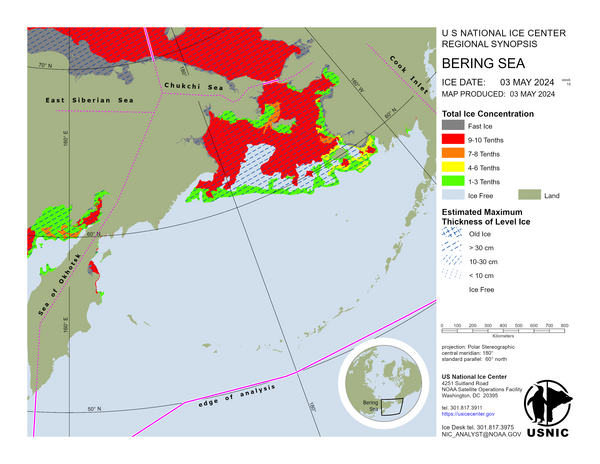
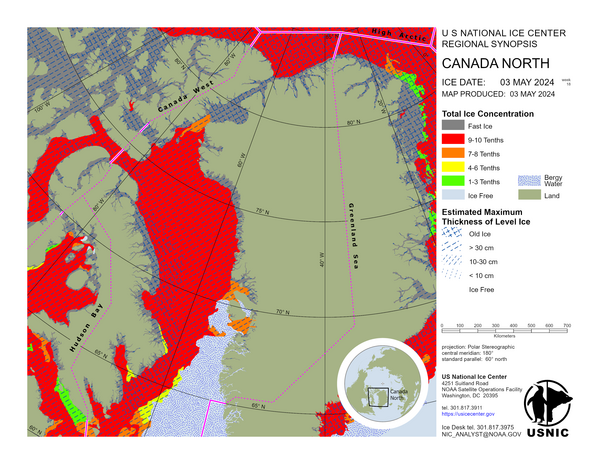
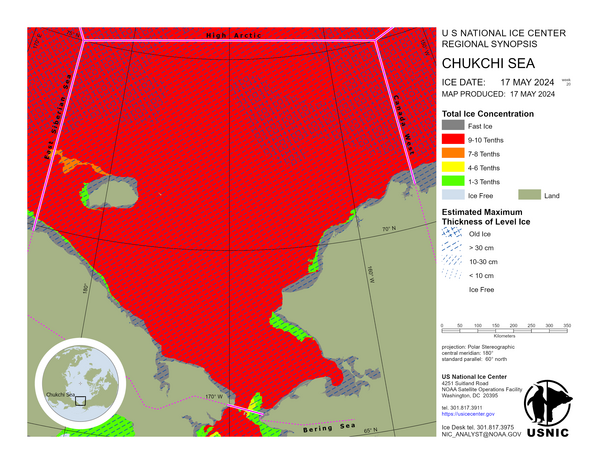
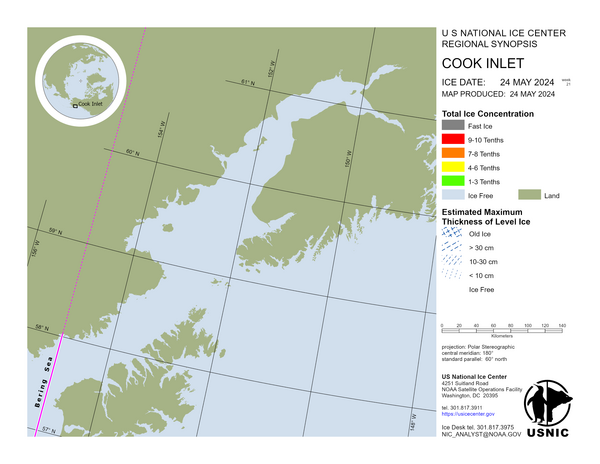
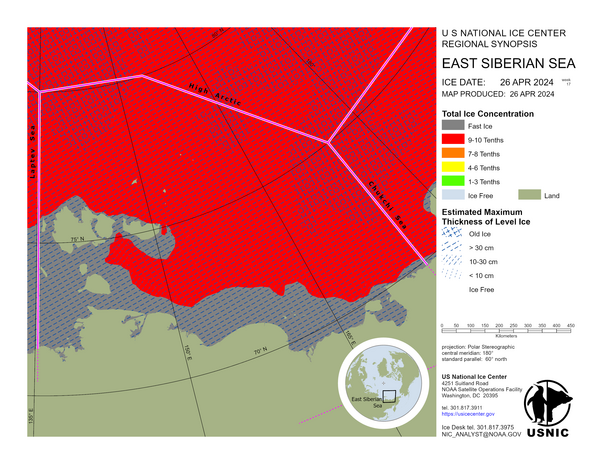
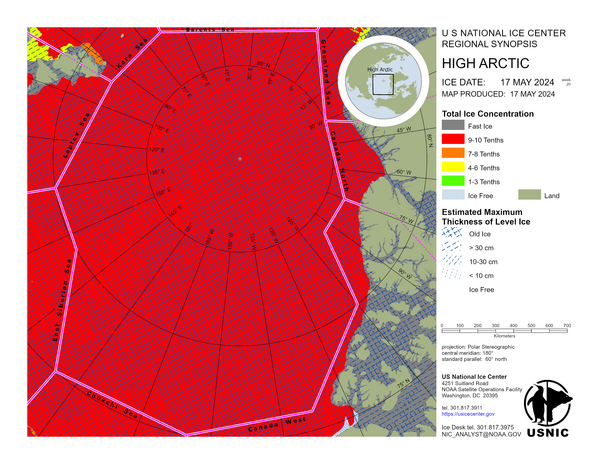
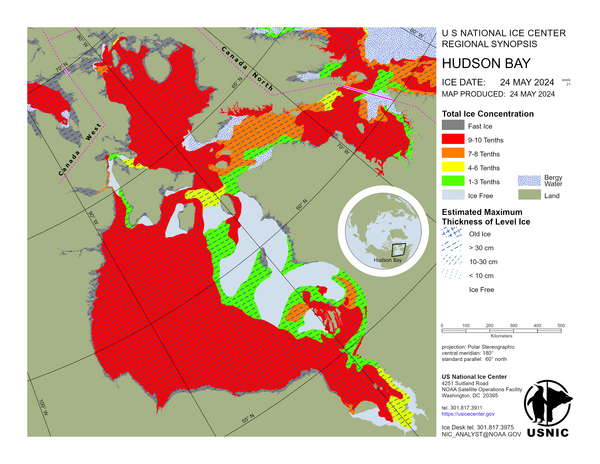
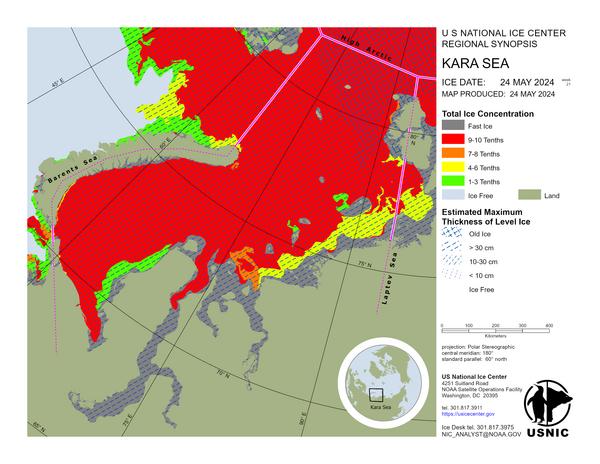
Arctic Regional Synopsis
Regional charts and associated synopsis write-up capture ice and environmental conditions throughout the Arctic which are based on the U.S. National Ice Center’s weekly analysis. Charts and synopses are updated weekly on Fridays. Note: Baltic Sea analysis is provided by the Finnish Meteorological Institute. The Canadian Archipelago (Canada East, Canada North, Canada West, and Hudson Bay) analysis is provided by the Canadian Ice Service.
Regional Quick Access
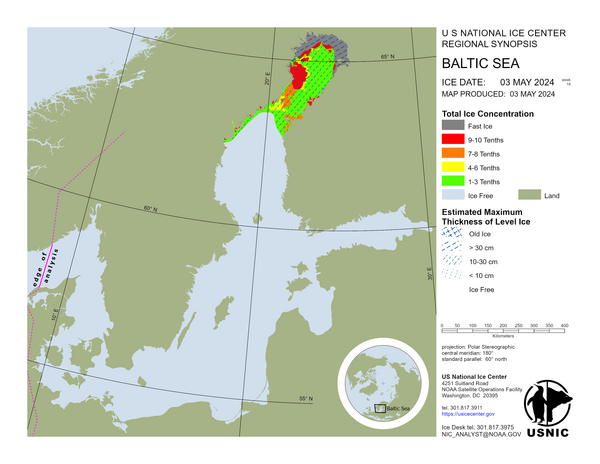
Baltic Sea
In the Northern Bay of Bothnia 35-80 cm thick fast ice and 20-45 cm thick consolidated drift ice to Kemi 2, Oulu 1 and Johan. Farther out 20-45 cm thick, in places ridged, very close ice. Ice pressure occurs in the ice field. In the Southern Bay of Bothnia 20-40 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago. Farther out 10-40 cm thick, in places ridged, very close ice. Cracks have been opened in the ice field. In the Quark 15-40 cm thick, in places ridged, close and very close ice and new ice. In the Vaasa archipelago 20-50 cm thick fast ice and consolidated drift ice to Utgrynnan. In the Sea of Bothnia 20-45 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago. At the fast ice edge consolidated brash ice. Farther out 5-20 cm thick close ice. In the Åland Sea new ice locally, mostly open water. In the Archipelago Sea 15-40 cm thick fast ice in the inner archipelago. In the outer archipelago 10-20 cm thick level ice to Utö. South of Utö a narrow brash ice barrier at the ice edge. In the western Gulf of Finland 15-40 cm thick fast ice and level ice in the archipelago. Farther out 10-25 cm thick in places ridged very close ice to the Tallinna Madal lighthouse. In the eastern Gulf of Finland 20-40 cm thick fast ice in the archipelago to Orrengrund. Off the fast ice 10-30 cm thick, in places ridged and rafted, very close ice to the Estonian coast. Ice pressure occurs in the ice field. In the Lake Saimaa 20-40 cm thick ice.
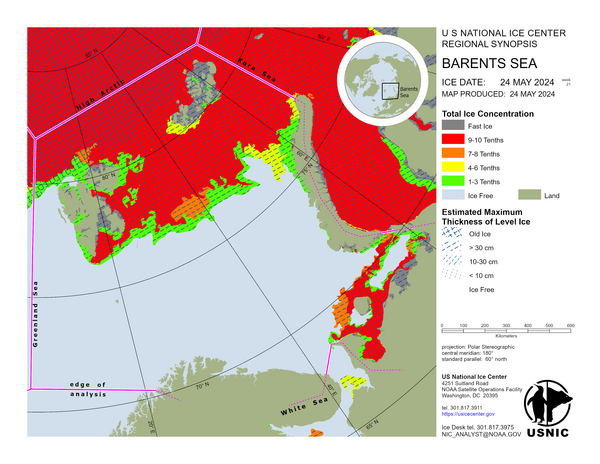
Barents Sea
In the northern Barents Sea, the sea ice drift is generally in a counter clockwise direction, northwestward near Franz Josef Land and southwestward near Svalbard. Due to strong katabatic winds off the Russian coast in the southern Barents Sea, the first year sea ice has drifted northward as much as 70 nautical miles allowing new and young ice to form in the space previously occupied by the first year ice.
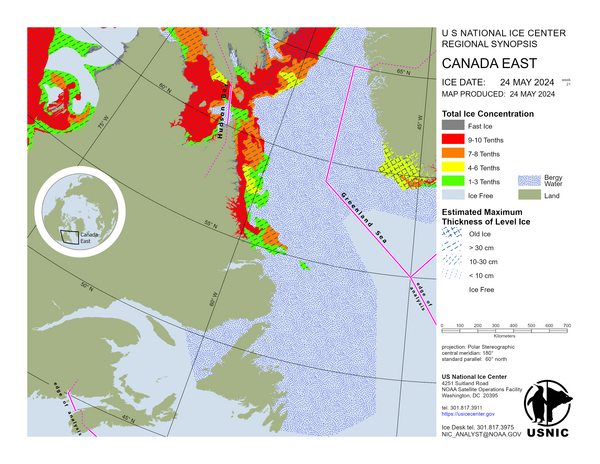
Canada East
Eureka Sound and Jones Sound contain first-year ice and some old ice. Lancaster Sound contain mostly first-year ice with some old ice. Baffin Bay and Davis Strait contain mostly first-year ice with some old ice. There is young ice present along the ice edge. Frobisher Bay and Cumberland Sound contain a mixture of first-year, young and new ice. A trace of old ice is present around Resolution Island. The Labrador Sea is bergy water.
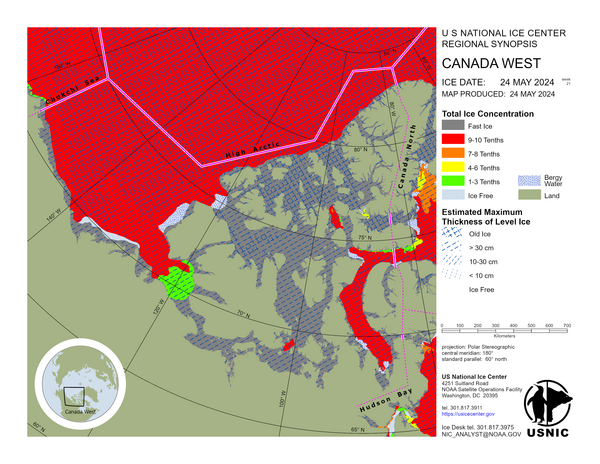
Canada West
The waters around the Queen Elizabeth Islands are fast old ice and first-year ice. M’Clure Strait and Viscount Melville Sound contain predominantly fast old ice with some first-year ice. Barrow Strait is fast first-year ice with some old ice in the western section; in the eastern section there is mobile first-year ice with a trace of old ice. M’Clintock Channel is fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice. Peel Sound is fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice. Victoria Strait is fast first-year ice. There is an area of mobile first-year ice in the southern section. Queen Maud Gulf and Coronation Gulf are fast first-year ice. Amundsen Gulf is mostly fast first-year ice with a trace of old ice in the northern section. Canada Basin is predominantly old ice with some first-year ice. The Beaufort Sea is predominantly first-year ice with some old ice. New and young ice formed during the movement of the ice.
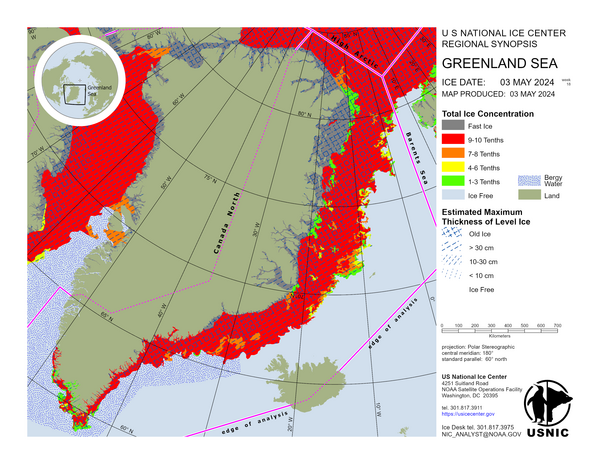
Greenland Sea
The East Greenland Current has drifted sea ice southward as much as 50 NM in northern Greenland and 120 NM within the Denmark Strait over the last week. This speed divergence has allowed first year ice to form between the old year ice floes, effectively lowering the concentration of the old ice. Air temperatures range from -32°C in northern Greenland to -2°C near Cape Farewell, allowing for normal ice growth.