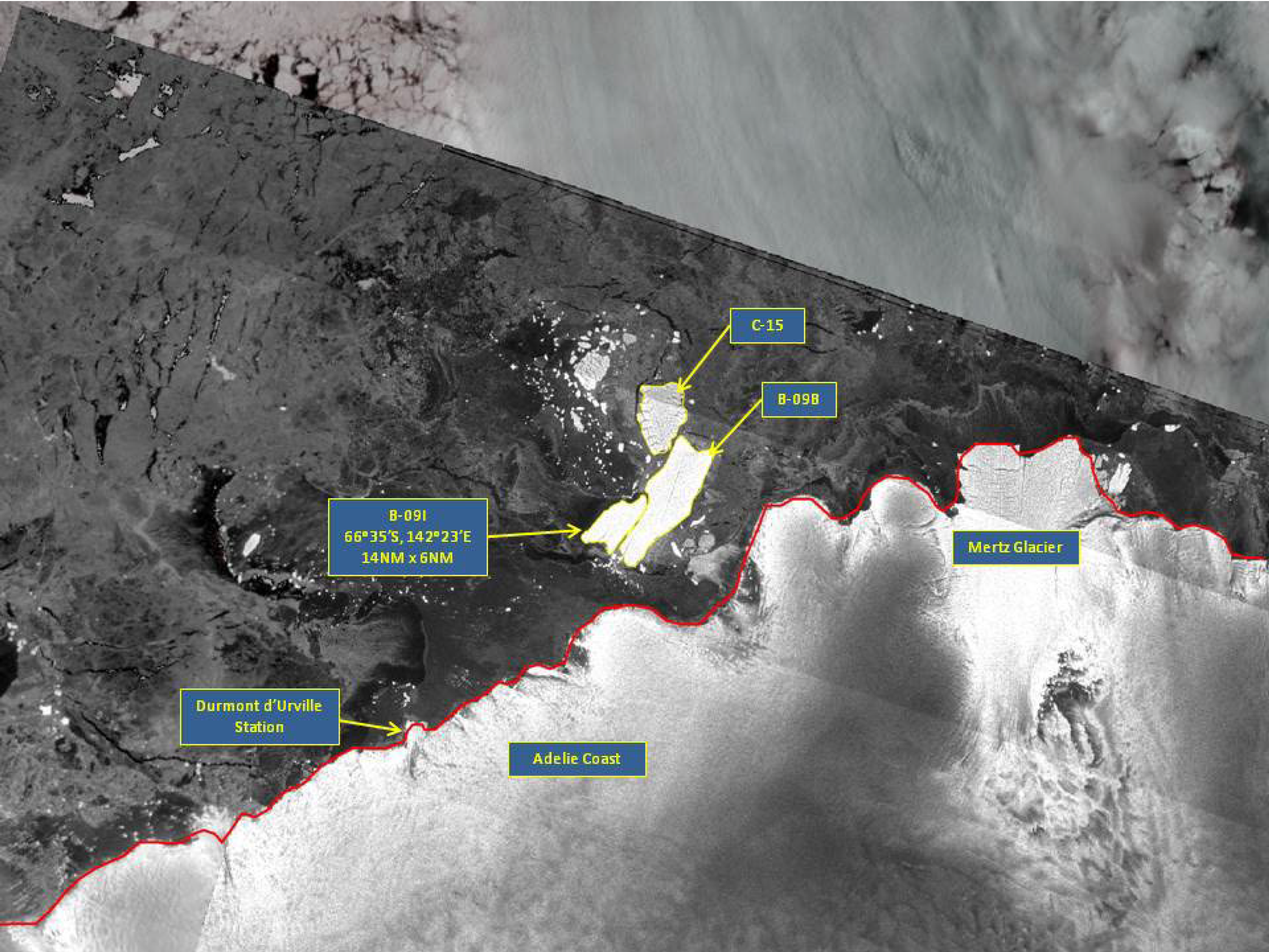
Press Release - Iceberg B-09I Found in the Wilkesland Sea
22 October 2015 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) discovered a new iceberg that meets the criteria for naming and tracking by the NIC. This particular iceberg calved from the previously named iceberg B-09B. B-09I is located at 66°35’ South, 142°23’ East in the Wilkesland Sea. Iceberg B-09I measures 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article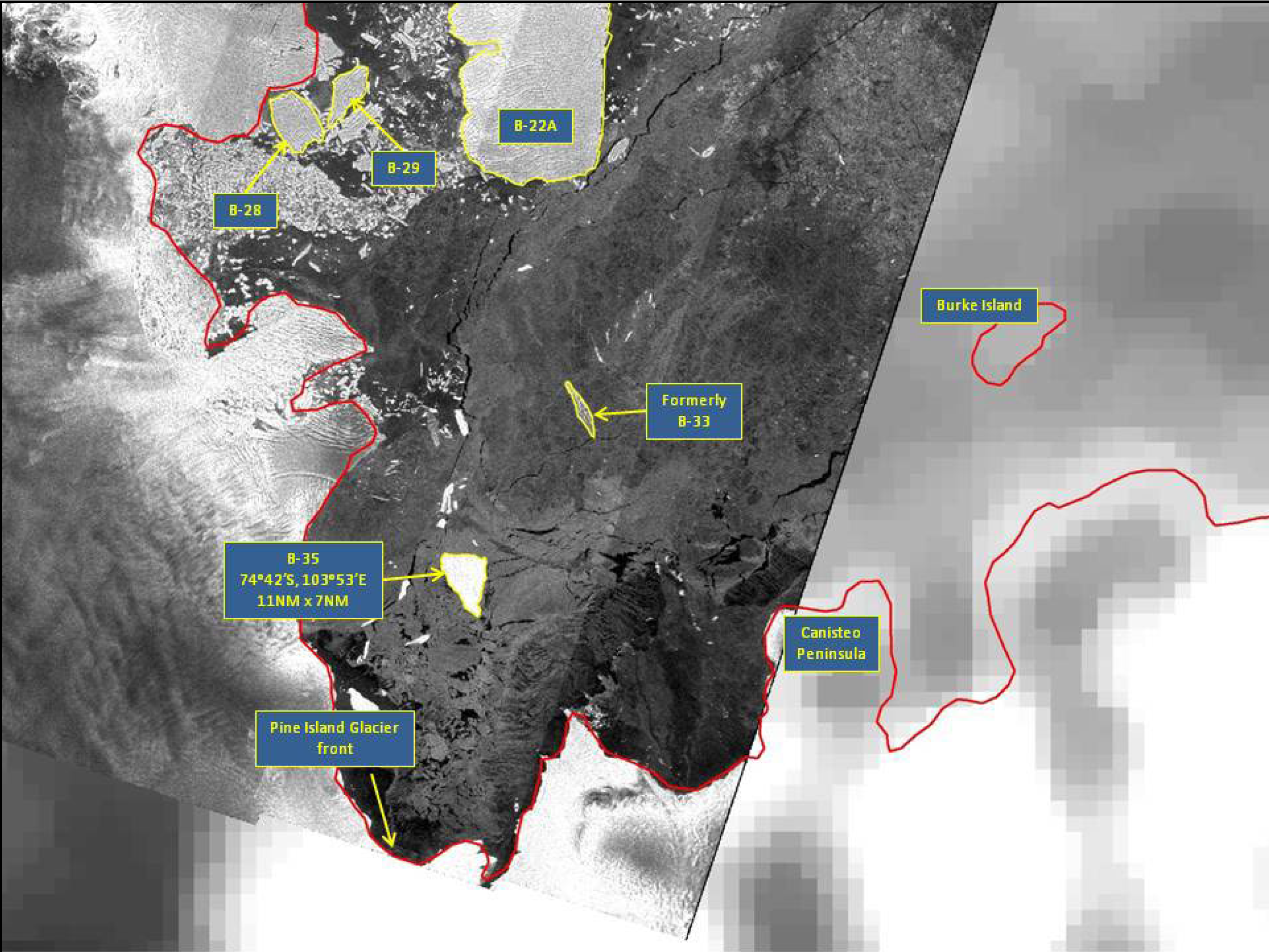
Press Release - Iceberg B-35 Calves off of Pine Island Glacier
11 October 2015 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from Pine Island Glacier in Pine Island Bay. Pine Island Glacier most recently calved iceberg B-31 in early August 2013. B-31 is still located in the Amundsen Sea, at 71°53’ South, 112°44’ West, approximately 245 nautical miles from where it originally calved. B-35 is located at 74°41’36” South, 103°53’12” West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 7 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article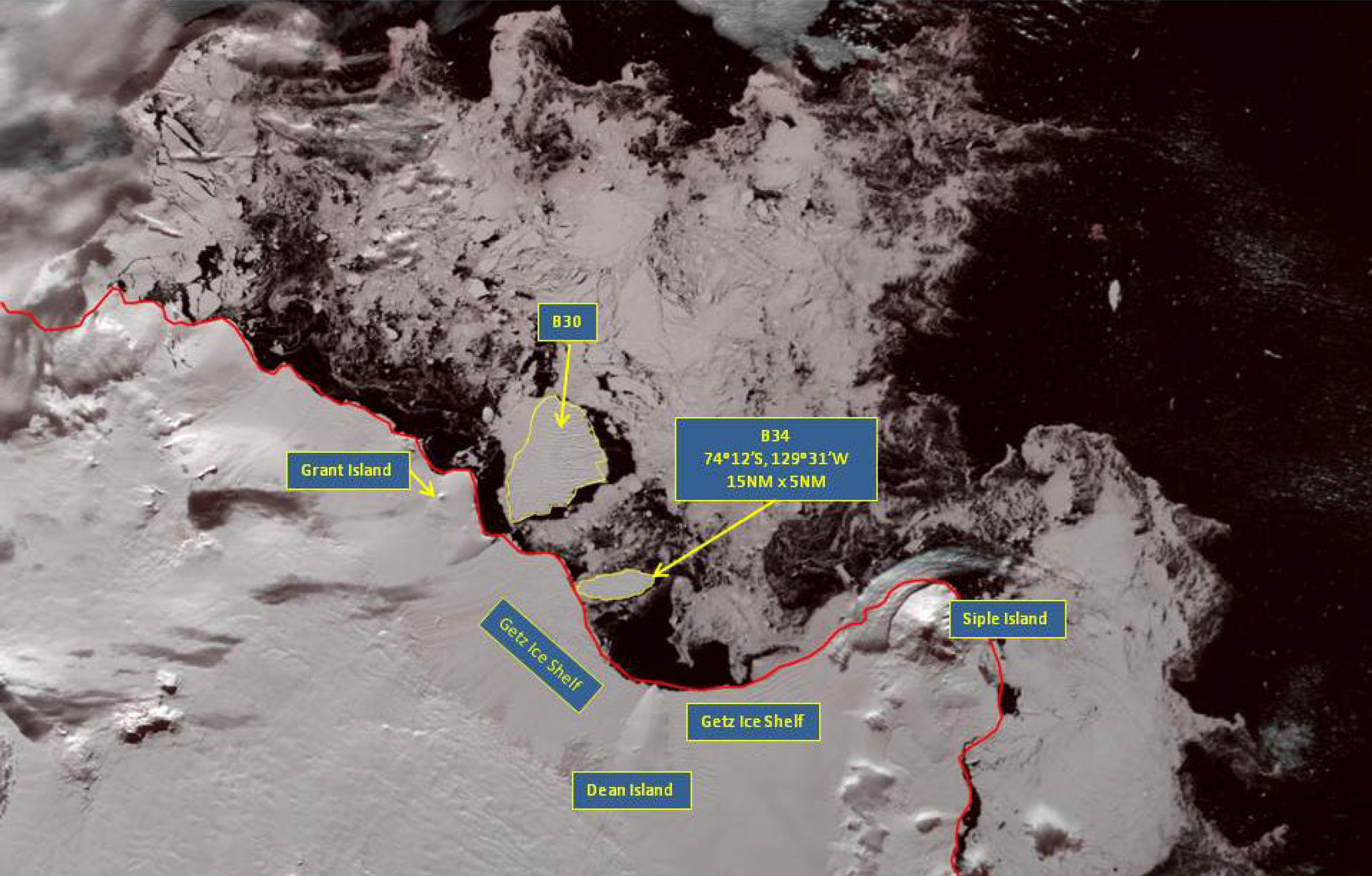
Press Release - Iceberg B-34 Found in the Amundsen Sea
06 March 2015 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) discovered a new iceberg that meets the criteria for naming and tracking by the NIC. This particular iceberg is believed to have calved from the Getz Ice Shelf and is named B-34. B-34 is located at 74°12’ South, 129°31’ West, in the Amundsen Sea. Iceberg B-34 measures 15 nautical miles on its longest axis and 5 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article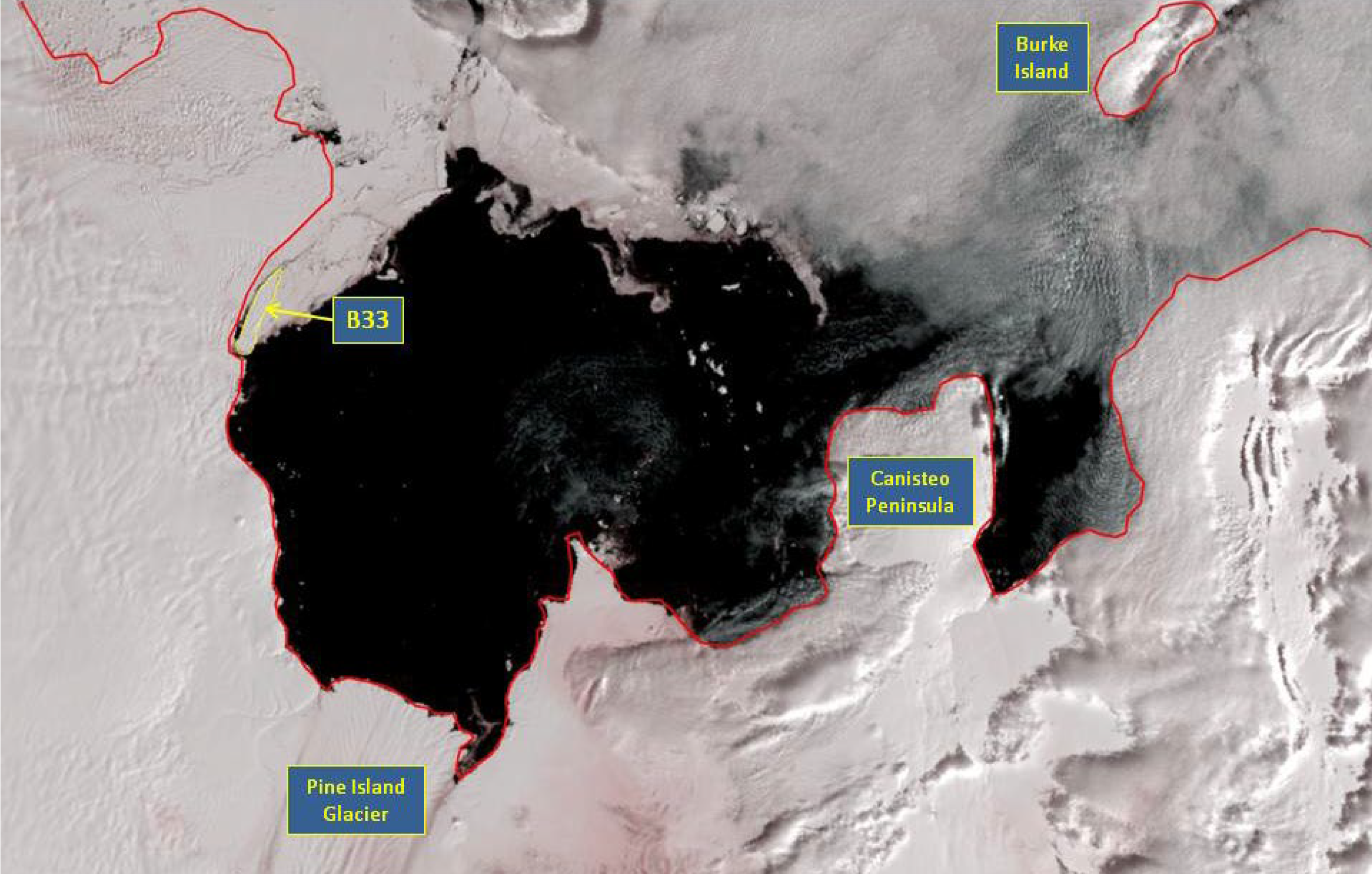
Press Release - Iceberg B-33 Calves near Pine Island Glacier
17 February 2015 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from an ice-shelf near Pine Island Glacier in Pine Island Bay. B-33 is located at 75°01’11” South, 104°48’38” West, in the Amundsen Sea. The iceberg measures 11 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article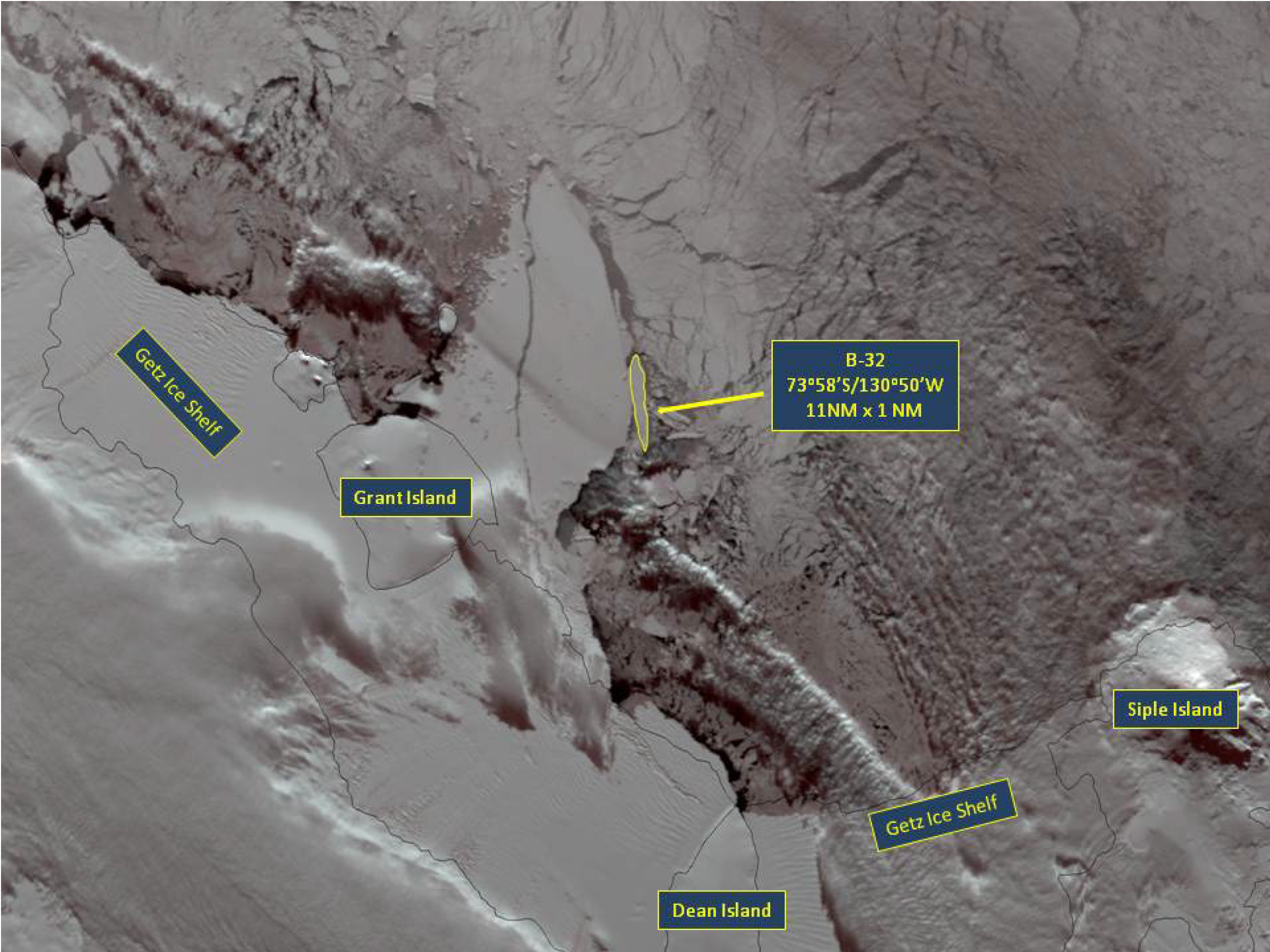
Press Release - Iceberg B-32 Found in the Amundsen Sea
17 September 2014 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) discovered a new iceberg that meets the criteria for naming and tracking by the NIC. This particular iceberg is believed to have calved from the Getz Ice Shelf and is named B-32. B-32 is located at 73°58’ South, 130°50’ West, in the Amundsen Sea. Iceberg B-32 measures 10.5 nautical miles on its longest axis and 2 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article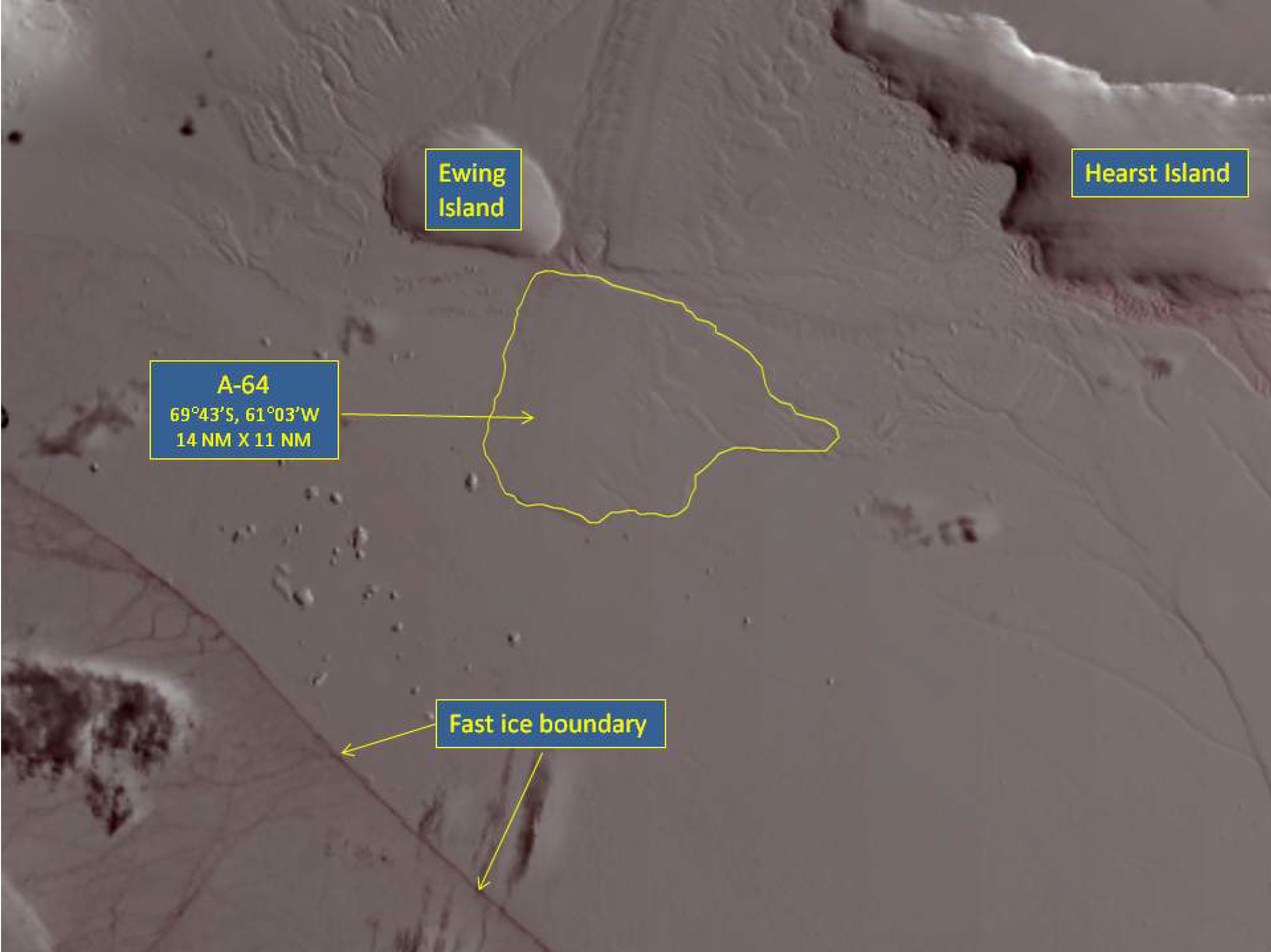
Press Release - Iceberg A-64 Calves off Larsen-D ice shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula
27 March 2014 - The U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC) named a new iceberg that calved from the Larsen-D ice shelf on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula. A-64 is located at 69°43’01” South, 61°03’39” West, in the Weddell Sea. The iceberg measures 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 11 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Go to Article